Содержание
- 2. Infectious diseases Are a group of diseases, which are caused by bacteria, viruses, Protozoa, etc A
- 3. In children's pathology The infectious diseases draw the main attention There is a great variety of
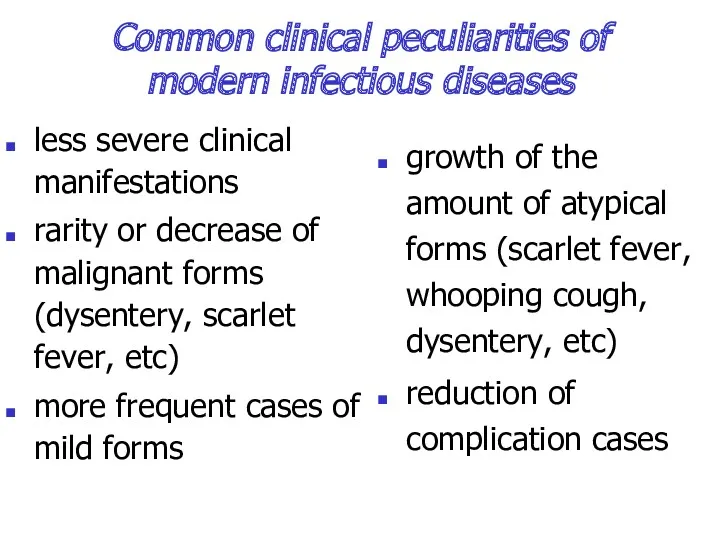
- 4. Common clinical peculiarities of modern infectious diseases less severe clinical manifestations rarity or decrease of malignant
- 5. Periods of Infectious Disease Course Clinically, acute epidemic diseases are characterized by a cyclic course and
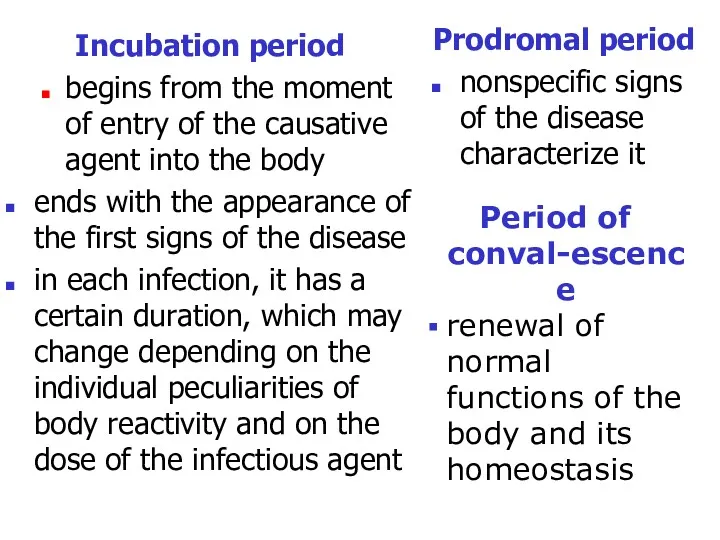
- 6. Incubation period begins from the moment of entry of the causative agent into the body ends
- 7. The period of full development maximally marked causative agent activity this period of the disease is
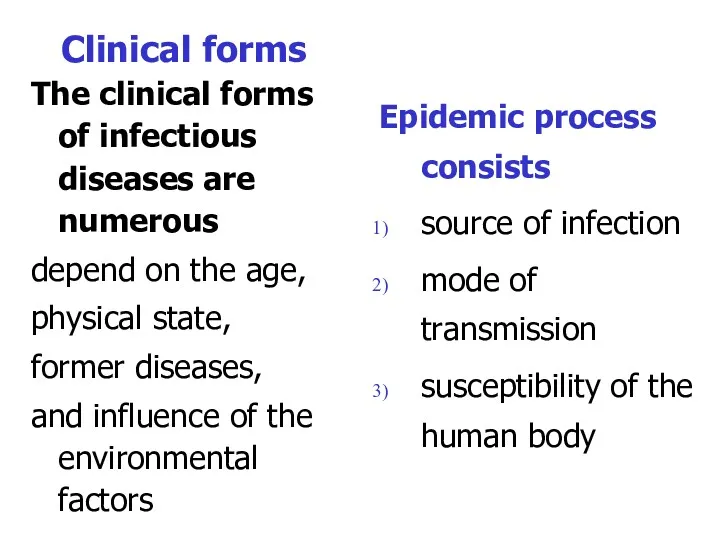
- 8. Clinical forms The clinical forms of infectious diseases are numerous depend on the age, physical state,
- 9. Sources of infection patients with clinically marked forms of infection like patients with attenuated and atypical
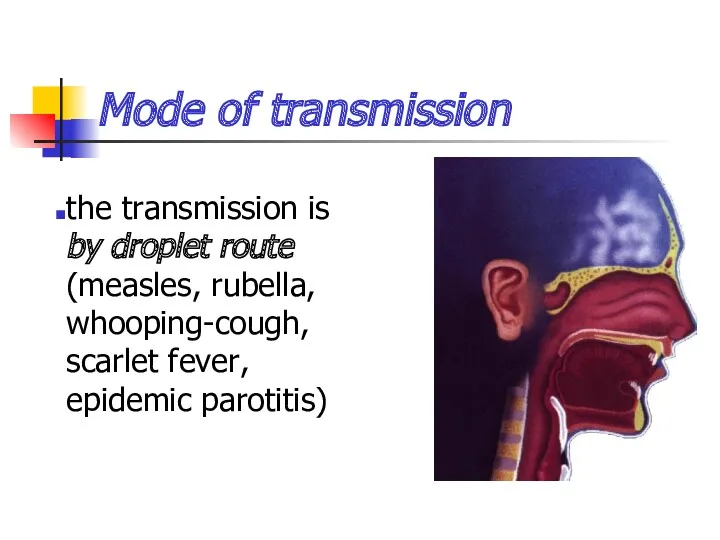
- 10. Mode of transmission the transmission is by droplet route (measles, rubella, whooping-cough, scarlet fever, epidemic parotitis)
- 11. Mode of transmission fecal-oral one (dysentery, salmonellosis, typhoid fever, paratyphoid A and B types, escherichiosis, viral
- 12. Mode of transmission occurs in direct entry of the causative agent into blood (viral hepatitis B,
