Содержание
- 2. Definition Amoebiasis is a parasitic protozoan disease that affects the gut mucosa and liver, resulting in
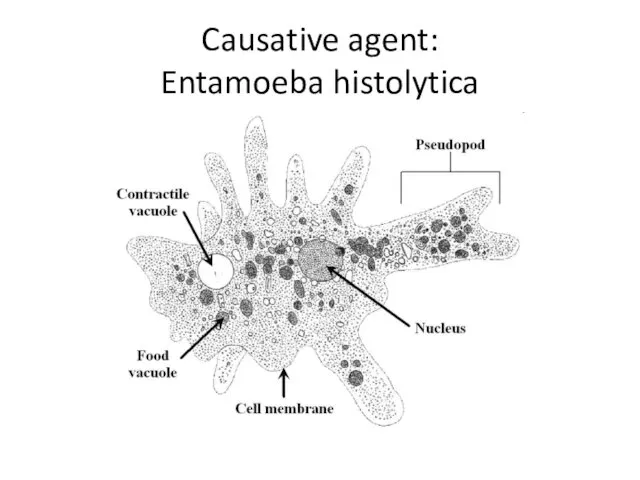
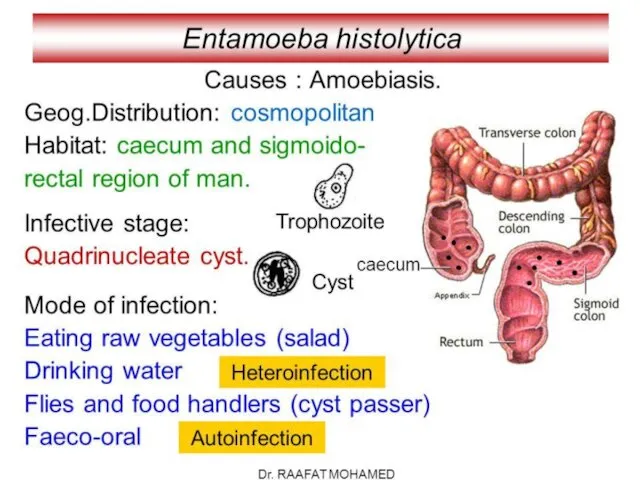
- 3. Causative agent: Entamoeba histolytica
- 4. Amoebiasis Harboring of protozoa E. histolytica inside the body with or without disease” only 10% of
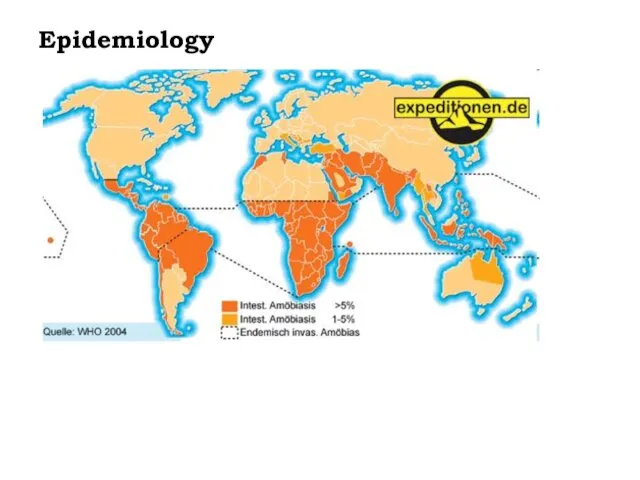
- 5. Epidemiology
- 6. Magnitude Global: - worldwide in distribution - 3rd most common parasitic death - India, China, Africa,
- 7. Transmission 1- Direct contact of person to person( fecal-oral) 2- Veneral transmission among homosexual males (oral-anal)
- 9. Host All age groups affected No gender or racial differences Institutional, community living, MSW Severe if
- 10. Host Factor Contributions Several factors contribute to influence infection 1 Stress 2 Malnutrition 3 Alcoholism 4
- 11. Risk factors People in developing countries that have poor sanitary conditions Immigrants from developing countries Travellers
- 13. Incubation period: 3 days in severe infection; several months in sub-acute and chronic form. In average
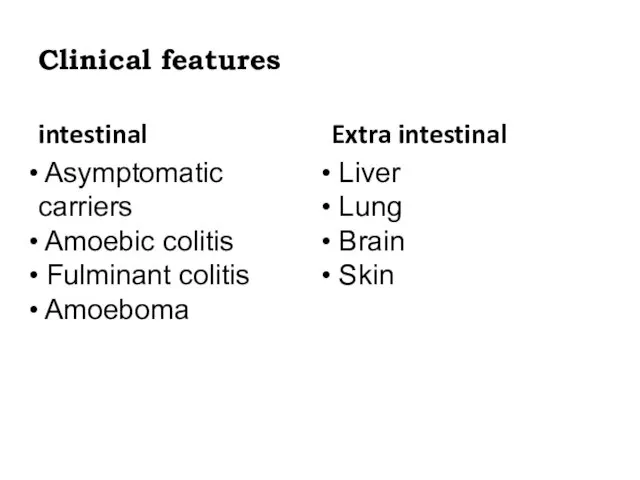
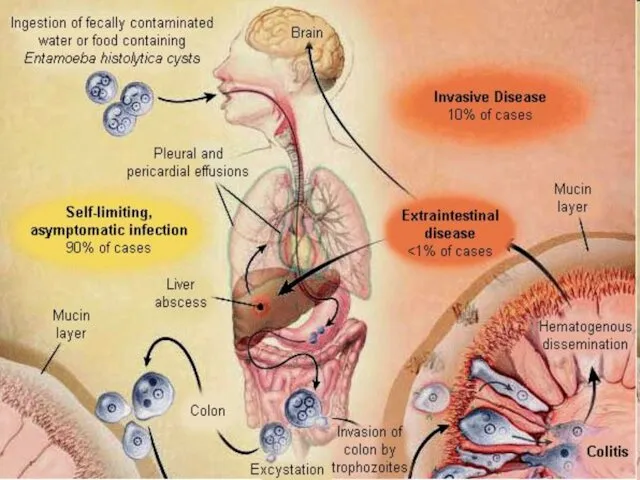
- 14. Clinical features intestinal Asymptomatic carriers Amoebic colitis Fulminant colitis Amoeboma Extra intestinal Liver Lung Brain Skin
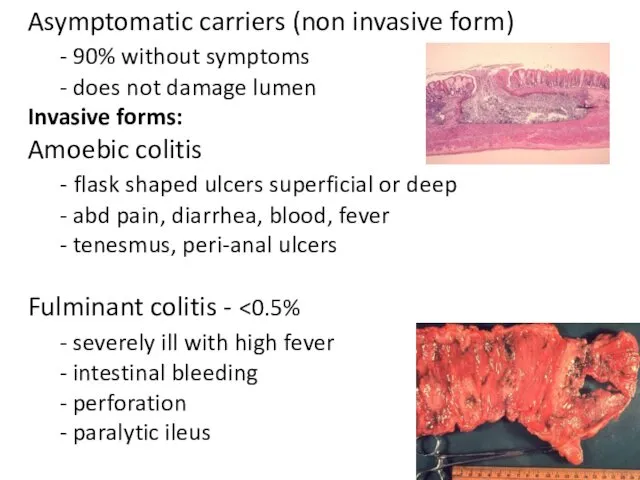
- 15. Asymptomatic carriers (non invasive form) - 90% without symptoms - does not damage lumen Invasive forms:
