Medication Safety Standard. Medication management processes, partnering with patients and carers презентация
Содержание
- 2. Medication management processes The clinical workforce is supported for the prescribing, administering, storing, manufacturing, compounding and
- 3. Medication management processes 4.9: Ensuring that current and accurate medicines information and decision support tools are
- 4. 4.9: Ensuring that current and accurate medicines information and decision support tools are readily available to
- 5. Medication management processes Clinical decision support for electronic medication management systems (EMMS) As a minimum the
- 6. Medication management processes 4.9: Ensuring that current and accurate medicines information and decision support tools are
- 7. Medication management processes 4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed and stored securely, safely (cont’d) What? Regular
- 8. Medication management processes 4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed and stored securely, safely (Cont’d) What? 4.10.2.
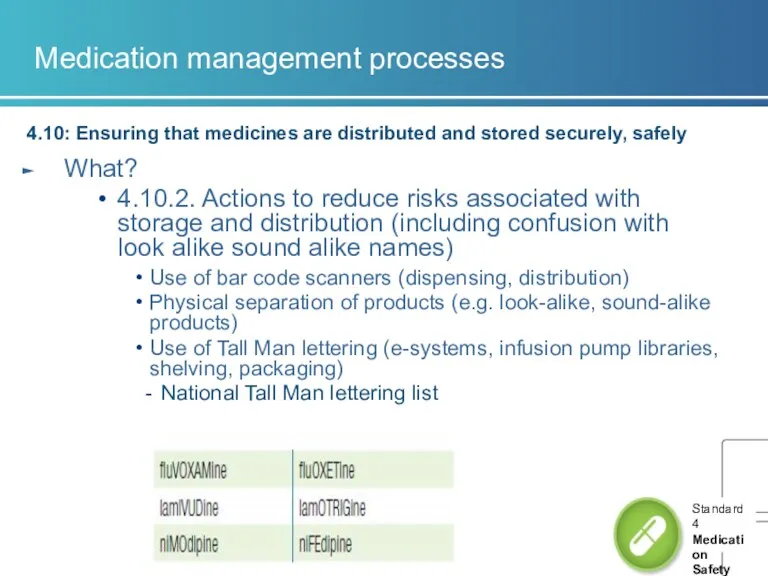
- 9. Medication management processes 4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed and stored securely, safely What? 4.10.2. Actions
- 10. Medication management processes 4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed and stored securely, safely What? Temperature sensitive
- 11. Medication management processes 4.10: Ensuring that medicines are distributed and stored securely, safely What? Workforce disposes
- 12. Medication management processes 4.10. 5 System for disposal of unused, unwanted or expired medicines is regularly
- 13. Medication management processes 4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in the organisation and ensuring they are stored,
- 14. Medication management processes 4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in the organisation and ensuring they are stored,
- 15. Audits of compliance 3. Medication management processes
- 16. Medication management processes 4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in the organisation and ensuring they are stored,
- 17. Medication management processes 4.11: Identifying high risk medicines in the organisation and ensuring they are stored,
- 18. Communicating with patients and carers The clinical workforce informs patients about their options, risks and responsibilities
- 19. Communicating with patients and carers 4.13: The clinical workforce informing patients and carers about medication treatment
- 20. Communicating with patients and carers 4.14: Developing a medication management plan in partnership with patients and
- 21. Communicating with patients and carers 4.14: Developing a medication management plan in partnership with patients and
- 22. Communicating with patients and carers 4.14 Developing a medication management plan in partnership with patients, carers
