Содержание
- 2. What is HIV? Human Immunodeficiency Virus “HIV is a virus spread through body fluids that affects
- 3. What is AIDS? AIDS is a late stage of the HIV infection Once diagnosed, body has
- 4. HIV-1 and HIV-2 • HIV-1 and HIV-2 are • Transmitted through the same routes • Associated
- 5. HIV-1 and HIV-2 HIV-2 is less easily transmitted HIV-2 is less pathogenic Duration of HIV-2 infection
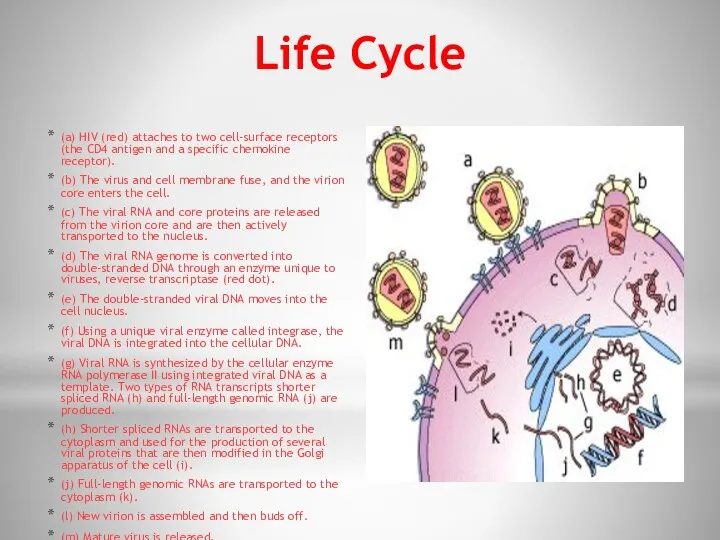
- 6. Life Cycle (a) HIV (red) attaches to two cell-surface receptors (the CD4 antigen and a specific
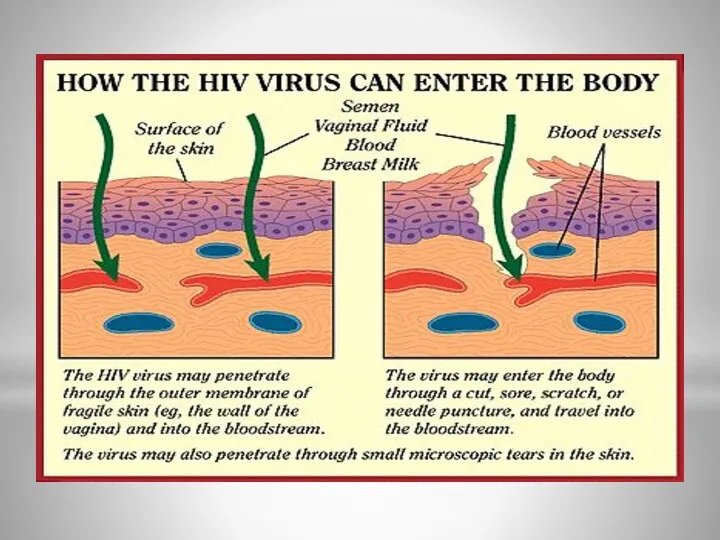
- 7. How is HIV Spread? HIV is passed from person to person through the exchange of bodily
- 8. What Fluids Can Transmit HIV? Blood Vaginal fluids Semen Breast Milk 8
- 9. HIV can enter the body through: -Mouth -Vagina -Nose -Penis -Eyes -Anus -Ears -Break in Skin
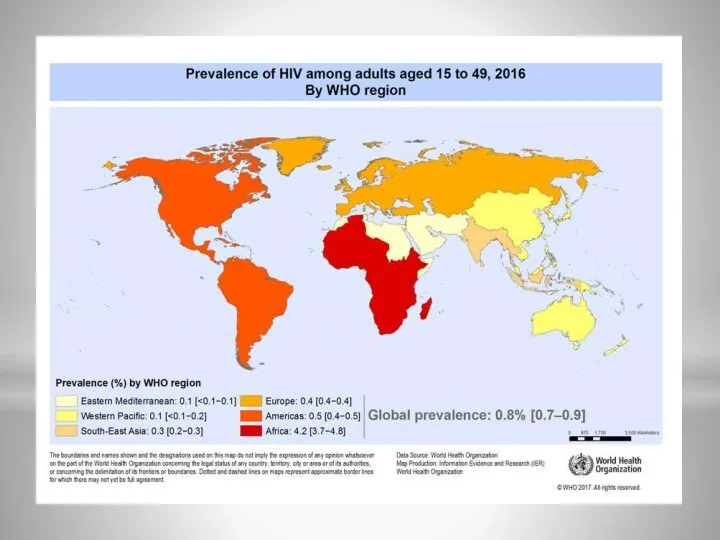
- 10. Transmission
- 11. HIV Disease Direct infection of organ systems: HIV can directly infect the; Brain (HIV dementia) Gut
- 12. Primary HIV Syndrome Mononucleosis-like, cold or flu-like symptoms may occur 6 to 12 weeks after infection.
- 13. Symptoms of HIV -Many people who are infected with HIV have NO symptoms at all for
- 14. The period of time after you may have been exposed to HIV, but before a test
- 16. HIV antibodies present Infected and can infect others Need to begin treatment No HIV antibodies detected
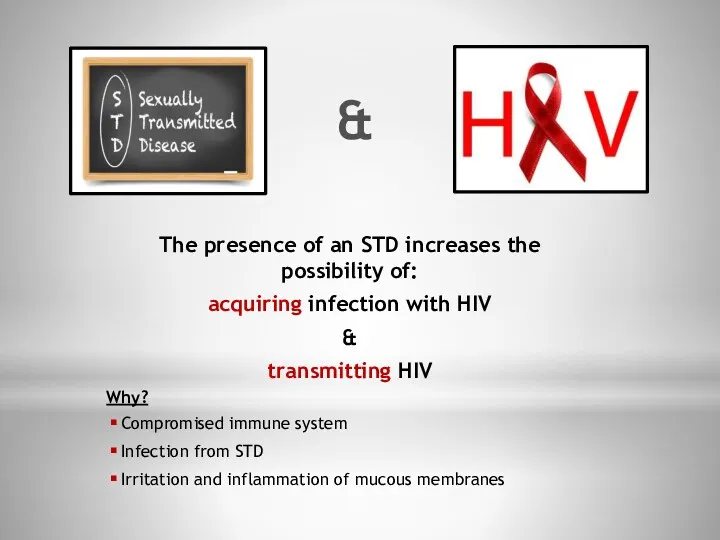
- 17. The presence of an STD increases the possibility of: acquiring infection with HIV & transmitting HIV
- 18. HIV Testing CDC recommends routine HIV testing for ALL patients: Aged 13-64 Initiating TB treatment Seeking