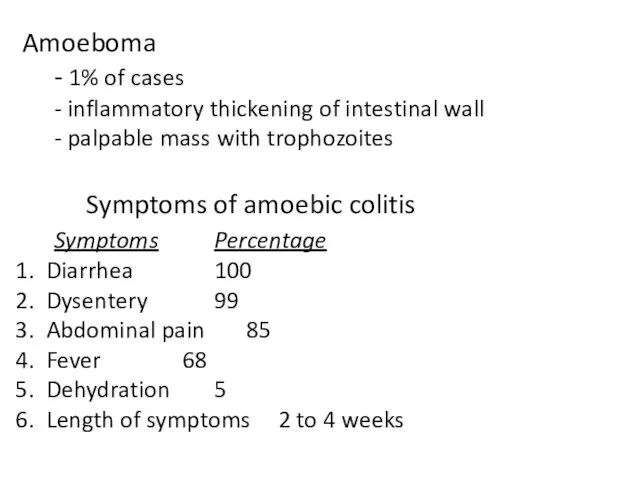
- 16. Amoeboma - 1% of cases - inflammatory thickening of intestinal wall - palpable mass with trophozoites
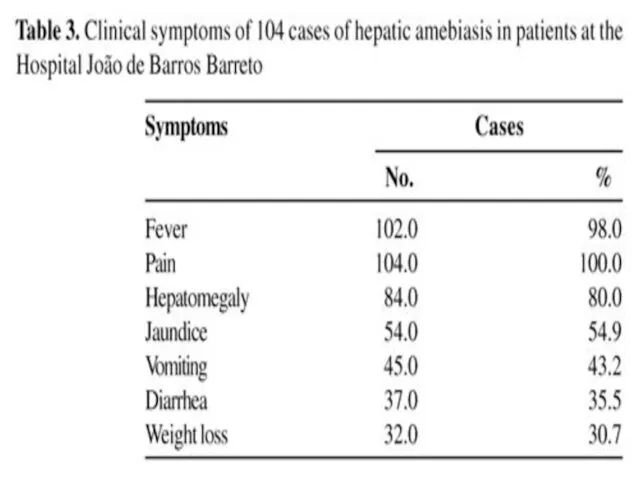
- 18. Extra-intestinal Amoebic liver abcess via portal system 5% of invasive disease 10 times more common in
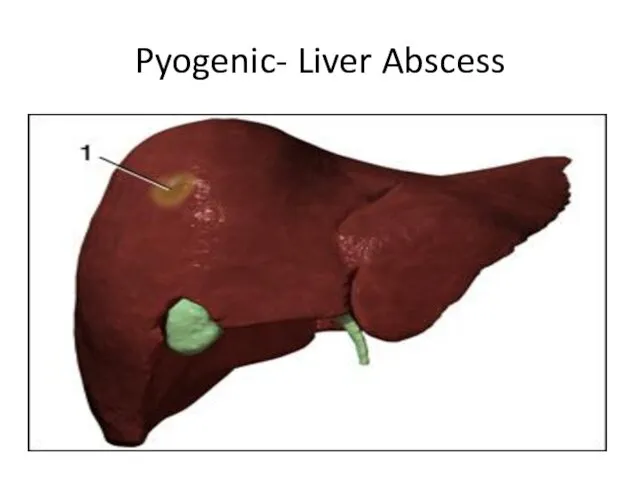
- 20. Pyogenic- Liver Abscess
- 23. Diagnosis M/E immediately before cooling - fresh mucus or rectal ulcer swab - colourless motile trophozoites
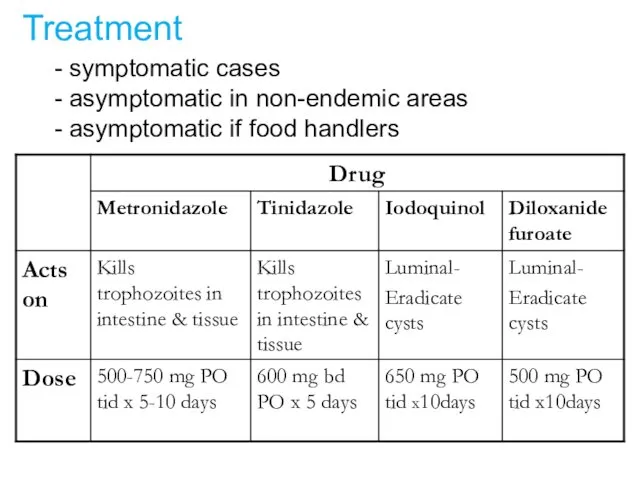
- 24. Treatment - symptomatic cases - asymptomatic in non-endemic areas - asymptomatic if food handlers
- 25. Prevention & Control Primary prevention - Safe excreta disposal - Safe water supply - Hygiene -
- 27. Скачать презентацию














 Первая доврачебная помощь при ДТП
Первая доврачебная помощь при ДТП Семейная гиперхолестеринемия
Семейная гиперхолестеринемия Требования к организации питания пациентов в буфетных. Обязанности старшей медицинской сестры
Требования к организации питания пациентов в буфетных. Обязанности старшей медицинской сестры Консервативное лечение атеросклероза
Консервативное лечение атеросклероза Қант диабеті кезіндегі пациентті және туыстарын оқыту
Қант диабеті кезіндегі пациентті және туыстарын оқыту Уход за онкологическими больными
Уход за онкологическими больными Вакцинация детей. Календарь прививок
Вакцинация детей. Календарь прививок Омытқа жотасының қызметі және маңызы
Омытқа жотасының қызметі және маңызы Нематодозы. Аскаридоз. Трихоцефалез