- 13. Susceptibility of population Susceptibility is defined by the index of susceptibility or contagion that is correlation
- 14. Age peculiarities of immunity formation 1. The younger is the child, the slower and the less
- 15. Differentiated peculiarities infectious disease of the babies Due to placental immunity babies are unsusceptible to most
- 16. Preventive measures The nonspecific prevention: includes measures directed at the improvement of general resistance of the
- 17. Elaborated complex of emergency measures are directed at the four stages of the infectious process isolation
- 18. Specific prevention Vaccination (groups of diseases where the epidemic structure may be changed call controlled infections)
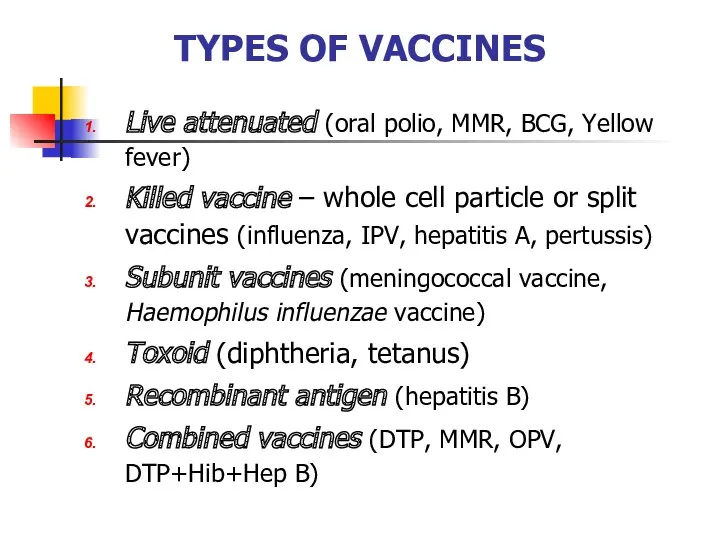
- 19. TYPES OF VACCINES Live attenuated (oral polio, MMR, BCG, Yellow fever) Killed vaccine – whole cell
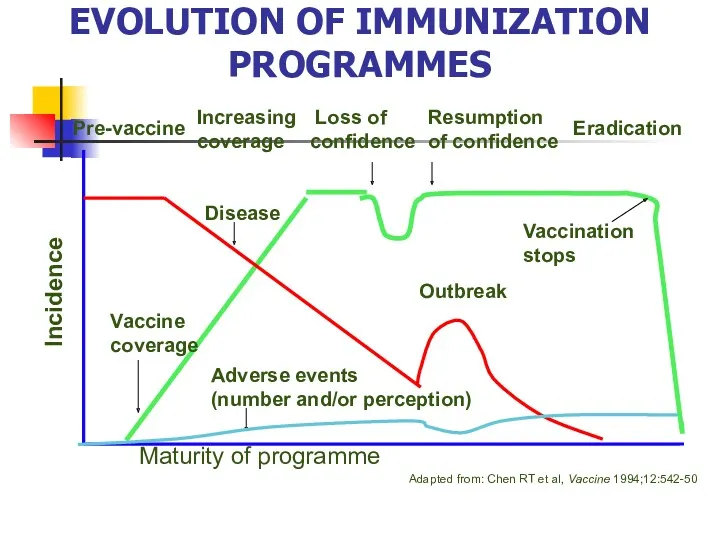
- 20. EVOLUTION OF IMMUNIZATION PROGRAMMES Incidence Vaccine coverage Adverse events (number and/or perception) Disease Outbreak Vaccination stops
- 21. Whooping-cough (H. Pertussis) ETIOLOGY Bordet-Gengou bacillus Haemophilia (Bordetella) pertussis Gram-negative Strictly aerobic Resistance is very low
- 22. Epidemiology the source of infection is a sick person particularly infective in the initial stage, but
- 23. Pathogenesis The portal of entry of infection is the respiratory tract H. pertussis settles in the
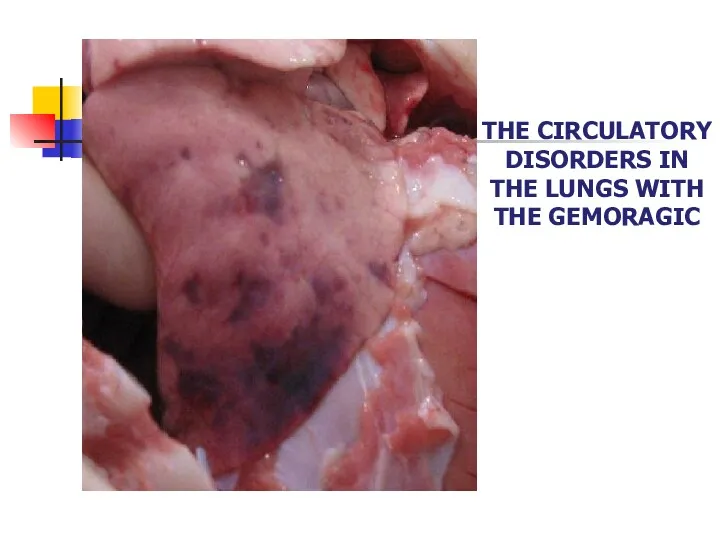
