Содержание
- 2. How do people spend their free time? go to the park work out go to the
- 3. What are we going to talk about? Theatre
- 4. Do you like to go to the theatre? What is your favourite play? What theatres do
- 5. Improvise Platform Dramatist Give definitions to the words:
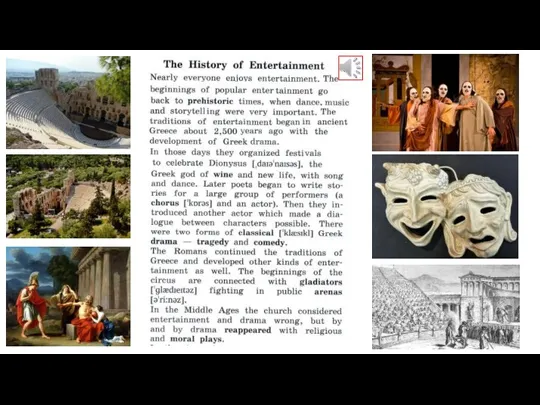
- 6. Prehistoric Wine Chorus Tragedy
- 9. Which of these ideas are not in it. 1.The history of entertainment is very old. 2.
- 10. Say the same in one word. The Renaissance a circus prehistoric a chorus ancient a drama
- 11. Answer the questions. Were music, dancing and storytelling in prehistoric times forms of entertainment or were
- 12. What do these words mean? An arena A high platform for performers A place with seats
- 13. What do these words mean? A chorus A song for a large group of singers A
- 14. Complete the text with theatre words. theatre plays audience theatres drama tragedies comedies theatres performers theatres
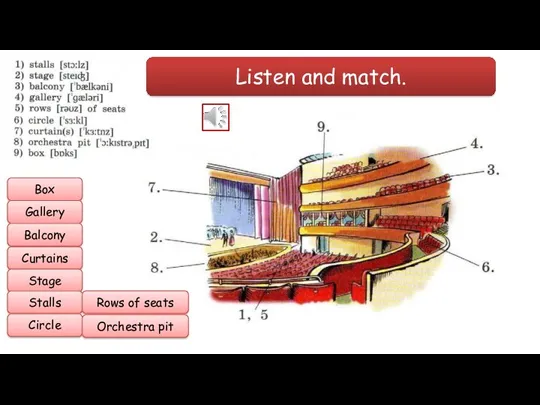
- 15. Listen and match. Box Gallery Balcony Curtains Stage Stalls Circle Rows of seats Orchestra pit
- 16. Listen and match the definition
- 17. What are these? cloakroom buffet usher foyer ticket opera glasses box office ticket 1 2 3
- 18. C. Born to be Famous 1 2 3 4 5 extra E. The Places Connected with
- 19. Listen again and answer the questions: How many houses did Shakespeare have? Where are they? What
- 20. Is it difficult to understand what Shakespeare wrote? 2. Who rewrote his plays? 3. How many
- 21. 1. How did Londoners get to the new Globe Theatre? 2. How did they know that
- 22. Listen again and answer the questions: What education did Shakespeare have? In what do people believe?
- 23. Read the text and complete it with the word combinations (a-h). Give the text a name.
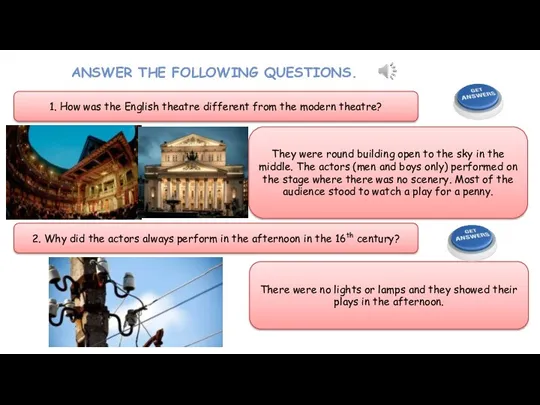
- 24. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS. 1. How was the English theatre different from the modern theatre? 2.
- 25. 3. How long did it take members of Shakespeare’s company to build The Globe? 4. Where
- 27. Скачать презентацию





















 Магия имени Кармен как притяжение в искусстве
Магия имени Кармен как притяжение в искусстве Ткачихи-рукодельницы
Ткачихи-рукодельницы Пам’ятники Тарасу Шевченку в Україні та світі
Пам’ятники Тарасу Шевченку в Україні та світі Современные танцы. Контемп
Современные танцы. Контемп Основы татарской культуры
Основы татарской культуры Интерьер жилого помещения
Интерьер жилого помещения Фильм - рассказ в картинках
Фильм - рассказ в картинках Ритм линий и пятен, цвет пропорции - средства выразительности
Ритм линий и пятен, цвет пропорции - средства выразительности Викторина о кино 90-х
Викторина о кино 90-х Пикча. Фотошкола
Пикча. Фотошкола Культурна різноманітність Японії
Культурна різноманітність Японії Welcome to Los Angeles
Welcome to Los Angeles Русская скульптура XVIII – первой половины XIX веков
Русская скульптура XVIII – первой половины XIX веков Загадочные животные нашего города
Загадочные животные нашего города Тимур Бекмамбетов
Тимур Бекмамбетов Творчество Ильи Репина (1844-1930)
Творчество Ильи Репина (1844-1930) Архитектура, скульптура и живопись раннего Ренессанса
Архитектура, скульптура и живопись раннего Ренессанса Цветы из бумаги
Цветы из бумаги Шаттык шенбери
Шаттык шенбери Реальность и фантазия в творчестве художников
Реальность и фантазия в творчестве художников Пьер Огюст Ренуар
Пьер Огюст Ренуар Урок декоративного рисования Эскиз матрёшки
Урок декоративного рисования Эскиз матрёшки Художественное эмалирование
Художественное эмалирование Деятельность театральных организаций
Деятельность театральных организаций Қазақ халқының ұлттық ойындары
Қазақ халқының ұлттық ойындары Основные периоды в истории мебели
Основные периоды в истории мебели Основы духовно-нравственной культуры народов России. 5 класс
Основы духовно-нравственной культуры народов России. 5 класс 傣族
傣族