Содержание
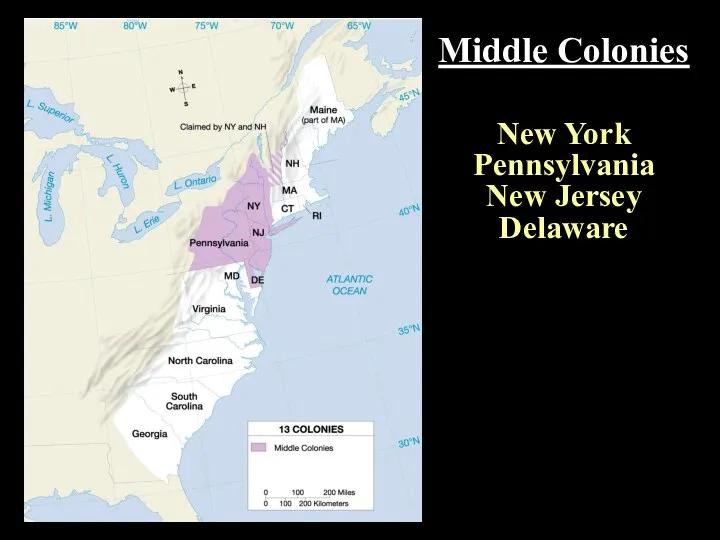
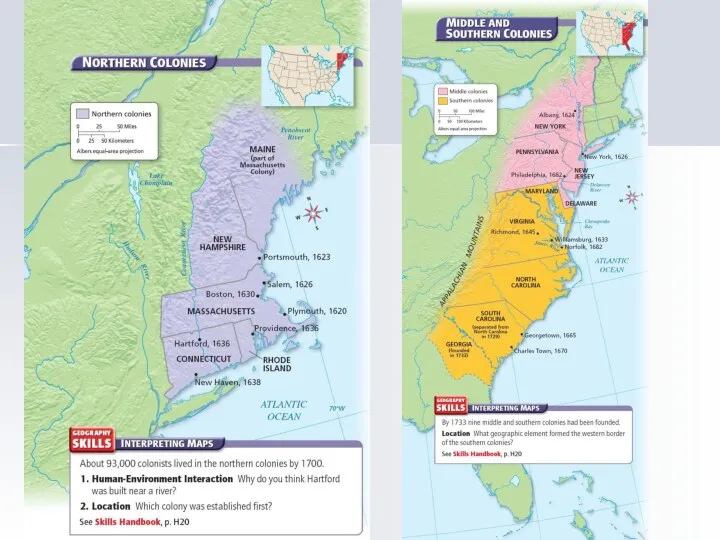
- 2. Middle Colonies New York Pennsylvania New Jersey Delaware
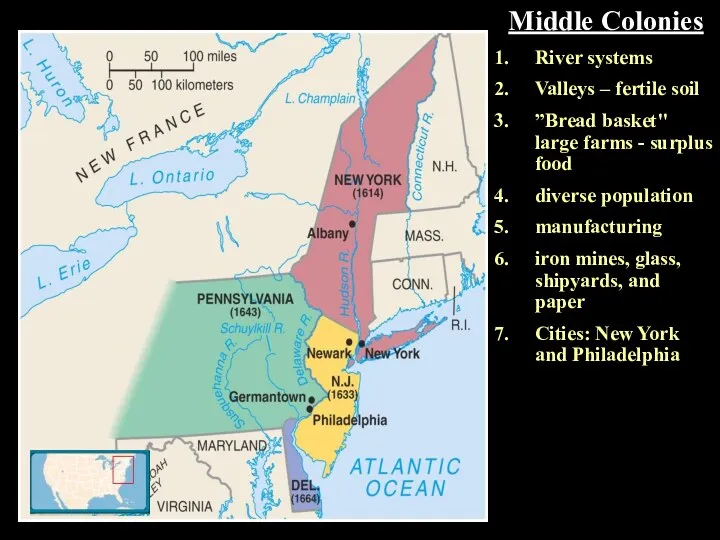
- 4. Middle Colonies River systems Valleys – fertile soil ”Bread basket" large farms - surplus food diverse
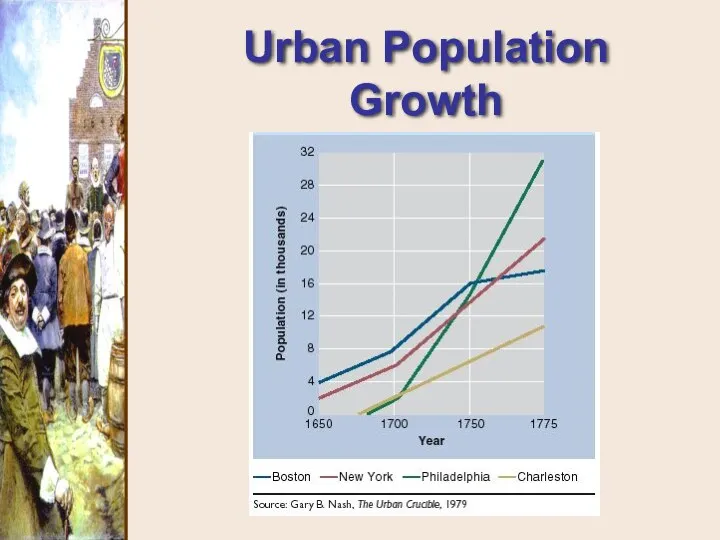
- 5. Urban Population Growth 1650 - 1775
- 6. New Netherland (New York) is first established by the Dutch 1609: Henry Hudson sailing for Dutch
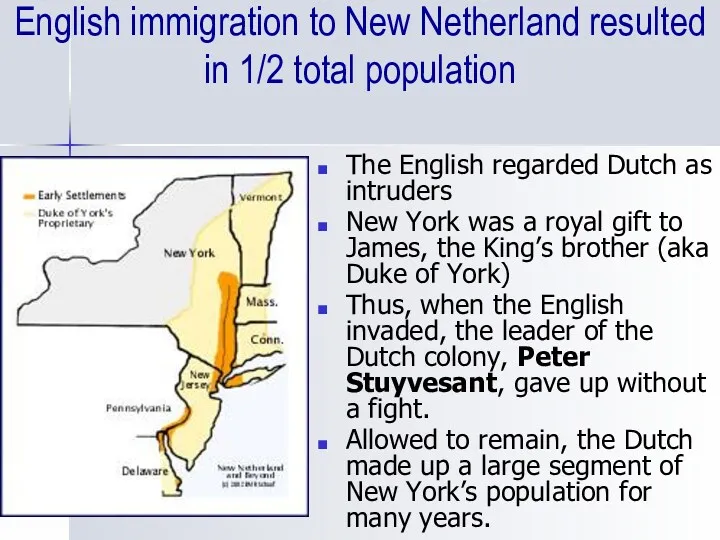
- 7. English immigration to New Netherland resulted in 1/2 total population The English regarded Dutch as intruders
- 8. New Jersey James gave 2 friends, Lord John Berkeley and Sir George Carteret, the section of
- 9. Mid-1600s: religious dissenters named Quakers arose in England Hated by authorities because they refused to pay
- 10. William Penn, a Quaker, was a close friend of King Charles II, and Charles granted Penn
- 11. Royal Land Grant to Penn
- 12. Penn's Holy Experiment Penn governs the colony Advertised in Europe, promising land & freedoms Frame of
- 14. Penn’s Treaty with the Native Americans
- 15. Penn & Native Americans Penn attempted to treat Native Americans more fairly than did other colonies.
- 16. Pennsylvania & Neighbors However, as non-Quaker immigrants came, they were less tolerant of Natives(Scots-Irish) Liberal features:
- 19. Скачать презентацию










 Быт и нравы Древней Руси
Быт и нравы Древней Руси Архетекуралық ғимараттардың талаптары
Архетекуралық ғимараттардың талаптары Культура Европейского просвещения
Культура Европейского просвещения Храм великомученика Георгия Победоносца в д.Понизовье Устюженского района
