Содержание
- 2. The Land * Rugged mountains covered about ¾ of ancient Greece * The changed of the
- 3. The Climate Varied Climate (Winter: 48 degrees, Summer: 80 degrees) Moderate temperature -> Important environmental influence
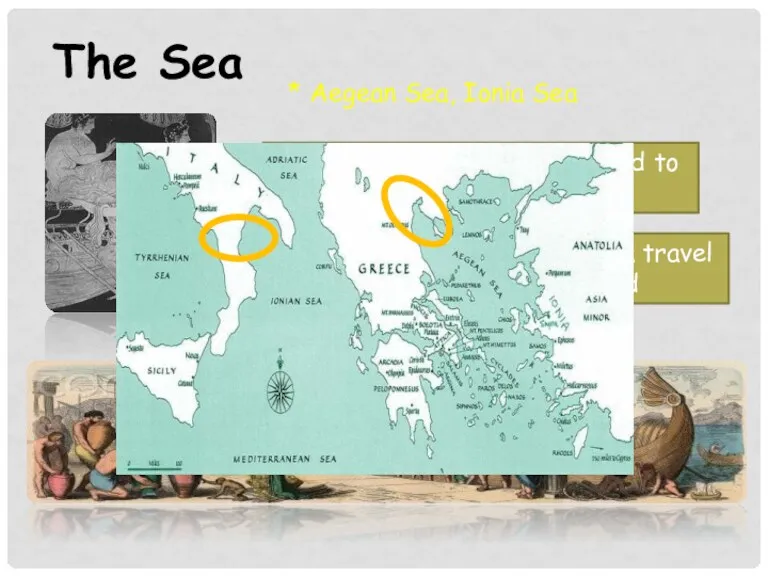
- 4. The Sea * Aegean Sea, Ionia Sea -> Important routes (connected to the most of parts
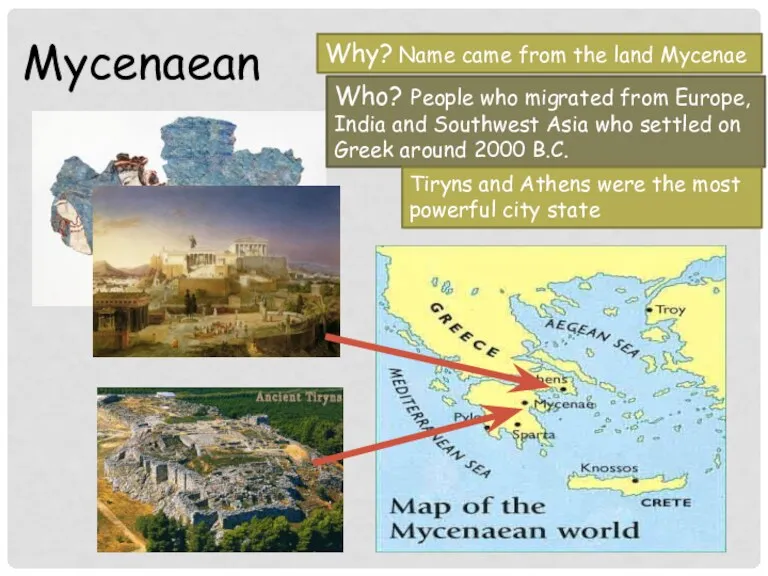
- 5. Mycenaean Who? People who migrated from Europe, India and Southwest Asia who settled on Greek around
- 6. Minoans Mycenaean had contacted the Minoan civilization which helped Mycenaean; the trade and system of Greek
