Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Define the consumer market and
- 3. Chapter Outline Model of Consumer Behavior Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Types of Buying Decision Behavior The
- 4. Model of Consumer Behavior Consumer buyer behavior refers to the buying behavior of final consumers—individuals and
- 5. Model of Consumer Behavior 5-5 Marketing stimuli consists of the 4 Ps Product Price Place Promotion
- 6. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-6 Cultural Factors Buyer’s culture Buyer’s subculture Buyer’s social class Social Factors
- 7. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-7 Personal Factors Age and life-cycle stage Occupation Economic situation Lifestyle Personality
- 8. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-8 Culture is the learned values, perceptions, wants, and behavior from family
- 9. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Subculture are groups of people within a culture with shared value systems
- 10. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-10 Social classes are society’s relatively permanent and ordered divisions whose members
- 11. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-11 The major American social classes Upper class Middle class Working class
- 12. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-12 Social Factors Groups Membership groups have a direct influence and to
- 13. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-13 Social Factors Groups Opinion leaders are people within a reference group
- 14. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-14 Social Factors Family is the most important consumer-buying organization in society
- 15. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-15 Personal Factors Personal characteristics Age and life-cycle stage Occupation Economic situation
- 16. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-16 Personal Factors Age and life-cycle stage RBC Royal Band stages: Youth—younger
- 17. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Personal Factors Occupation affects the goods and services bought by consumers Economic
- 18. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-18 Personal Factors Lifestyle is a person’s pattern of living as expressed
- 19. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-19 Personal Factors SRI Consulting’s Values and Lifestyle (VALS) typology Classifies people
- 20. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-20 Personal Factors Primary motivations Ideals Achievement Self-expression
- 21. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-21 Personal Factors Resources High resources Innovators exhibit all primary motivations Low
- 22. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-22 Personal Factors Personality and Self-Concept Personality refers to the unique psychological
- 23. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Personal Factors Personality and Self-Concept Brand personality refers to the specific mix
- 24. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-24 Personal Factors Personality and Self-Concept Self-concept refers to people’s possessions that
- 25. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-25 Psychological Factors Motivation Perception Learning Beliefs and attitudes
- 26. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-26 Psychological Factors Motivation A motive is a need that is sufficiently
- 27. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-27 Psychological Factors Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs People are driven by
- 28. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-28 Psychological Factors Perception is the process by which people select, organize,
- 29. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-29 Psychological Factors Selective attention is the tendency for people to screen
- 30. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-30 Psychological Factors Learning is the changes in an individual’s behavior arising
- 31. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior 5-31 Psychological Factors Beliefs and Attitudes Belief is a descriptive thought that
- 32. Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior Attitudes describe a person’s relatively consistent evaluations, feelings, and tendencies toward an
- 33. Types of Buying Decision Behavior 5-33 Complex buying behavior Dissonance-reducing buying behavior Habitual buying behavior Variety-seeking
- 34. Types of Buying Decision Behavior 5-34 Complex Buying Behavior When consumers are highly motivated in a
- 35. Types of Buying Decision Behavior 5-35 Dissonance-reducing buying behavior occurs when consumers are highly involved with