- 24. Because of the frequent and prolonged paroxysms of coughing, and the circulatory disorders in the lungs,
- 25. Clinical manifestations The incubation period of whooping-cough is 3 to 15 days. The course of the
- 26. Catarrhal stage is manifested by a moderate rise in temperature, but it may sometimes be subfebrile,
- 27. Paroxysmal stage Paroxysms of coughing develop. The paroxysm consists of a series of short coughs following
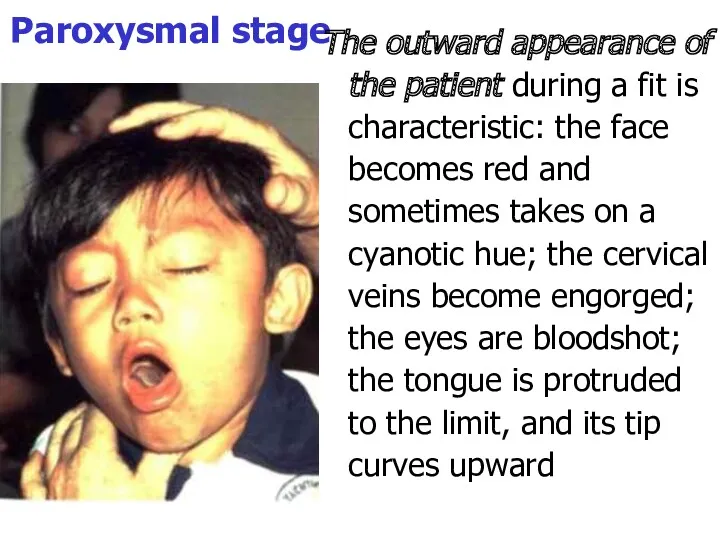
- 28. Paroxysmal stage The outward appearance of the patient during a fit is characteristic: the face becomes
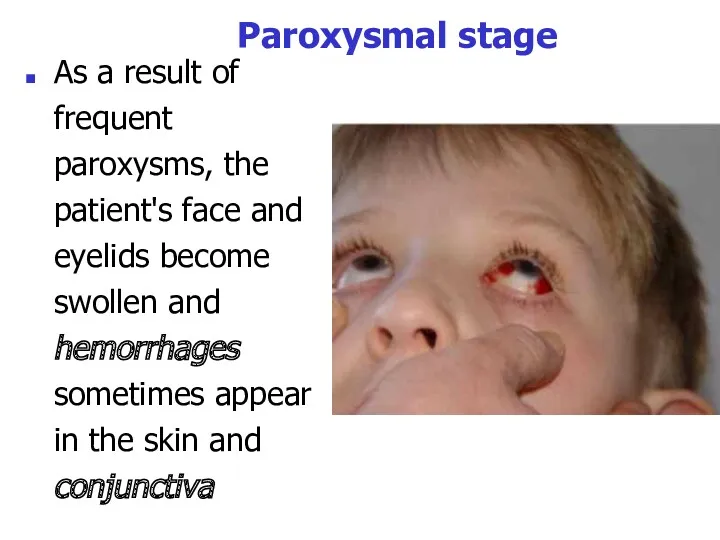
- 29. Paroxysmal stage As a result of frequent paroxysms, the patient's face and eyelids become swollen and
- 30. The ulcer on the tongue results from mechanical rubbing of the frenulum against the sharp edges
- 31. Clinical forms There are three principal forms of whooping-cough: mild, moderate, and severe In the mild
- 32. In the moderate form the number of fits varies between 15 and 24 with several whoops
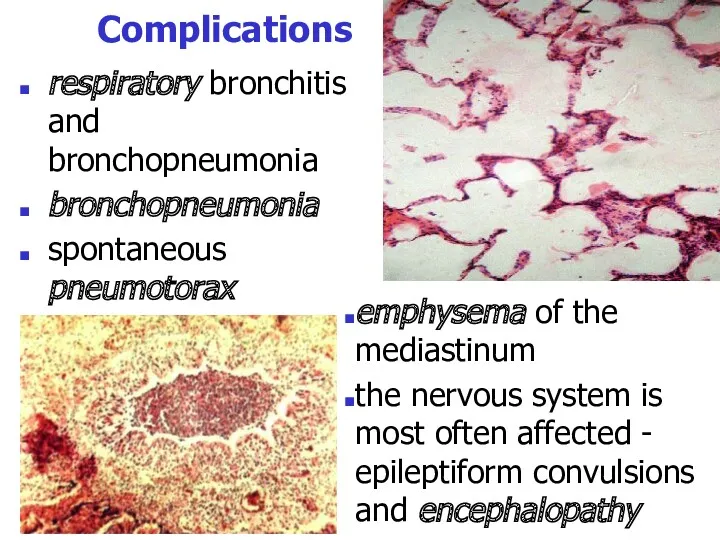
- 33. Complications respiratory bronchitis and bronchopneumonia bronchopneumonia spontaneous pneumotorax emphysema of the mediastinum the nervous system is
- 34. THE CIRCULATORY DISORDERS IN THE LUNGS WITH THE GEMORAGIC
- 35. In one year old babies whooping-cough incubation period and catarrhal stage is usually shorter the fits
