Содержание
- 2. Cellulite From a scientific point of view, the term “Cellulite” is incorrect, i.e. the suffix "ite"
- 3. Cellulite is Changes in the structural organization of the surface layers of the subcutaneous tissue, which
- 4. The following factors promote cellulite development: Lifestyle (overeating, lack of exercise, and bad habits); Circulatory disorders
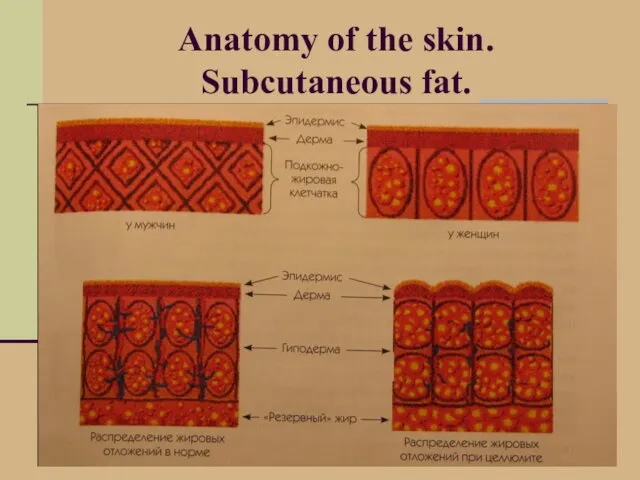
- 5. Anatomy of the skin. Subcutaneous fat.
- 6. Alpha 2 receptors (lipogenesis), beta receptors (lipolysis) , Lipogenesis is accomplished by synthesis in adipocytes of
- 7. Features of fat cells In women, the number of alpha2 receptors is 6 times more in
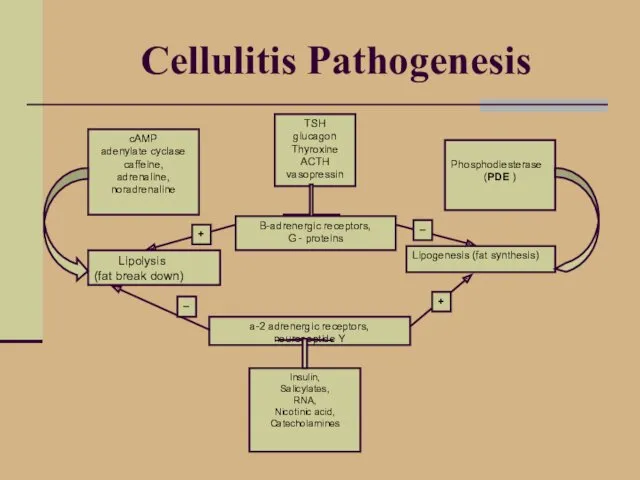
- 8. Cellulitis Pathogenesis TSH glucagon Thyroxine ACTH vasopressin B-adrenergic receptors, G - proteins Lipogenesis (fat synthesis) Lipolysis
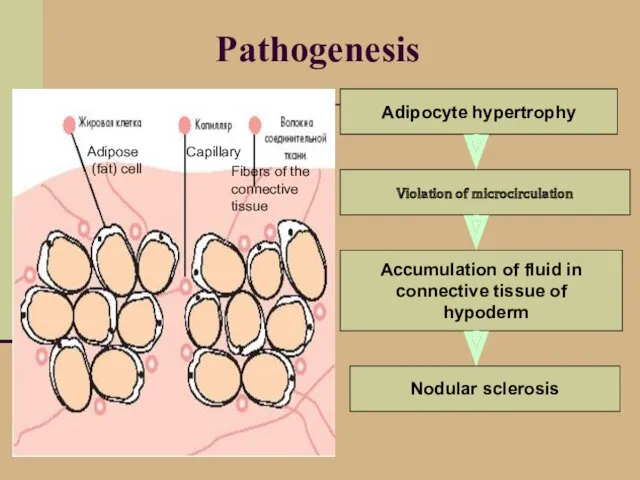
- 9. Pathogenesis Violation of microcirculation Accumulation of fluid in connective tissue of hypoderm Nodular sclerosis Adipocyte hypertrophy
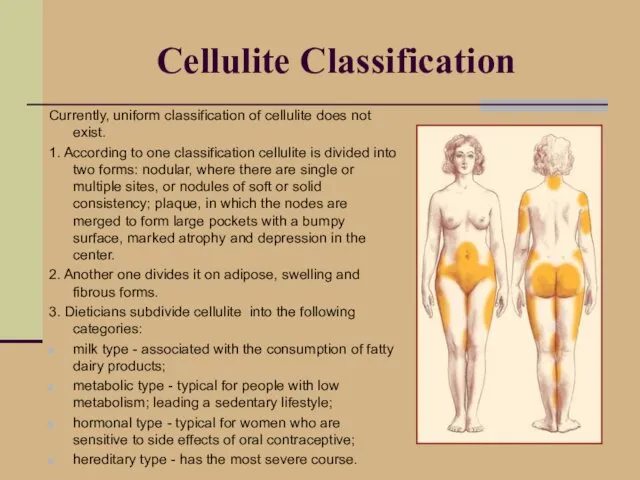