Нематодозы. Аскаридоз. Трихоцефалез Заболевания детей раннего возраста. Заболевания слизистой полости рта (стоматиты, молочница)
Заболевания детей раннего возраста. Заболевания слизистой полости рта (стоматиты, молочница) Аутоиммунный гепатит и беременность
Аутоиммунный гепатит и беременность Нарушения липидного обмена
Нарушения липидного обмена Кровотечения в последовом и раннем послеродовом периоде
Кровотечения в последовом и раннем послеродовом периоде Меридиан почек VIII
Меридиан почек VIII Ауыз қуысы және оның ағзаларының дамуы (онтогенез). Ақаулары
Ауыз қуысы және оның ағзаларының дамуы (онтогенез). Ақаулары Сестринская помощь при пиелонефритах
Сестринская помощь при пиелонефритах Мочевыделительная система
Мочевыделительная система Клиническая анатомия головы и шеи
Клиническая анатомия головы и шеи Принципы купирования острого инфаркта миокарда
Принципы купирования острого инфаркта миокарда Психические расстройства при сосудистых заболеваниях головного мозга
Психические расстройства при сосудистых заболеваниях головного мозга Методы радионуклидной диагностики органов и систем человека
Методы радионуклидной диагностики органов и систем человека Болезни печени
Болезни печени Балалардағы безгек
Балалардағы безгек Врожденный вывих бедра
Врожденный вывих бедра Синдром Прадера- Вилли
Синдром Прадера- Вилли Устройство стоматологического кабинета
Устройство стоматологического кабинета Тері биохимиясы
Тері биохимиясы Теоретическое пособие по массажу
Теоретическое пособие по массажу