Содержание
- 2. SM Lecture 2: Understanding Service Consumers Lecturer: Makhsuma Abdullaeva Contact email: mabdullaeva@wiut.uz Office hours: By appointment
- 3. Customer Decision Making: Three-Stage Model of Service Consumption
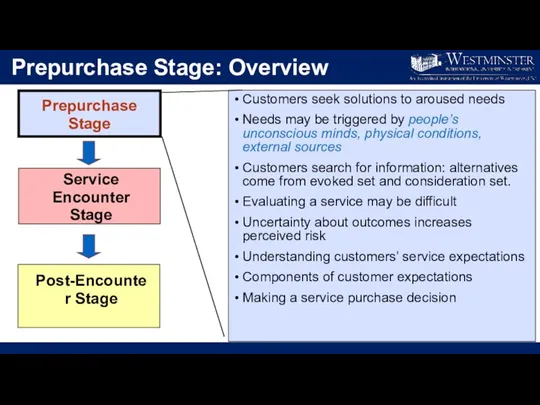
- 4. Prepurchase Stage: Overview Prepurchase Stage Service Encounter Stage Post-Encounter Stage Customers seek solutions to aroused needs
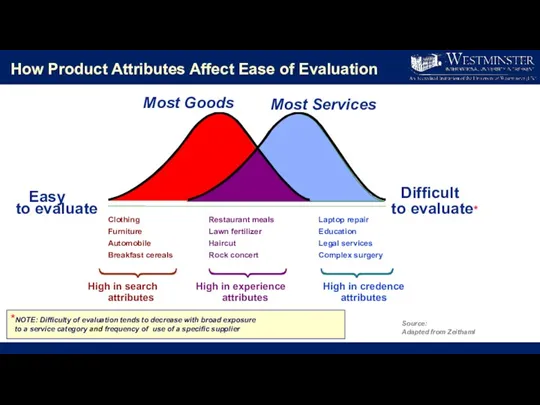
- 5. Evaluating a Service May Be Difficult Search attributes are tangible characteristics that customers can evaluate before
- 6. Restaurant dining experience
- 7. How Product Attributes Affect Ease of Evaluation
- 8. Perceived Risks in Purchasing and Using Services Functional—unsatisfactory performance outcomes Financial—monetary loss, unexpected extra costs Temporal—wasted
- 9. Strategic Responses to Managing Customer Perceptions of Risk Offer performance warranties, guarantees to protect against fears
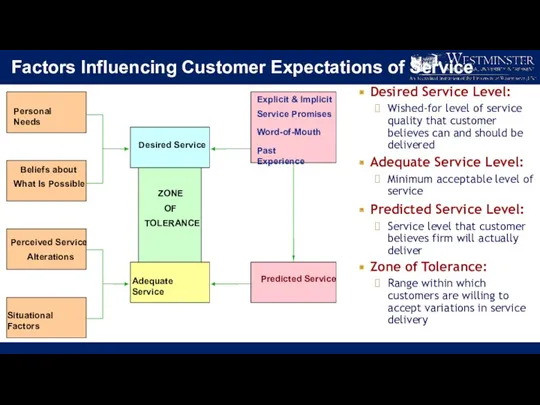
- 10. Understanding Customers’ Service Expectations Customers evaluate service quality by comparing what they expect against what they
- 11. Factors Influencing Customer Expectations of Service Desired Service Level: Wished-for level of service quality that customer
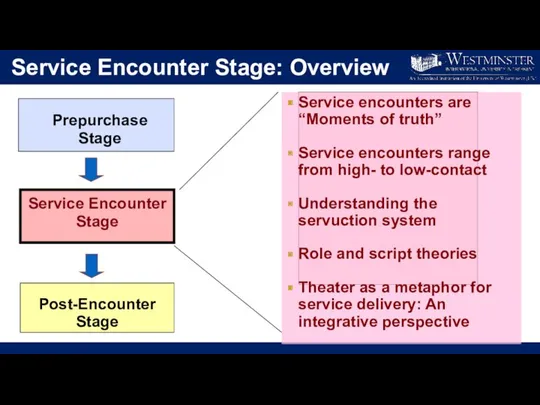
- 12. Service Encounter Stage: Overview Prepurchase Stage Service Encounter Stage Post-Encounter Stage Service encounters are “Moments of
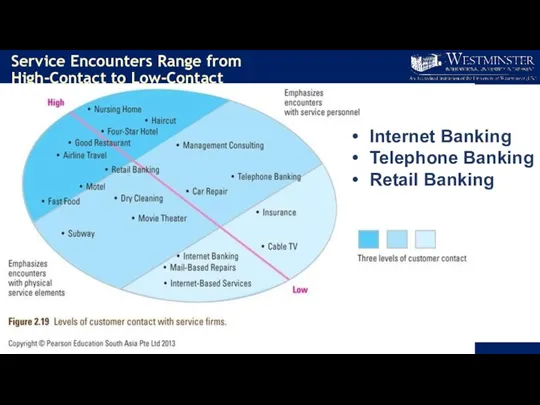
- 13. Service Encounters Range from High-Contact to Low-Contact Internet Banking Telephone Banking Retail Banking
- 14. High-Contact and Low-Contact Services High-Contact Services Customers visit service facility and remain throughout service delivery Active
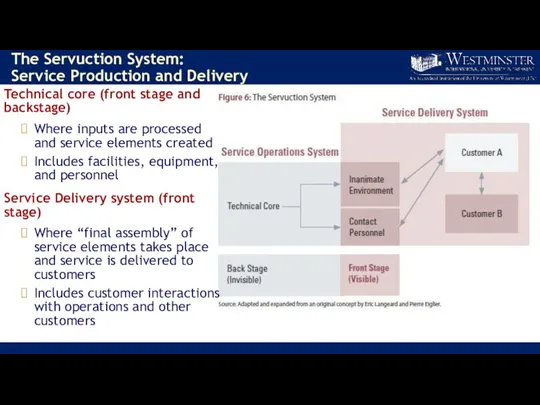
- 15. The Servuction System: Service Production and Delivery Technical core (front stage and backstage) Where inputs are