- 19. Reducing your risk of HIV No Risk — Abstinence (sex): not having oral, vaginal or anal
- 20. Male Condoms More than 98% effective when used correctly and consistently Different kinds:19 Latex Polyurethane (“Non-Latex”)
- 21. Do’s and Don’ts of male condom use21 Do’s DO keep condoms in a cool, dry place
- 22. Female Condoms Worn inside the vagina or anus Thicker, more tear-resistant Always latex-free Wider opening covers
- 23. World Health Organisation (WHO) has recommended a combination of antiretroviral drugs for people starting HIV treatment:
- 24. Diagnosis of HIV Antibody test These tests check for a kind of protein that your body
- 25. Antibody antigen test The CDC recommends these blood tests. They can detect HIV as soon as
- 26. Treatment does extend the lives of many people living with HIV, however…. Medication can be: Expensive
- 28. Скачать презентацию





















 Проблема вкусовой привлекательности рациона при ХБП и способы ее повышения
Проблема вкусовой привлекательности рациона при ХБП и способы ее повышения БМСК жағдайында көмек көрсету қағидалары
БМСК жағдайында көмек көрсету қағидалары Становление теоретической и клинической медицины Нового времени. Научные революции в медицине. Лекция 7
Становление теоретической и клинической медицины Нового времени. Научные революции в медицине. Лекция 7 Атопический дерматит
Атопический дерматит Лабораторные методы исследования системы крови
Лабораторные методы исследования системы крови Осторожно: грипп и орви
Осторожно: грипп и орви Вакцина против полиомиелита
Вакцина против полиомиелита Әйелдердегі маскүнемдік
Әйелдердегі маскүнемдік Медико-соціальна експертиза при захворюваннях органів дихання