- 7. The Trojan War War erupt because a Trojan Prince; Paris kidnapped Helen who is the most
- 8. Dorian Age Beginning of Greek culture declination Temporarily lost the art of writing during Dorian age;
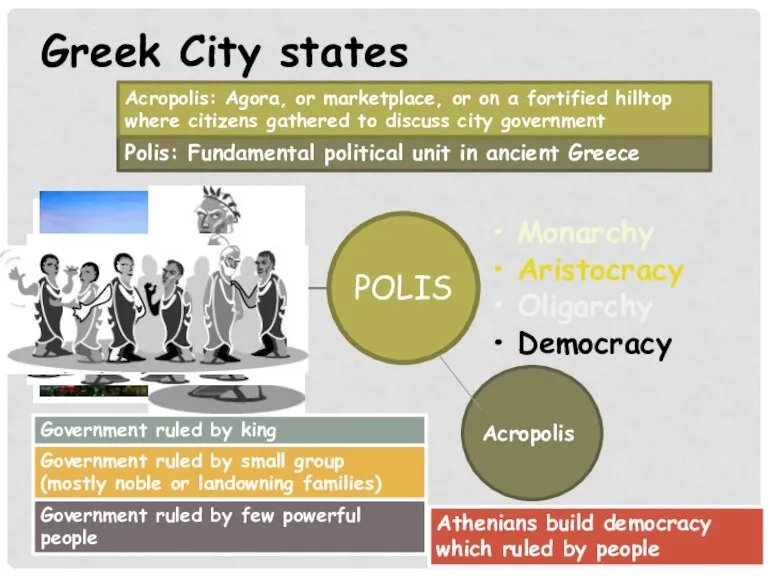
- 9. Greek City states Monarchy Aristocracy Oligarchy Democracy Polis: Fundamental political unit in ancient Greece Acropolis: Agora,
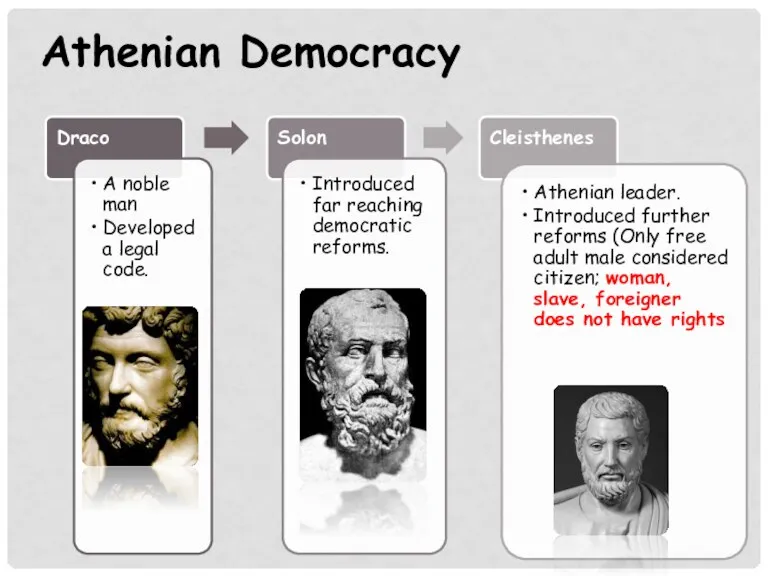
- 10. Athenian Democracy Draco Solon Cleisthenes
- 11. Athenians Boys: Wealthy kids received formal education -> Attend school around age 7; also receives training
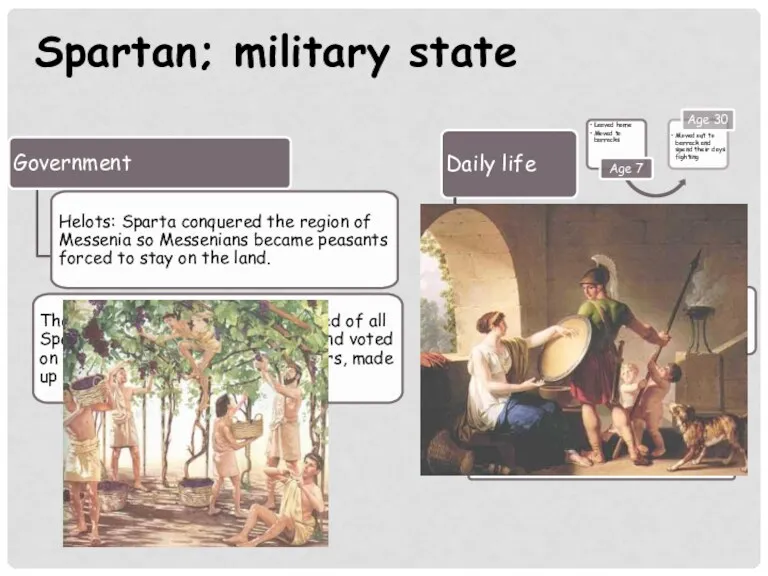
- 12. Spartan; military state Government Helots: Sparta conquered the region of Messenia so Messenians became peasants forced
