Содержание
- 2. Global Market Segmentation Identifying consumers in different countries who share similar needs and desires (not identical)
- 3. Demographic segmentation Measurables characteristics of people such as population, income, age distribution, gender, education, occupation Q
- 4. Segmenting Global markets by income and population: the number of consumers is more important than the
- 5. While providing some measures of market potential, such macro level demographic data should not be used
- 6. A3: Although mandarin is the dominant laguage, there are 8 major languages and several dialects and
- 7. Age segmentation To understand better how this demographic is assesed by marketers lets look at some
- 8. Global elite: wealthy in search of prestige and exclusivity.Old business men, musicians, elite athletes, movie stars,
- 9. Gender Segmentation The obvious segmentation is male female, however there are other sexual orientation groups to
- 10. Psychographic Segmentation Grouping people in terms of their attitudes, values, and lifestyles. Usually measure by using
- 11. Behaviour Segmentation Focuses on whether people buy and use a product as well as how often
- 12. The 80/20 rule (law of disproportionality or pareto´s law) An 80% of a company revenues must
- 13. Benefit Segmentation It focuses on a superior understanding of the problem a product solves, the benefit
- 14. Etnic Segmentation This segmentation approach addresses the specific needs of ethnic groups or appeals to their
- 15. Global Market Targeting Assesing Market Potential and Choosing Target Markets or Segments Assessing the attractiveness of
- 16. Arnold´s framework is a "bottom-up" approach that goes beyond demographic data and begins at the product-market
- 17. Market entry After model drivers and enabling conditions have been identified the estimated costs of entry
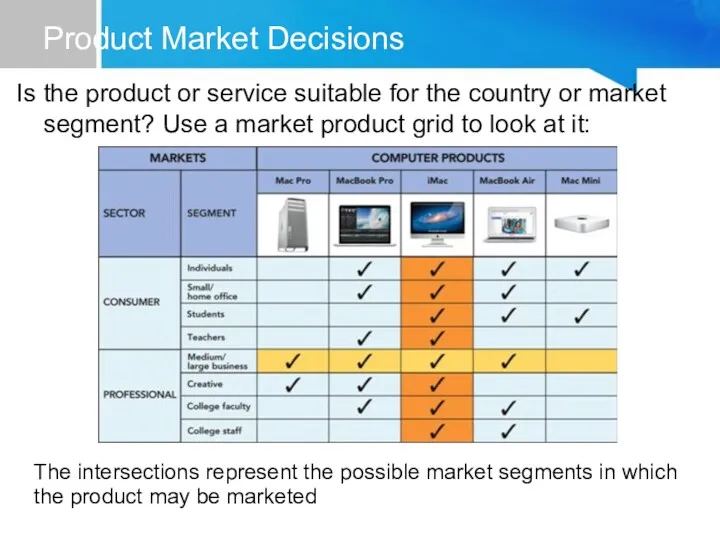
- 18. Product Market Decisions Is the product or service suitable for the country or market segment? Use
- 19. Q11: To face the problem of high temperatures in India what are some entry strategies suitable
- 20. Target market Strategy Options After analysing the market and deciding to go ahead companies must develop
- 21. Positioning Strategies Refers to the differentiation of a brand in customers´ mind in relation to competitors
- 22. Q13: How does people evaluate high tech products? Q14: How does people relate to high touch
- 24. Скачать презентацию

















 Алгоритм работы с покупателем
Алгоритм работы с покупателем Социальный франчайзинг. Часть 2
Социальный франчайзинг. Часть 2 Коммерческое предложение. Гостиница Президент-Отель
Коммерческое предложение. Гостиница Президент-Отель Техника проведения биржевого торга
Техника проведения биржевого торга Корпоративная программа лояльности САО ВСК
Корпоративная программа лояльности САО ВСК Кросс-маркетинг
Кросс-маркетинг Завдання на розробку контенту порталу з врахуванням ваги пошукових запитів
Завдання на розробку контенту порталу з врахуванням ваги пошукових запитів Современные подходы к применению аутсорсинга маркетинга в системе предпринимательства
Современные подходы к применению аутсорсинга маркетинга в системе предпринимательства Алгоритм работы с пациентом в оптике
Алгоритм работы с пациентом в оптике Виды доходов в компании Орифлэйм
Виды доходов в компании Орифлэйм Анализ бренда Nestle
Анализ бренда Nestle Реклама. Magic Toys - це іграшки для дітей будь-якого віку!
Реклама. Magic Toys - це іграшки для дітей будь-якого віку! Анализ рынка
Анализ рынка Особенности маркетинга инноваций
Особенности маркетинга инноваций Линия средств PERFECT
Линия средств PERFECT Стандарт работы продавца-консультанта в магазинах сети Буквоед
Стандарт работы продавца-консультанта в магазинах сети Буквоед Выгодное предложение компании Tele2
Выгодное предложение компании Tele2 Маркетинговая стратегия Starbucks: как создать запоминающийся бренд
Маркетинговая стратегия Starbucks: как создать запоминающийся бренд Рынок как объект маркетинга
Рынок как объект маркетинга Сущность и принципы маркетинга
Сущность и принципы маркетинга Разработка стратегии маркетинга компании
Разработка стратегии маркетинга компании Project: Global Social Media Plan November Topic:Hill-Start Assist Subline: Highlight the Hill-Start Assist feature using nature
Project: Global Social Media Plan November Topic:Hill-Start Assist Subline: Highlight the Hill-Start Assist feature using nature Обновление бренда Моё солнышко. Детская косметика
Обновление бренда Моё солнышко. Детская косметика Skin session
Skin session Отель Red Stars (Санкт-Петербург)
Отель Red Stars (Санкт-Петербург) Управленческий менеджмент и маркетинг. Лекция 8
Управленческий менеджмент и маркетинг. Лекция 8 Квалификация исследовательской компании РАДАР
Квалификация исследовательской компании РАДАР Фулфилмент. Первый гипермаркет мебели
Фулфилмент. Первый гипермаркет мебели