Содержание
- 2. agenda principles of good design grid and layout feedback, feedforward, affordance visual hierarchy typography
- 3. Good design is innovative Possibilities always there Technology pushes the edges of possible, so design should
- 4. Good design makes a product useful A product is bought to be used. It has to
- 5. Good design is aesthetic The aesthetic quality of a product is integral to its usefulness because
- 6. Good design makes a product understandable It clarifies the product’s structure. Better still, it can make
- 7. Good design is unobtrusive Products fulfilling a purpose are like tools. They are neither decorative objects
- 8. Good design is honest It does not make a product more innovative, powerful or valuable than
- 9. Good design is long-lasting It avoids being fashionable and therefore never appears antiquated. Unlike fashionable design,
- 10. Good design is thorough down to the last detail Nothing must be arbitrary or left to
- 11. Good design is environmentally-friendly Design makes an important contribution to the preservation of the environment. It
- 12. Good design is as little design as possible Less, but better – because it concentrates on
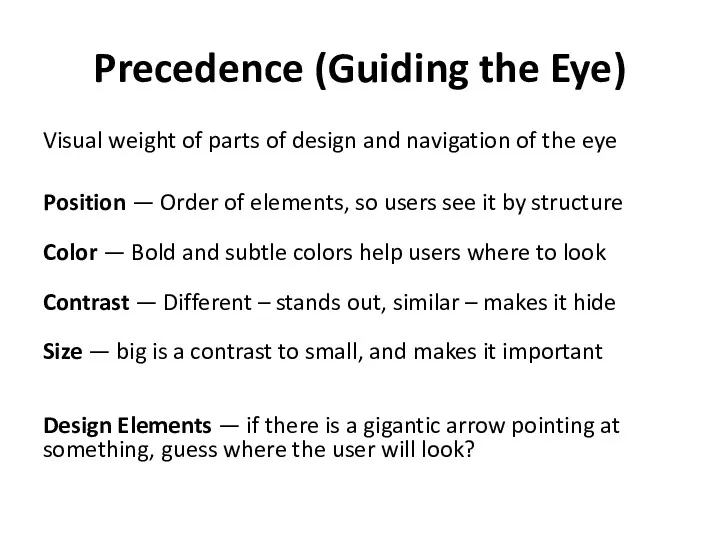
- 13. Precedence (Guiding the Eye) Visual weight of parts of design and navigation of the eye Position
- 14. Spacing Empty space seemed wasteful. In fact the opposite is true. Line Spacing – too little
- 15. Navigation One of the most frustrating experiences: failing to figure out where to go or where
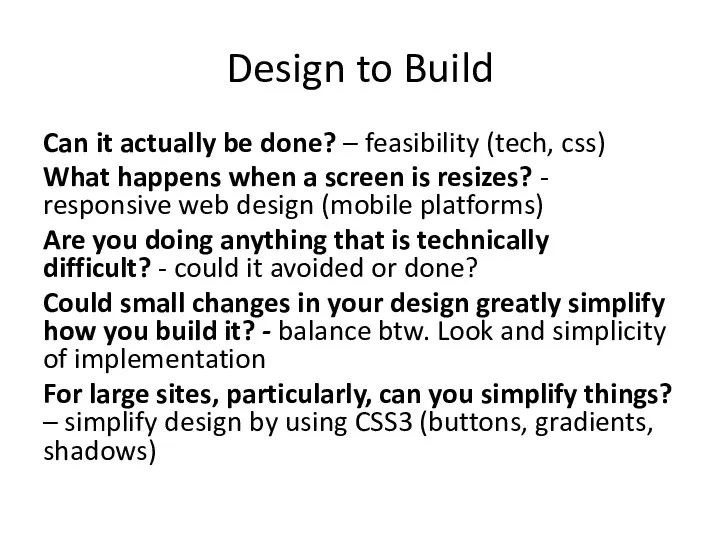
- 16. Design to Build Can it actually be done? – feasibility (tech, css) What happens when a
- 17. Typography The most common element in design of UI Font Choices – modern, retro, old, futuristic
- 18. Usability (we learned a lot here) Design is about how it works, not how it looks.
