Содержание
- 2. A Dictator in the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R) Joseph Stalin Came into power after Lenin’s death in
- 3. Fascists in Italy Benito Mussolini seized power in Italy in 1922 Played on Italian anger about
- 4. Invading Ethiopia Mussolini used foreign conquest to distract Italians from economic problems at home Committed acts
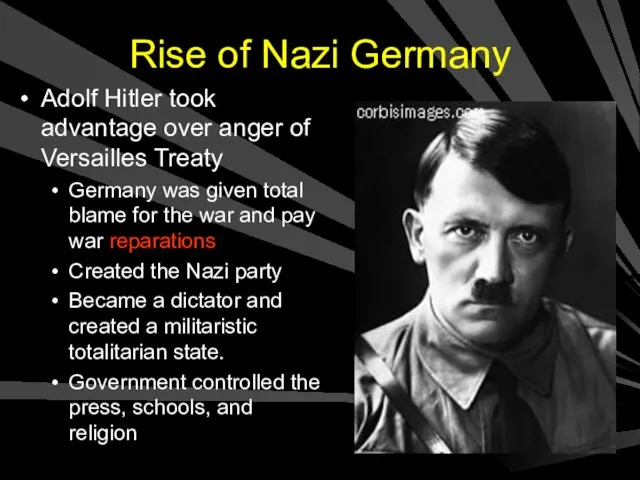
- 5. Rise of Nazi Germany Adolf Hitler took advantage over anger of Versailles Treaty Germany was given
- 6. Attacks on Jews Hitler and the Nazis preached a message of racial and religious hatred Blamed
- 7. German Military Buildup Germany built up its armed forces in violation of the Versailles Treaty League
- 8. Military Rule in Japan In the early 1930’s, military leaders took power in Japan Japan believed
- 9. American Foreign Policy Americans were too concerned about the depression to care about events overseas The
- 10. Conclusion How did dictators threaten world peace in the 1930’s? Built militaristic totalitarian states Committed acts
- 11. What were the primary causes of World War II?
- 12. War In Europe German expansion Hitler annexed (took over) Austria Claimed the Sudetenland Part of Czechoslovakia
- 13. Munich Conference Leaders of Britain, France, Italy, and Germany met in Munich in 1938 Britain and
- 14. Munich Conference Appeasement Fails!
- 15. Hitler invades Poland Hitler and Stalin sign a non-aggression pact Promised not to attack each other
- 16. A Global Conflict After the invasion of Poland: Britain and France declare war on Germany Later,
- 17. FRANCE SURRENDERS!!! Spring 1940 Hitler’s armies smashed through Denmark, Norway, Holland, and Belgium German armies marched
- 18. Hitler in France
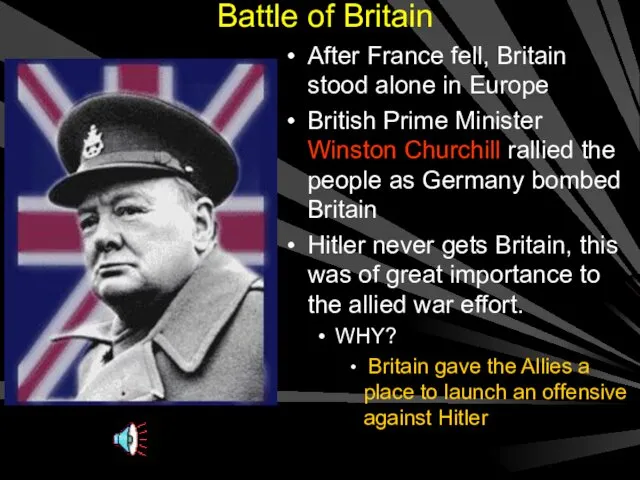
- 19. Battle of Britain After France fell, Britain stood alone in Europe British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
- 20. Scenes from “The Battle of Britain” Germany’s massive bombardment of Britain
- 21. FDR and American Policy FDR tried to help the allies Asked for repeal of Neutrality laws,
- 22. U.S.A. as the “Arsenal of Democracy” FDR asked Congress to pass the Lend-Lease act The US
- 23. The US enters the War! Japan’s war in Asia continued at a brutal pace The US
- 25. Скачать презентацию



















 Вспомним всех поименно
Вспомним всех поименно Москва – столица России. 8 класс
Москва – столица России. 8 класс Урок истории в 9 классе Внешняя политика России в нач.20 века. Русско-японская война.
Урок истории в 9 классе Внешняя политика России в нач.20 века. Русско-японская война. Дизайн в автомобилестроении
Дизайн в автомобилестроении Первая российская революция 1905-1907 гг. Изменения в политической системе Российской империи
Первая российская революция 1905-1907 гг. Изменения в политической системе Российской империи Промышленный переворот в Англии. Противоречия промышленной эпохи
Промышленный переворот в Англии. Противоречия промышленной эпохи Серебряный век русского искусства
Серебряный век русского искусства Страницы истории храма села Дебесы
Страницы истории храма села Дебесы Всемирный день писателя
Всемирный день писателя Поэты, погибшие на войне
Поэты, погибшие на войне Презентация к уроку Кавказская война 1817-1864 гг.
Презентация к уроку Кавказская война 1817-1864 гг. Московский Кремль
Московский Кремль Полисы Древней Греции
Полисы Древней Греции Отмена крепостного права в России. ХIХ век
Отмена крепостного права в России. ХIХ век Методическая разработка раздела Великая Отечественная война 1941-1945 гг.. 9 класс
Методическая разработка раздела Великая Отечественная война 1941-1945 гг.. 9 класс Мультимедийная презентация Нашествие с Востока
Мультимедийная презентация Нашествие с Востока Этот День Победы
Этот День Победы Письмо. Этапы его развития
Письмо. Этапы его развития Олимпийские игры в древности
Олимпийские игры в древности Интерактивная игра Знаешь ли ты свой город? (Санкт-Петербург)
Интерактивная игра Знаешь ли ты свой город? (Санкт-Петербург) Всеволод Юрьевич Большое Гнездо
Всеволод Юрьевич Большое Гнездо Семь граней Великой Степи Н.А.Назарбаев
Семь граней Великой Степи Н.А.Назарбаев Древний Египет
Древний Египет Борьба с нашествием Орды в ХIII веке. Зависимость Руси от Орды
Борьба с нашествием Орды в ХIII веке. Зависимость Руси от Орды Орден Кутузова, Орден Суворова
Орден Кутузова, Орден Суворова Презентация к уроку истории России Реформаторская деятельность М.М. Сперанского.
Презентация к уроку истории России Реформаторская деятельность М.М. Сперанского. Я помню. Я горжусь
Я помню. Я горжусь Материалы Средневековой иллюминированной книги
Материалы Средневековой иллюминированной книги