- 36. Diagnosis clinical course cyclic character, paroxysmal bouts of coughing with whoops, ending with vomiting, typical appearance
- 37. Treatment Properly organized regimen and nursing Cold fresh air has a wonderful effect on patients. Antibiotics
- 38. Prophylaxis Measures to be taken in an epidemic focus The patient is usually left at home
- 40. Скачать презентацию






















 Психология пациента
Психология пациента Заболевания периферической нервной системы
Заболевания периферической нервной системы Основные понятия клинической химии
Основные понятия клинической химии Ткани челюстно-лицевой области
Ткани челюстно-лицевой области Инфекционные болезни
Инфекционные болезни Основы успешного грудного вскармливания
Основы успешного грудного вскармливания Ортопедическое лечение
Ортопедическое лечение Принципы лечения основных офтальмологических синдромов
Принципы лечения основных офтальмологических синдромов Опухоли мягких тканей и костей
Опухоли мягких тканей и костей Переломы костй, вывихи, закрытые повреждения мягких тканей. Транспортная иммобилизация
Переломы костй, вывихи, закрытые повреждения мягких тканей. Транспортная иммобилизация Врачебные ошибки
Врачебные ошибки Неправильные положения плода
Неправильные положения плода Развитие спортивно-оздоровительного туризма в России
Развитие спортивно-оздоровительного туризма в России Поиск информации с использованием фильтров доказательной медицины. Систематические обзоры и мета-анализ статей