- 36. Types of Buying Decision Behavior 5-36 Habitual buying behavior occurs when consumers have low involvement and
- 37. The Buyer Decision Process 5-37 Five stages in the buyer decision process Need recognition Information search
- 38. The Buyer Decision Process Need Recognition Need recognition occurs when the buyer recognizes a problem or
- 39. The Buyer Decision Process 5-39 Information Search Information search is the amount of information needed in
- 40. The Buyer Decision Process 5-40 Information Search Sources of information: Personal sources—family and friends Commercial sources—advertising,
- 41. The Buyer Decision Process 5-41 Evaluation of Alternatives Evaluation of alternatives is how the consumer processes
- 42. The Buyer Decision Process 5-42 Purchase Decision The purchase decision is the act by the consumer
- 43. The Buyer Decision Process 5-43 Post-Purchase Decision The post-purchase decision is the satisfaction or dissatisfaction the
- 44. The Buyer Decision Process 5-44 Post-Purchase Decision The larger the gap between expectation and performance, the
- 45. The Buyer Decision Process Customer satisfaction is a key to building profitable relationships with consumers—to keeping
- 46. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-46 New product is a good, service, or idea
- 47. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-47 Stages in the Adoption Process Awareness Interest Evaluation
- 48. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-48 Stages in the Adoption Process Awareness is when
- 49. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-49 Stages in the Adoption Process Evaluation is when
- 50. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-50 Stages in the Adoption Process Adoption is when
- 51. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-51 Individual Differences in Innovation Early adopters are opinion
- 52. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-52 Influence of Product Characteristics on Rate of Adoption
- 53. The Buyer Decision Process for New Products 5-53 Influence of Product Characteristics on Rate of Adoption
- 55. Скачать презентацию












































 Маркетинговые исследования
Маркетинговые исследования Особливості копірайтингу у PR-діяльності
Особливості копірайтингу у PR-діяльності Система предоставления услуг. Специфика системы предоставления услуг
Система предоставления услуг. Специфика системы предоставления услуг Концепция маркетинга магазина женской одежды Versal в Петрозаводске
Концепция маркетинга магазина женской одежды Versal в Петрозаводске Компания “DeSheli”. Эксклюзивная дистрибуция профессиональной космецевтической продукции
Компания “DeSheli”. Эксклюзивная дистрибуция профессиональной космецевтической продукции Рестайлинг и фейслифтинг
Рестайлинг и фейслифтинг Manpower Russia & Region для СКБ-Контур
Manpower Russia & Region для СКБ-Контур Услуги компании. Сервис Интернет-магазин акций
Услуги компании. Сервис Интернет-магазин акций Интернет-магазин ArtDrink
Интернет-магазин ArtDrink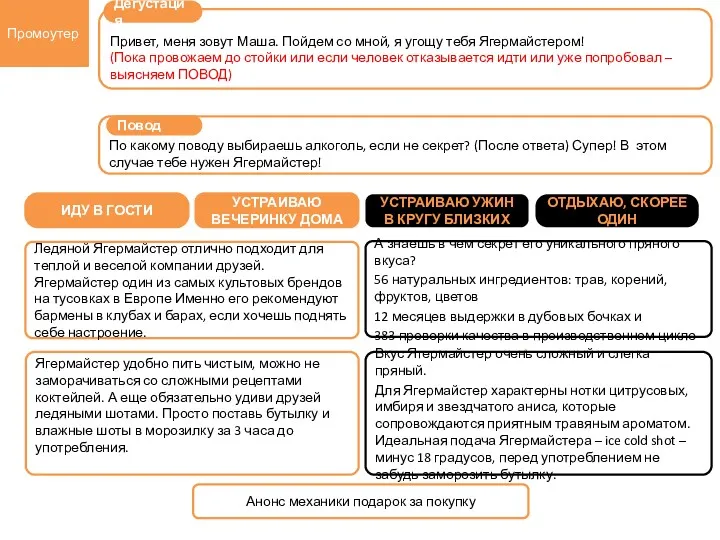 Дегустация промоутер. Сценарии действий промоутера и бармена Ягермайстера
Дегустация промоутер. Сценарии действий промоутера и бармена Ягермайстера Розничная торговая сеть
Розничная торговая сеть Маркетинговые исследования. Разработка анкеты и форм для записей
Маркетинговые исследования. Разработка анкеты и форм для записей Управление рекламным агентством
Управление рекламным агентством Еңбекті ұйымдастырудың мәні мен мақсаттары
Еңбекті ұйымдастырудың мәні мен мақсаттары План маркетинговой поддержки B2C
План маркетинговой поддержки B2C SEO-продвижение сайта
SEO-продвижение сайта Каналы продаж
Каналы продаж MEGA – Казақстандағы әлем деңгейіндегі ең ірі сауда-ойын-сауық орталықтарының желісі
MEGA – Казақстандағы әлем деңгейіндегі ең ірі сауда-ойын-сауық орталықтарының желісі Прибыльная клиника 2.0. Продвижение медицинской клиники в интернете
Прибыльная клиника 2.0. Продвижение медицинской клиники в интернете Oriflame. Формула успеха
Oriflame. Формула успеха Что предлагает интернет-реклама
Что предлагает интернет-реклама Воркбук. Маркетинг-кит
Воркбук. Маркетинг-кит Группа проектно-строительных компаний ЭталонСтрой
Группа проектно-строительных компаний ЭталонСтрой Маркетингтік орталар
Маркетингтік орталар Размещение рекламы на АЗС
Размещение рекламы на АЗС Ведущая светских мероприятий
Ведущая светских мероприятий Двери СТЕЛ и ДПН. Складская программа. ООО Торэкс Северо-Запад
Двери СТЕЛ и ДПН. Складская программа. ООО Торэкс Северо-Запад Комплексная продажа к пылесосам Doffler
Комплексная продажа к пылесосам Doffler