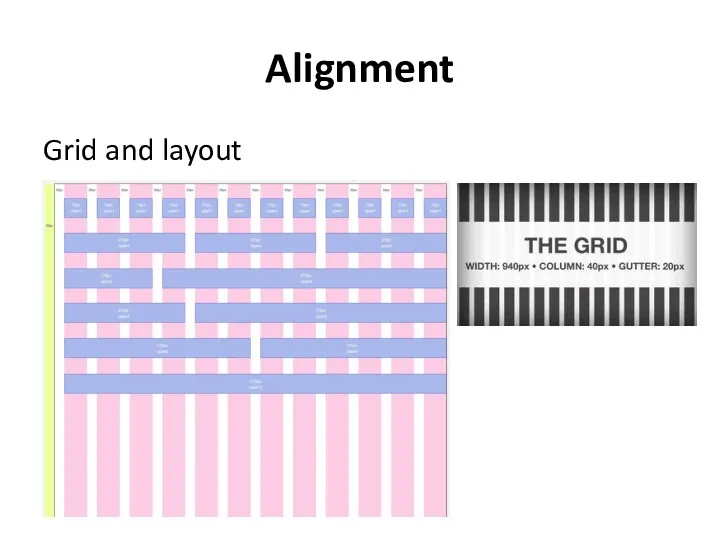
- 19. Alignment Grid and layout
- 20. Clarity (Sharpness) Keeping the design crisp and sharp Edges – snapped to the pixels Anti-aliasing in
- 21. Consistency making everything match. Heading sizes, font choices, coloring, button styles, spacing, design elements, illustration styles,
- 25. Line things up
- 26. Balance the page & leave some white space
- 27. Use designer fonts
- 28. Texts should not be very long
- 29. Left-align in most cases (center for unity)
- 30. USE COLORS TO COMMUNICATE & MAKE THINGS POP DON’T USE THEM FRIVOLOUSLY
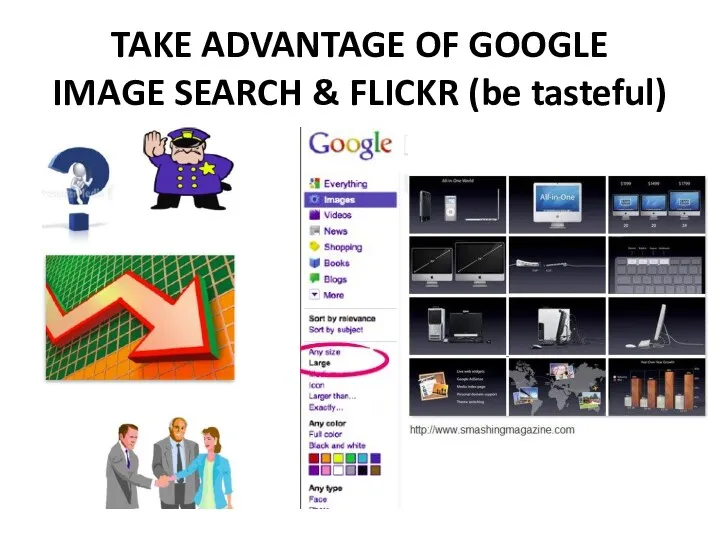
- 31. TAKE ADVANTAGE OF GOOGLE IMAGE SEARCH & FLICKR (be tasteful)
- 32. Rules Are Made To Be Broken
- 34. Скачать презентацию

























 Театр – синтетический вид искусства
Театр – синтетический вид искусства Синие цветы Гжель
Синие цветы Гжель Викторина 100 лет Карелии
Викторина 100 лет Карелии Жизнь каждого дня - большая тема в искусстве
Жизнь каждого дня - большая тема в искусстве Характер линий
Характер линий Фактура. Фактура в ландшафтном дизайне
Фактура. Фактура в ландшафтном дизайне Декоративно-ужиткове мистецтво
Декоративно-ужиткове мистецтво Съемка с двумя источниками света
Съемка с двумя источниками света Перспектива. Тональная и воздушная, геометрическая перспективы
Перспектива. Тональная и воздушная, геометрическая перспективы Кукла Тильда. Прикладной дизайн
Кукла Тильда. Прикладной дизайн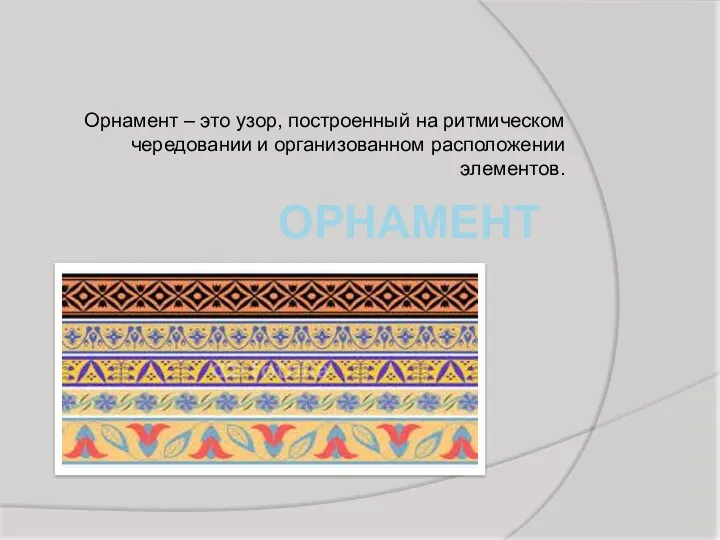 Орнамент в полосе
Орнамент в полосе Цумами Канзаши
Цумами Канзаши Народные промыслы России
Народные промыслы России Культурное наследние древних цивилизаций. Египет
Культурное наследние древних цивилизаций. Египет Міський шик. Стиль одягу
Міський шик. Стиль одягу Портфолио обучающегося
Портфолио обучающегося Узелковый батик
Узелковый батик Козеро́г (лат. Capricornus, Сapra - коза, Cornu рог) — зодиакальное созвездие южного полушария неба
Козеро́г (лат. Capricornus, Сapra - коза, Cornu рог) — зодиакальное созвездие южного полушария неба Пам'ятки Канади
Пам'ятки Канади Широкая масленица
Широкая масленица Новый год в Тайване
Новый год в Тайване Обычаи, обряды и традиции русского народа Чем дальше в будущее входим, тем больше прошлым дорожим…
Обычаи, обряды и традиции русского народа Чем дальше в будущее входим, тем больше прошлым дорожим… Сочетание традиций и инноваций в дизайне Японии
Сочетание традиций и инноваций в дизайне Японии Жанры живописи (для дошкольников)
Жанры живописи (для дошкольников) Серебряный век русской культуры
Серебряный век русской культуры Утренние бхаджаны
Утренние бхаджаны Экранные искусства. Телевидение
Экранные искусства. Телевидение Свет в фотографии
Свет в фотографии