- 10. Cellulite Classification Currently, uniform classification of cellulite does not exist. 1. According to one classification cellulite
- 11. 1. Thick cellulite - in young women with active lifestyles. Cellulite manifestations do not vary depending
- 12. Clinical Stages of Cellulite 1. Pre –cellulite stage or stage (grade) 0; 2.Primary stage or stage
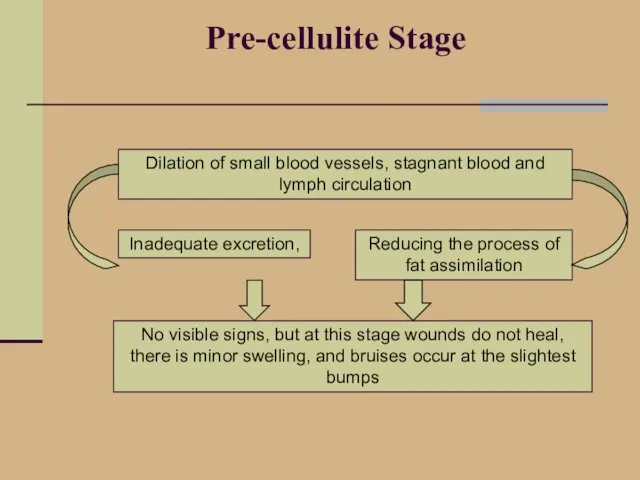
- 13. Pre-cellulite Stage Dilation of small blood vessels, stagnant blood and lymph circulation Inadequate excretion, Reducing the
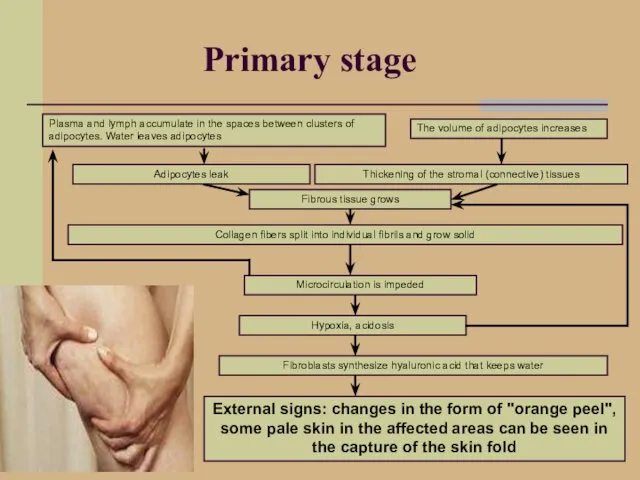
- 14. Primary stage Plasma and lymph accumulate in the spaces between clusters of adipocytes. Water leaves adipocytes
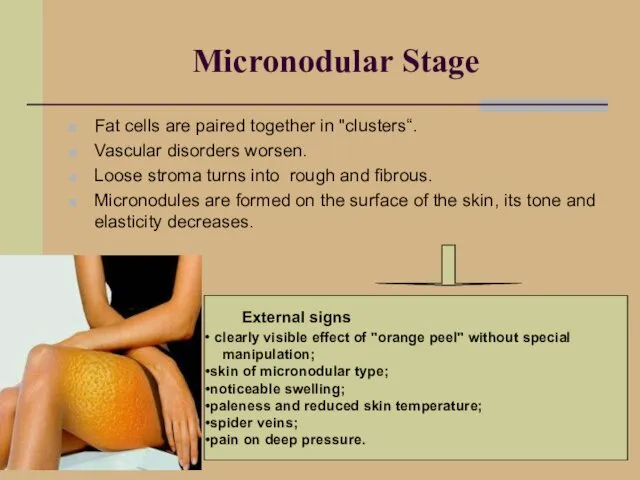
- 15. Micronodular Stage Fat cells are paired together in "clusters“. Vascular disorders worsen. Loose stroma turns into
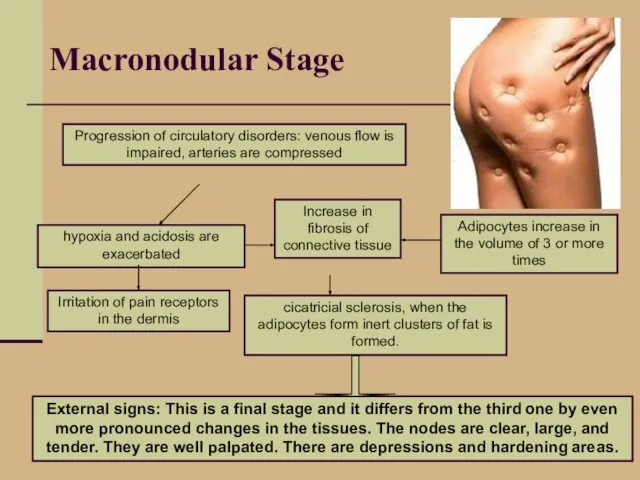
- 16. Macronodular Stage Progression of circulatory disorders: venous flow is impaired, arteries are compressed hypoxia and acidosis
- 17. Methods of Cellulite Diagnostics 1. Anthropometric data. 2. Anode thermography. 3. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance
- 18. Prevention of cellulitis 1. Proper nutrition; 2. Break bad habits;. 3. Keep exercising; 4. Clothing and
- 19. Methods of Cellulite Treatment 1. Activation of beta-receptors and stimulation of lipolysis. 2. Inhibition of alpha-receptors
- 20. Drugs for Oral Use 1. Antioxidants and vitamins for cellulite treatment: E, vitamin C, A, B5,
- 21. Internal Use Preparations Bioflavonoids: 1. Means stimulating blood circulation (ginkgo biloba extract, centella asiatica, grape seed,
- 22. External Use Preparations 1. Vegetable oil for cellulite: jojoba oil, sage, evening primrose, shea butter, wheat
- 23. External Use Preparations 4. Drugs splitting fats: caffeine and other xanthine derivatives, cola extract, guarana, mate
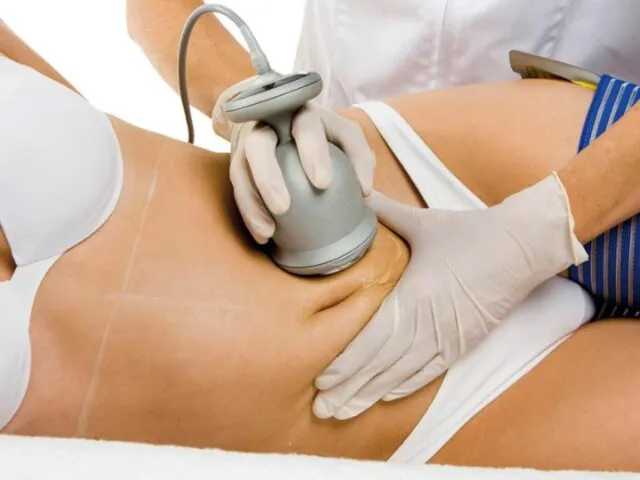
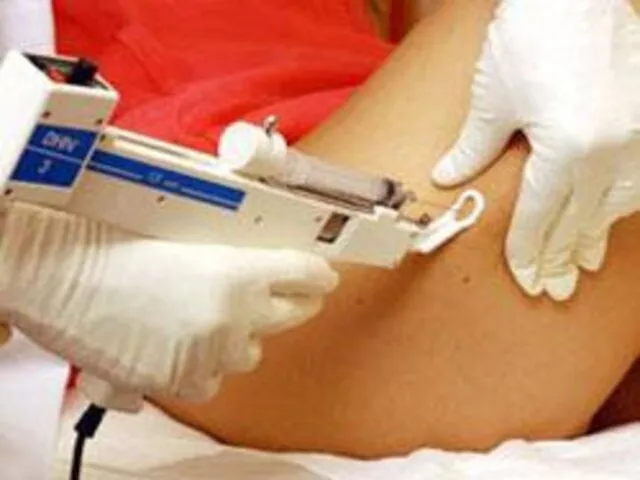
- 24. Physical Therapeutic Methods 1. Massage; 2. Electromyostimulation; 3. Microcurrents; 4. Electrolipolysis; 5. Cavitation; 6. RF-therapy; 7.
- 30. Obesity It is a chronic recurring disease, which is accompanied by a significant increase in fat
- 35. 1. Рypodinamia. 2. Dehydration. 3. Genetic factors, in particular: Increase in activity of the enzymes of