- 13. The Persian Wars The Persian War: War between Greece and the Persian Empire (Began in Ionia
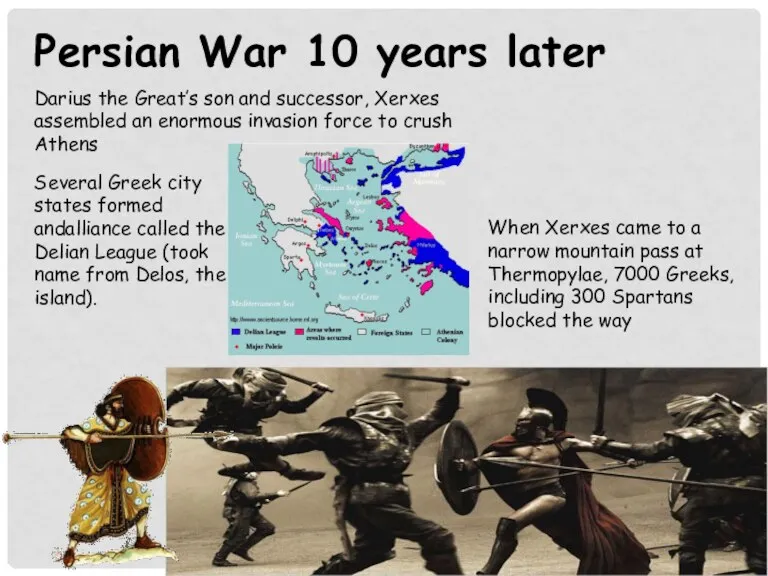
- 14. Persian War 10 years later Darius the Great’s son and successor, Xerxes assembled an enormous invasion
- 15. Glorify Athen -> Bought huge amounts of gold, ivory and marble -> Also paid the artists,
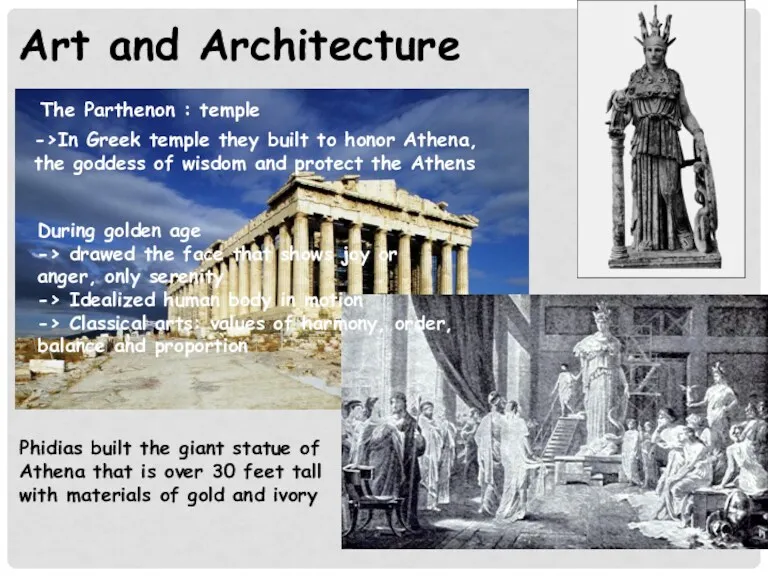
- 16. Art and Architecture The Parthenon : temple ->In Greek temple they built to honor Athena, the
- 17. Drama and History
- 18. Athenians vs Spartans Peloponnesian War : War between two city states; Athens had the stronger navy.