Медико-соціальна експертиза при захворюваннях органів дихання Идиопатические заболевания пародонта
Идиопатические заболевания пародонта Семинар по классификации в Бочча
Семинар по классификации в Бочча ВКР: Течение и лечение катаральных (альвеолярных) маститов в ООО РУСЬ
ВКР: Течение и лечение катаральных (альвеолярных) маститов в ООО РУСЬ Тактика медперсонала при выявлении у пациентов факторов риска или клинических симптомов наркологического заболевания
Тактика медперсонала при выявлении у пациентов факторов риска или клинических симптомов наркологического заболевания Созылмалы бүйрек шамасыздығы
Созылмалы бүйрек шамасыздығы Предмет и задачи психиатрии
Предмет и задачи психиатрии Детская городская клиническая больница имени Н.Ф. Филатова
Детская городская клиническая больница имени Н.Ф. Филатова Электрокардиография при нарушениях ритма сердца
Электрокардиография при нарушениях ритма сердца Шап жарығы
Шап жарығы Нагноительные заболевания легких. Заболевания плевры
Нагноительные заболевания легких. Заболевания плевры Деформация зубных рядов. Зубочелюстная аномалия
Деформация зубных рядов. Зубочелюстная аномалия Харчування дітей старше року
Харчування дітей старше року Физиология крови. Лейкоциты
Физиология крови. Лейкоциты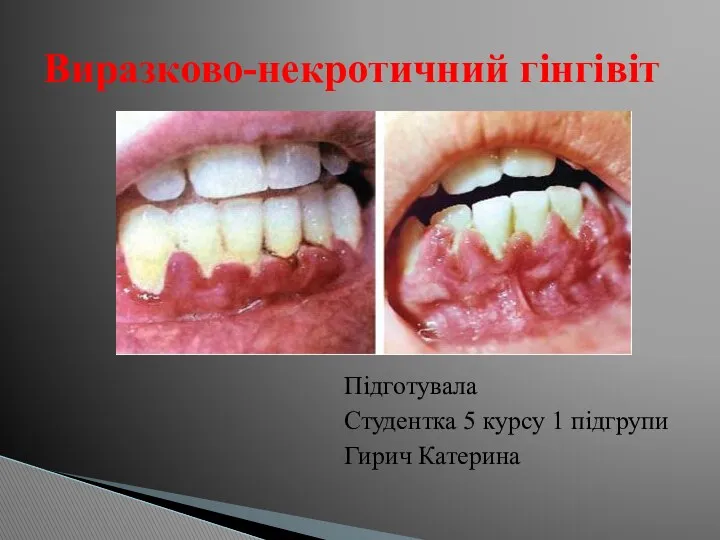 Виразково-некротичний гінгівіт
Виразково-некротичний гінгівіт Современная антимикробная терапия
Современная антимикробная терапия Современные подходы к образованию обучающихся с ОВЗ
Современные подходы к образованию обучающихся с ОВЗ Анаэробная инфекция
Анаэробная инфекция Противоопухолевый иммунитет
Противоопухолевый иммунитет Физиолечение флегмоны кисти
Физиолечение флегмоны кисти