- 36. Classification I. Primary Obesity. II. Secondary Obesity.
- 37. I. Primary Obesity. 1. Alimentary and constitutive (exogenous-constitutional); Constitutional – hereditary; 2. With eating disorders (night
- 38. II. Secondary Obesity 1. With revealed genetic defects 2. Cerebral obesity (brain tumors, skull base trauma
- 39. Stages and Types of Obesity Stages of Obesity а) progressive, б) persistent Types of Obesity 1.
- 40. Fat Can Be Distributed: 1. In the subcutaneous adipose tissue (subcutaneous fat) 2. around internal organs
- 41. Abdominal Fat
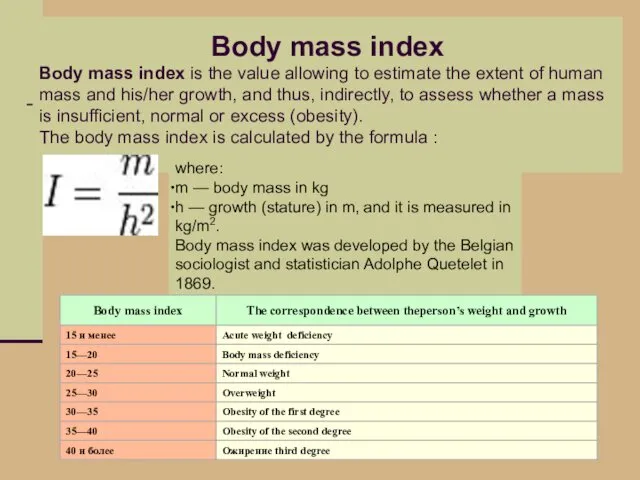
- 42. Body mass index Body mass index is the value allowing to estimate the extent of human
- 43. Four Degrees of Obesity: I degree -- body weight of the patient exceeds the normal one
- 44. Methods of General Correction Examination by an endocrinologistor gynecologist. A diet with reduced fat, carbohydrates intake.
- 45. Liposuction - operative method of vacuum liposuction after mechanical or ultrasonic disruption. In recent years, liposuction
- 46. THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION!