- 19. Socrates: Believed in absolute standard exist in justice. Encouraged Greeks to go farther and question for
- 20. Philip II Philip builds Macedonian Power Macedonian: Rough terrain and cold climate -> have important resource
- 21. Alexander the great At age 20 he became king He was well prepared to lead ->
- 22. Hellenistic Culture Hellenistic: Blending cultures of Egypt, Persia, and Indian -> Koine: The direct language Alexandria:
- 23. Science and Technology Astronomy: Alexandria’s museum contained a small observatory in which astronomers could study the
- 24. Philosophy and Art Stoic: People should live virtuous lives in harmony with the will of god
- 26. Скачать презентацию
















 Государство и право России в период становления парламентаризма (1900 – окт. 1917 гг.). Тема 9
Государство и право России в период становления парламентаризма (1900 – окт. 1917 гг.). Тема 9 Первая русская революция
Первая русская революция Восстание Спартака
Восстание Спартака Сокровища родного языка. Кроссворд
Сокровища родного языка. Кроссворд Хранить память предков
Хранить память предков Древние славяне
Древние славяне Индустриальное общество: новые проблемы и новые ценности
Индустриальное общество: новые проблемы и новые ценности Герб города Поронайск
Герб города Поронайск The Walt Disney Company. Индустрия развлечений в мире
The Walt Disney Company. Индустрия развлечений в мире Нашествие персидских войск на Элладу
Нашествие персидских войск на Элладу Древние люди и их стоянки на территории современной России
Древние люди и их стоянки на территории современной России Тоталитарные режимы в Европе 30-х годов XX века
Тоталитарные режимы в Европе 30-х годов XX века Герои Первой Мировой войны
Герои Первой Мировой войны Битва за Москву
Битва за Москву Формирование греческих ордеров в архитектуре архаического периода
Формирование греческих ордеров в архитектуре архаического периода Кавалер ордена славы
Кавалер ордена славы Михаил Романов (1613-1645)
Михаил Романов (1613-1645) Картографические рисунки древнего мира
Картографические рисунки древнего мира Древний Египет
Древний Египет CССР накануне Великой Отечественной войны
CССР накануне Великой Отечественной войны Крестьянская реформа 1861 г
Крестьянская реформа 1861 г Политический портрет В. И. Ленина
Политический портрет В. И. Ленина Монеты – свидетели истории
Монеты – свидетели истории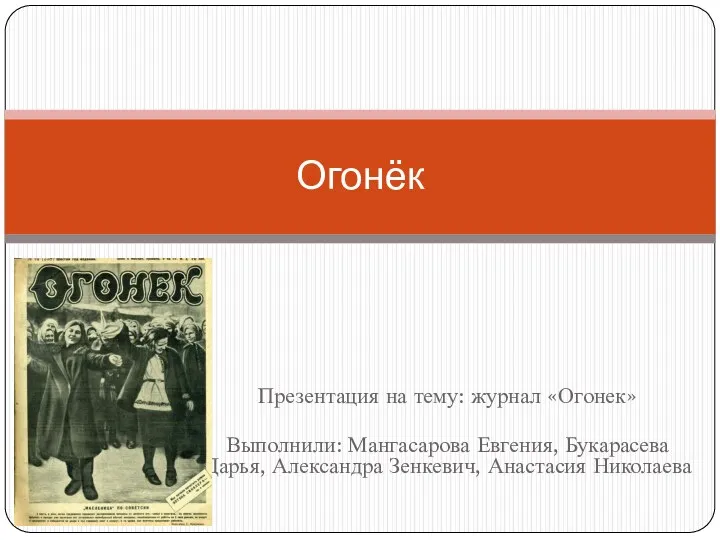 Журнал Огонек
Журнал Огонек История праздника 1 мая
История праздника 1 мая Поповский сельский клуб
Поповский сельский клуб Историческая школа в фольклористике
Историческая школа в фольклористике Дети войны. Дню Победы и Детям войны
Дети войны. Дню Победы и Детям войны