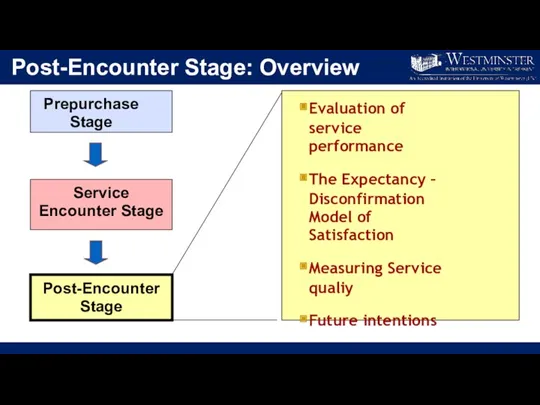
- 16. Post-Encounter Stage: Overview Prepurchase Stage Service Encounter Stage Post-Encounter Stage Evaluation of service performance The Expectancy
- 17. Customer Satisfaction Satisfaction defined as attitude-like judgment following a service purchase or series of service interactions
- 18. Customer Delight: Going Beyond Satisfaction Research shows that delight is a function of three components: Unexpectedly
- 19. Service Quality Excellent service quality means that a firm consistently meets or exceeds customer expectations In
- 20. Capturing the Customer’s Perspective of Service Quality: SERVQUAL Survey research instrument based on premise that customers
- 21. E Sample of questionnaire based on SERVQUAL model
- 22. Lecture 2 Part.2. Positioning Services in Competitive Markets
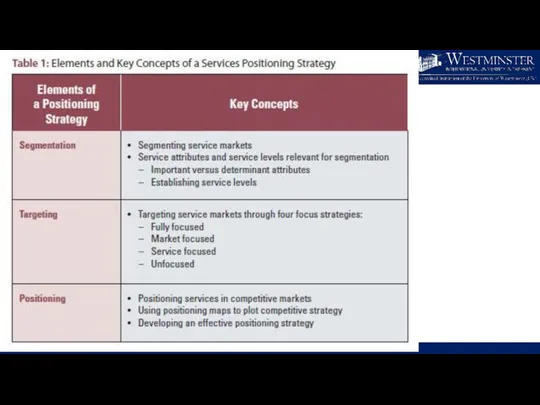
- 24. Important vs Determinant Service Attributes Consumers usually choose between alternative service offerings based on perceived differences
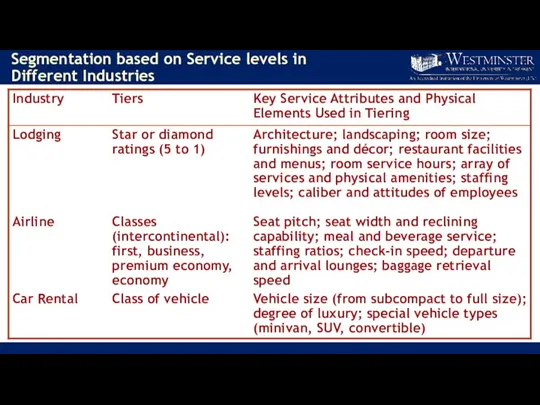
- 25. Segmentation based on Service levels in Different Industries
- 26. Capsule Hotels
- 27. Targeting Service Markets
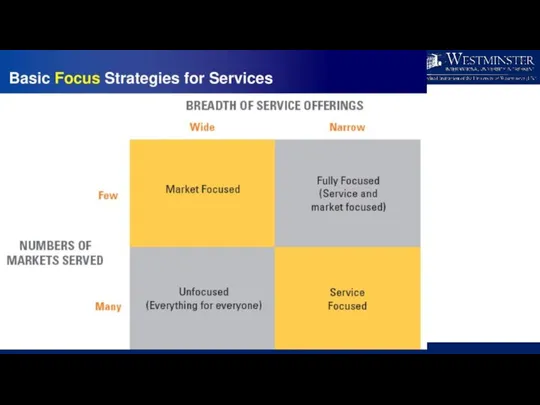
- 29. Four Principles of Positioning Strategy Must establish position for firm or product in minds of customers
- 31. Скачать презентацию


















 Алгоритм работы с покупателем
Алгоритм работы с покупателем Социальный франчайзинг. Часть 2
Социальный франчайзинг. Часть 2 Коммерческое предложение. Гостиница Президент-Отель
Коммерческое предложение. Гостиница Президент-Отель Техника проведения биржевого торга
Техника проведения биржевого торга Корпоративная программа лояльности САО ВСК
Корпоративная программа лояльности САО ВСК Кросс-маркетинг
Кросс-маркетинг Завдання на розробку контенту порталу з врахуванням ваги пошукових запитів