- 48. Скачать презентацию




























 Вилочковая железа
Вилочковая железа Рак предстательной железы
Рак предстательной железы Вазоренальная гипертензия
Вазоренальная гипертензия Травмы глаз
Травмы глаз Гранулематоз Вегенера
Гранулематоз Вегенера Инфекциялық наркотиктерді қолданушылардағы, соның ішінде бас бостандығынан айыру жерлеріндегі адамдардағы АИВТ инфицирлену
Инфекциялық наркотиктерді қолданушылардағы, соның ішінде бас бостандығынан айыру жерлеріндегі адамдардағы АИВТ инфицирлену Медицинская информатика: основы защиты данных. Лекция 2
Медицинская информатика: основы защиты данных. Лекция 2 Болезнь Пертеса у детей
Болезнь Пертеса у детей Кровосберегающие технологии в акушерской практике
Кровосберегающие технологии в акушерской практике Нормальная анатомия и заболевания позвоночного столба
Нормальная анатомия и заболевания позвоночного столба Антиаритмические лекарственные средства
Антиаритмические лекарственные средства Молодечненский государственный медицинский колледж
Молодечненский государственный медицинский колледж Арнайы және жоғары мамандандырылған медициналық көмек
Арнайы және жоғары мамандандырылған медициналық көмек Вирусный гепатит
Вирусный гепатит Балалардағы бауыр ауруларының ерекшеліктері
Балалардағы бауыр ауруларының ерекшеліктері Химиотерапевтические средства
Химиотерапевтические средства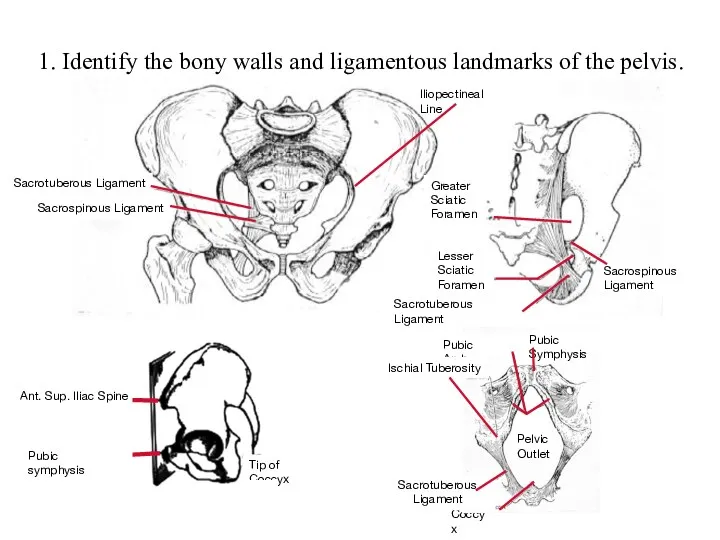 Identify the bony walls and ligamentous landmarks of the pelvis
Identify the bony walls and ligamentous landmarks of the pelvis Микобактерии. Коринебактерии. Бордетеллы
Микобактерии. Коринебактерии. Бордетеллы Невропатология. Сенсорные системы
Невропатология. Сенсорные системы Вторичные артериальные гипертензии
Вторичные артериальные гипертензии Емдеу сауықтыру мекемелерінін түрлері. Аурухана ішілік инфекция
Емдеу сауықтыру мекемелерінін түрлері. Аурухана ішілік инфекция Перкуссия легких
Перкуссия легких Организация школ здоровья для пациентов в первичном звене здравоохранения
Организация школ здоровья для пациентов в первичном звене здравоохранения Эндодонтия. Виды эндодонтического лечения. Эндодонтический инструментарий и материалы
Эндодонтия. Виды эндодонтического лечения. Эндодонтический инструментарий и материалы Облитерирующий атеросклероз артерий нижних конечностей
Облитерирующий атеросклероз артерий нижних конечностей Заболевания щитовидной железы
Заболевания щитовидной железы Қоғамдық тамақтандыру кәсіпорындарындағы санитарлық талаптар
Қоғамдық тамақтандыру кәсіпорындарындағы санитарлық талаптар Миокардиты
Миокардиты