- 23. Communicating with patients and carers 4.15: Providing current medicines information to patients in a format that
- 24. Communicating with patients and carers
- 26. Скачать презентацию




















 Медицина и стоматология. Одонтон и его филогенез
Медицина и стоматология. Одонтон и его филогенез ГУЗ Сретенская ЦРБ. Информация о больнице
ГУЗ Сретенская ЦРБ. Информация о больнице Коклюш. Паракоклюш
Коклюш. Паракоклюш Балалардағы қант диабетінің алдын алу
Балалардағы қант диабетінің алдын алу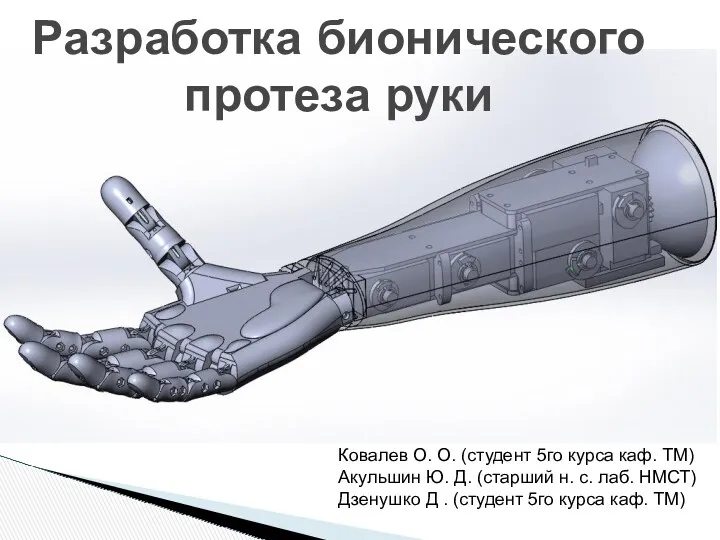 Разработка бионического протеза руки
Разработка бионического протеза руки Гельмінтози у дітей
Гельмінтози у дітей Брюшной тиф. Паратифы А и В
Брюшной тиф. Паратифы А и В Лечебная физическая культура в медицинской реабилитации
Лечебная физическая культура в медицинской реабилитации Курсовая работа по Внутренним незаразным болезням
Курсовая работа по Внутренним незаразным болезням Организация лекарственного обеспечения лечебно-профилактических учреждений (БА, МБА)
Организация лекарственного обеспечения лечебно-профилактических учреждений (БА, МБА) Жүре пайда болған (ЖИТС, СПИД ағылш. AIDS) иммундық дефицитiнiң синдромы
Жүре пайда болған (ЖИТС, СПИД ағылш. AIDS) иммундық дефицитiнiң синдромы Деменция. Классификации деменций
Деменция. Классификации деменций использование партограммы
использование партограммы Туберкулинодиагностика
Туберкулинодиагностика Переливание крови. История. Изогемагглютинация, группы крови. Механизм действия перелитой крови
Переливание крови. История. Изогемагглютинация, группы крови. Механизм действия перелитой крови Заряди организм жизнью
Заряди организм жизнью Скринингтік бағдарламалардың мониторингі, оларды өткізу және ұйымдастыру. (Курс 1)
Скринингтік бағдарламалардың мониторингі, оларды өткізу және ұйымдастыру. (Курс 1) Классификация ассортимента. Компания Tentorium (бады)
Классификация ассортимента. Компания Tentorium (бады) Инфекционные болезни. Полиомиелит, бешенство
Инфекционные болезни. Полиомиелит, бешенство Жарақаттар (буынның шығуы, сынық)
Жарақаттар (буынның шығуы, сынық) Клиникалық эпидемиология
Клиникалық эпидемиология Современная стоматологическая клиника социальной направленности (на примере р.п. Кантемировка)
Современная стоматологическая клиника социальной направленности (на примере р.п. Кантемировка) Рентгенодиагностика травматических повреждений костей и суставов
Рентгенодиагностика травматических повреждений костей и суставов Эндодонтический инструментарий
Эндодонтический инструментарий Организация безопасной больничной среды в лечебно-профилактическом учреждении
Организация безопасной больничной среды в лечебно-профилактическом учреждении Способы заготовки лекарственного сырья из листьев
Способы заготовки лекарственного сырья из листьев Расстройства чувствительности, боль. Атаксии
Расстройства чувствительности, боль. Атаксии Нарушения памяти
Нарушения памяти