Завдання на розробку контенту порталу з врахуванням ваги пошукових запитів Современные подходы к применению аутсорсинга маркетинга в системе предпринимательства
Современные подходы к применению аутсорсинга маркетинга в системе предпринимательства Алгоритм работы с пациентом в оптике
Алгоритм работы с пациентом в оптике Виды доходов в компании Орифлэйм
Виды доходов в компании Орифлэйм Анализ бренда Nestle
Анализ бренда Nestle Реклама. Magic Toys - це іграшки для дітей будь-якого віку!
Реклама. Magic Toys - це іграшки для дітей будь-якого віку! Анализ рынка
Анализ рынка Особенности маркетинга инноваций
Особенности маркетинга инноваций Линия средств PERFECT
Линия средств PERFECT Стандарт работы продавца-консультанта в магазинах сети Буквоед
Стандарт работы продавца-консультанта в магазинах сети Буквоед Выгодное предложение компании Tele2
Выгодное предложение компании Tele2 Маркетинговая стратегия Starbucks: как создать запоминающийся бренд
Маркетинговая стратегия Starbucks: как создать запоминающийся бренд Рынок как объект маркетинга
Рынок как объект маркетинга Сущность и принципы маркетинга
Сущность и принципы маркетинга Разработка стратегии маркетинга компании
Разработка стратегии маркетинга компании Project: Global Social Media Plan November Topic:Hill-Start Assist Subline: Highlight the Hill-Start Assist feature using nature
Project: Global Social Media Plan November Topic:Hill-Start Assist Subline: Highlight the Hill-Start Assist feature using nature Обновление бренда Моё солнышко. Детская косметика
Обновление бренда Моё солнышко. Детская косметика Skin session
Skin session Отель Red Stars (Санкт-Петербург)
Отель Red Stars (Санкт-Петербург) Управленческий менеджмент и маркетинг. Лекция 8
Управленческий менеджмент и маркетинг. Лекция 8 Квалификация исследовательской компании РАДАР
Квалификация исследовательской компании РАДАР Фулфилмент. Первый гипермаркет мебели
Фулфилмент. Первый гипермаркет мебели