Содержание
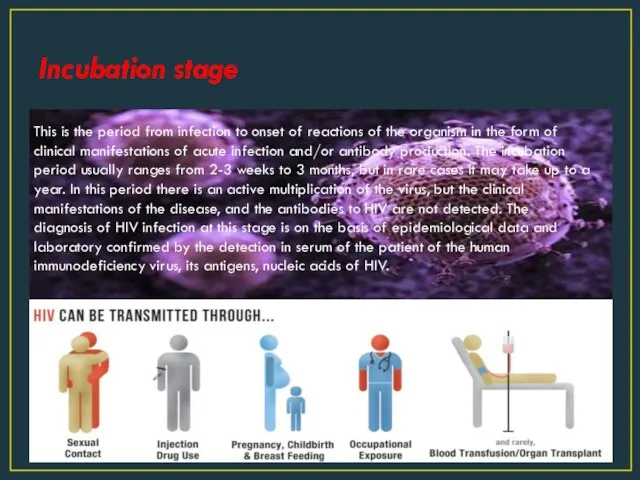
- 2. Incubation stage This is the period from infection to onset of reactions of the organism in
- 3. Stage of primary manifestations Stage of primary manifestations This stage should be regarded as actual HIV
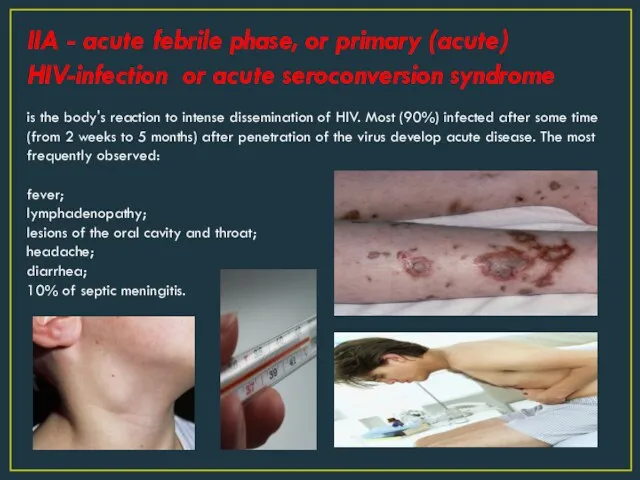
- 4. IIA - acute febrile phase, or primary (acute) HIV-infection or acute seroconversion syndrome is the body's
- 5. IIB - asymptomatic phase is characterized by a decrease in average 25% of the relative content
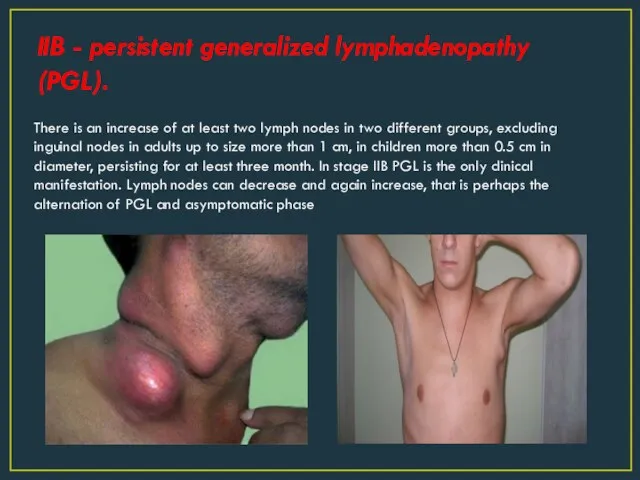
- 6. IIB - persistent generalized lymphadenopathy (PGL). There is an increase of at least two lymph nodes
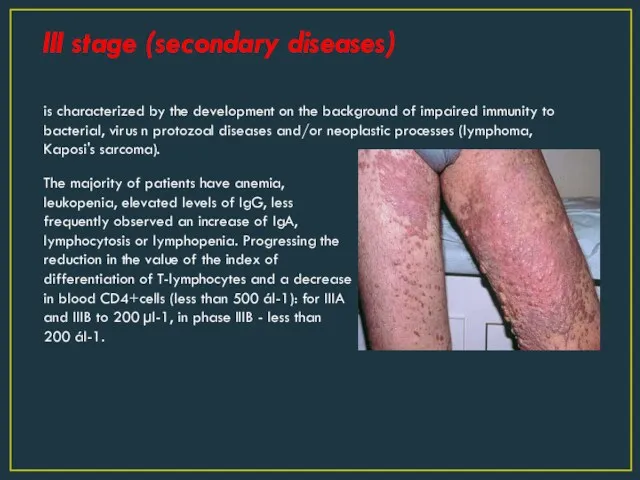
- 7. III stage (secondary diseases) is characterized by the development on the background of impaired immunity to
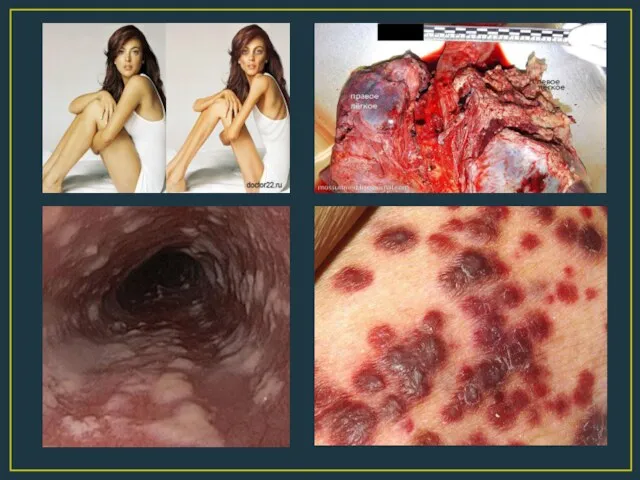
- 8. Depending on the severity of secondary diseases distinguish 3 periods of flow. 4A – loss of
- 10. In the terminal stage of HIV infection are secondary diseases that have developed in a patient
- 11. Stage of HIV infection in adults and adolescents, based on the classification The World Health Organization
- 12. Clinical stage III 7. Weight loss: loss of >10 percent of body weight. 8. Unexplained chronic
- 13. 16. Toxoplasmosis of the brain. 17. Cryptosporidiosis with diarrhoea for more than 1 month. 18. Extrapulmonary
- 14. ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY ART goals ART is currently the major component of treatment of patients with HIV
- 15. Tasks ART ~ clinical prevention of the development of opportunistic infections and HIV associated non-communicable diseases:
- 16. Indications ART should be appointed · all patients with the number of CD4+ all patients, regardless
- 17. all patients regardless of CD4+ and stage of the disease the following situation: patients with active
- 18. Antiretroviral drugs Antiretroviral drugs targeted at vulnerable stages of the life cycle HIV and thus prevent
- 20. Скачать презентацию









 Первая помощь пострадавшим и её значение
Первая помощь пострадавшим и её значение Инородное тело глотки
Инородное тело глотки Профилактическая косметология