Храм великомученика Георгия Победоносца в д.Понизовье Устюженского района Город Бугуруслан в Оренбургской области РФ
Город Бугуруслан в Оренбургской области РФ Новое российское общество (1991-2000 гг.)
Новое российское общество (1991-2000 гг.) Кузнецк в XVII-XVIII
Кузнецк в XVII-XVIII Иван Фёдоров
Иван Фёдоров История государства и права зарубежных стран
История государства и права зарубежных стран Вклад Генри Форда(1863-1947) в развитие управленческой деятельности
Вклад Генри Форда(1863-1947) в развитие управленческой деятельности У истоков Российской модернизации
У истоков Российской модернизации Журналистика Великобритании ХХ века
Журналистика Великобритании ХХ века Золотой век театра и музыки
Золотой век театра и музыки Самара – город памятников
Самара – город памятников Ленинград 1941-1944
Ленинград 1941-1944 Презентация к курсу Лики истории 10 класс
Презентация к курсу Лики истории 10 класс Советское государство в 20-30-е годы XX века
Советское государство в 20-30-е годы XX века Первая Мировая война
Первая Мировая война История рубля в России
История рубля в России Экскурсия: Псков – Ольгин город
Экскурсия: Псков – Ольгин город Начало Великой Отечественной войны и первый ее этап
Начало Великой Отечественной войны и первый ее этап Німеччина в ХІХ столітті
Німеччина в ХІХ столітті Герои Великой Отечественной войны 1941-1945 гг
Герои Великой Отечественной войны 1941-1945 гг Эпоха Петра I (1682-1725 гг.)
Эпоха Петра I (1682-1725 гг.) Вклад народов Центральной Азии в развитие мировой культуры
Вклад народов Центральной Азии в развитие мировой культуры День Неизвестного солдата
День Неизвестного солдата Реконкиста. Начало
Реконкиста. Начало Боги славянского пантеона. Язычество древних славян
Боги славянского пантеона. Язычество древних славян