Содержание
- 2. Literary Devices of Fiction Setting Plot Character Conflict Point of View Theme Mood Dialogue Rhetorical Devices
- 3. Setting (element) The setting of a story is the time and place in which it occurs.
- 4. Mood (element) The mood of a story is the atmosphere or feeling created by the writer
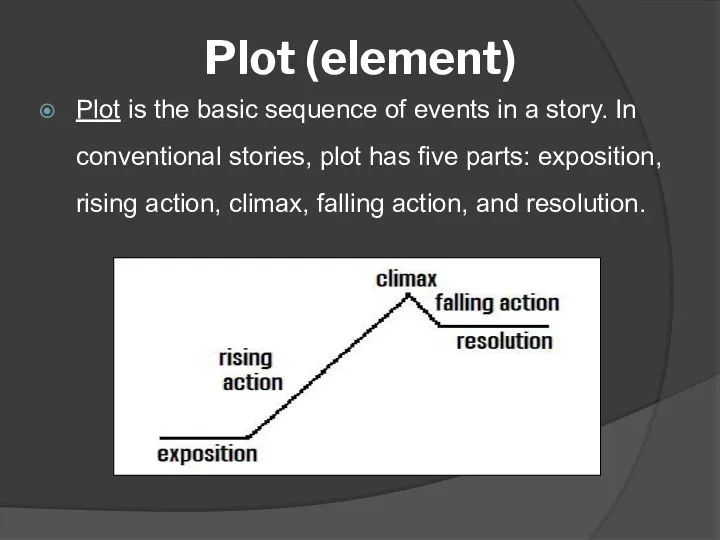
- 5. Plot (element) Plot is the basic sequence of events in a story. In conventional stories, plot
- 6. Flashback (technique) A flashback is a literary device by which a work presents material that occurred
- 7. Foreshadowing (technique) Foreshadowing is the presentation of material in a work in such a way that
- 8. Figurative Language (technique)
- 9. Figurative Language Simile Metaphor A comparison of two things that are essentially different, usually using the
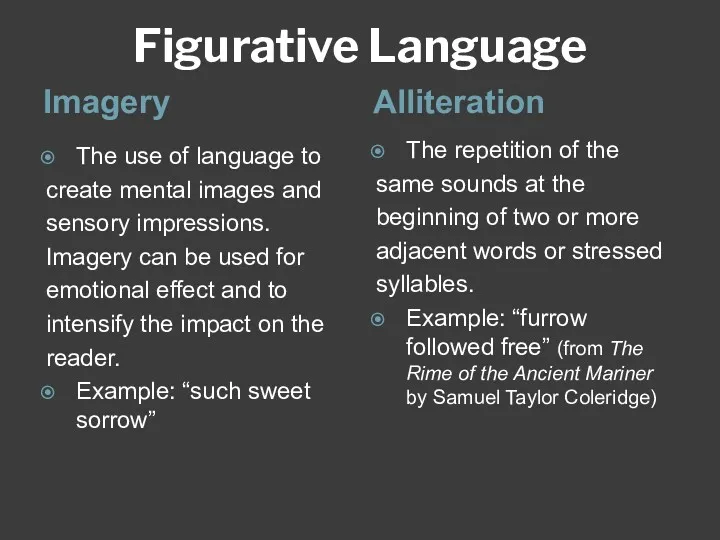
- 10. Figurative Language Imagery Alliteration The use of language to create mental images and sensory impressions. Imagery
- 11. Figurative Language Personification Onomatopoeia Nonhuman things or abstractions are represented as having human qualities. Example: “A
- 12. Figurative Language Hyperbole Idiom An intentionally exaggerated figure of speech for emphasis or effect. Example: "All
- 13. Rhetorical Device (technique) A technique that an author or speaker uses to evoke an emotional response
- 14. Types of Characters (element) Dynamic character—a character which changes during the course of a story or
- 15. Types of Characters Protagonist—the story’s main character Antagonist—a character in opposition of the protagonist Character Foil—a
- 16. Characterization Characterization is the creation of imaginary persons so that they seem lifelike. There are three
- 17. Characterization The representation from within a character, without comment by the author, of the impact of
- 18. Character Development Internal Character Development Feelings Thoughts Emotions External Character Development Actions Relationships Dialogues
- 19. Irony (technique) Irony– the use of words to express something other than, and especially the opposite
- 20. Allusion (techniques) An allusion is a reference within a literary work to another work of literature,
- 22. Скачать презентацию

















 Путин Владимир Владимирович
Путин Владимир Владимирович Чарльз Пирс
Чарльз Пирс Уроженцы Ельниковского района - участники Великой Отечественной войны
Уроженцы Ельниковского района - участники Великой Отечественной войны Виртуальная выставка Дорогие мои мальчишки (к 115-летию Льва Кассиля)
Виртуальная выставка Дорогие мои мальчишки (к 115-летию Льва Кассиля) Сборник стихов очёрских поэтов Лира
Сборник стихов очёрских поэтов Лира А.П. Чехов. Рассказ Хамелеон
А.П. Чехов. Рассказ Хамелеон Основная идея произведений поэтов эпохи Зар заман
Основная идея произведений поэтов эпохи Зар заман Человек во времени. Ян Сатуновский
Человек во времени. Ян Сатуновский Константин Николаевич Батюшков 18(29) мая 1787 - 7(19) июля 1855
Константин Николаевич Батюшков 18(29) мая 1787 - 7(19) июля 1855 Россия в поэме Н.В. Гоголя Мёртвые души
Россия в поэме Н.В. Гоголя Мёртвые души Қазанбай Ғалия Тілектесқызы
Қазанбай Ғалия Тілектесқызы Поэзия Анны Ахматовой. Жизнь Анны Ахматовой
Поэзия Анны Ахматовой. Жизнь Анны Ахматовой Владислав Крапивин
Владислав Крапивин Фёдор Ивановчи Тютчев (1803-1873)
Фёдор Ивановчи Тютчев (1803-1873) Воланд и его свита в Москве
Воланд и его свита в Москве Тео Ван Дусбург
Тео Ван Дусбург War of the worlds
War of the worlds Викторина Приключения Незнайки и его друзей
Викторина Приключения Незнайки и его друзей Музей Щелкунчик
Музей Щелкунчик Урок обучение грамоте. Знакомство с буквой Бб. Чтение слогов и слов
Урок обучение грамоте. Знакомство с буквой Бб. Чтение слогов и слов Культурное пространство Российской империи во второй половине 19 века. Русская литература. Тест
Культурное пространство Российской империи во второй половине 19 века. Русская литература. Тест Ли Куан Ю (Ли Гуанъяо)
Ли Куан Ю (Ли Гуанъяо) Презентация по литературе Ночь перед Рождеством.Н.В.Гоголь
Презентация по литературе Ночь перед Рождеством.Н.В.Гоголь Печорин и его двойники: Грушницкий и Вернер. М.Ю. Лермонтов
Печорин и его двойники: Грушницкий и Вернер. М.Ю. Лермонтов Анна Павлова
Анна Павлова Леонард Эйлер: жизнь, творчество, служение России
Леонард Эйлер: жизнь, творчество, служение России Проблематика повести К. Воробьева Это мы, господи!
Проблематика повести К. Воробьева Это мы, господи! В.М.Севергин 1765—1826
В.М.Севергин 1765—1826