Профилактическая косметология Косметические средства по уходу за кожей рук
Косметические средства по уходу за кожей рук Жедел көмей стенозы
Жедел көмей стенозы ХҚТУ. ПИ, Рамфьорда, КПИ индекстері
ХҚТУ. ПИ, Рамфьорда, КПИ индекстері Системы здравоохранения
Системы здравоохранения Влияние никотина и алкоголя на организм беременной женщины
Влияние никотина и алкоголя на организм беременной женщины Бүйрек обыры
Бүйрек обыры Чувствительная кожа
Чувствительная кожа Системная красная волчанка
Системная красная волчанка Диабеттік ретинопатия
Диабеттік ретинопатия Искусственное пришлифовывание зубов
Искусственное пришлифовывание зубов Метод сухой химии в исследовании мочи
Метод сухой химии в исследовании мочи Тұқым қуалаушылық жүйке-бұлшықет аурулары
Тұқым қуалаушылық жүйке-бұлшықет аурулары Опухоли. Опухолевый процесс
Опухоли. Опухолевый процесс Психические болезни и наркология. Психозы
Психические болезни и наркология. Психозы Организация работы специализированных и линейных бригад скорой помощи
Организация работы специализированных и линейных бригад скорой помощи Жидкие лекарственные формы. Лекция № 9. Растворы ВМВ
Жидкие лекарственные формы. Лекция № 9. Растворы ВМВ Стволовые клетки
Стволовые клетки Анатомо-физиологические особенности эндокринной системы у детей
Анатомо-физиологические особенности эндокринной системы у детей Общая онкология. История онкологии. Этиология ЗНО. Организация онкослужбы. Деонтология в онкологии. Лекция №1
Общая онкология. История онкологии. Этиология ЗНО. Организация онкослужбы. Деонтология в онкологии. Лекция №1 Лекарственные средства для парентерального применения
Лекарственные средства для парентерального применения Еліміздегі денсаулық сақтау саласы әлеуметтік-экономикалық жағдайдың мониторингі бойынша ақпарат
Еліміздегі денсаулық сақтау саласы әлеуметтік-экономикалық жағдайдың мониторингі бойынша ақпарат Антибактериальные средства в интенсивной терапии
Антибактериальные средства в интенсивной терапии Общие принципы строения слизистой оболочки полости рта
Общие принципы строения слизистой оболочки полости рта Фізіологічні основи оздоровчої фізичної культури
Фізіологічні основи оздоровчої фізичної культури Нейроэндокринды синдромдар
Нейроэндокринды синдромдар