Поиск информации с использованием фильтров доказательной медицины. Систематические обзоры и мета-анализ статей Туберкулездің алдын алу. Туберкулездің алдын алу туралы тұрғындар арасындағы санитарлы - ағарту жұмысы
Туберкулездің алдын алу. Туберкулездің алдын алу туралы тұрғындар арасындағы санитарлы - ағарту жұмысы Логопедические технологии
Логопедические технологии Дамудың қатерлі кезеңдері
Дамудың қатерлі кезеңдері Профилактика нарушений осанки, плоскостопия и миопии средствами ФВ
Профилактика нарушений осанки, плоскостопия и миопии средствами ФВ Контроль за нервно-психическим развитием детей 2-3 года жизни
Контроль за нервно-психическим развитием детей 2-3 года жизни Қарыншалар гипертрофиясының ЭКГ белгілері
Қарыншалар гипертрофиясының ЭКГ белгілері Оказание первой медицинской помощи детям
Оказание первой медицинской помощи детям Здоровый день - здоровая жизнь
Здоровый день - здоровая жизнь Нормативная база службы крови
Нормативная база службы крови Asepsis
Asepsis Препараты стероидных гормонов, их синтетических заменителей и антагонистов
Препараты стероидных гормонов, их синтетических заменителей и антагонистов Социально-правовые аспекты оказания психиатрической помощи. Проблема стигматизации
Социально-правовые аспекты оказания психиатрической помощи. Проблема стигматизации Морфология органов периферической эндокринной системы
Морфология органов периферической эндокринной системы Расстройства питания и пищеварения. Дистрофия
Расстройства питания и пищеварения. Дистрофия