Содержание
- 2. Opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae
- 3. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS PNEUMONIA ABDOMINAL SEPSIS MENINGITIS SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL
- 4. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS Life-threatening Usually nosocomial Commonly caused by E. coli PATHOGENESIS: Early
- 5. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Usually ascending infection, not hematogenous route Greatest incidence in young
- 6. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) ABDOMINAL SEPSIS Caused by flora of the GI tract Infections usually polymicrobial MENINGITIS
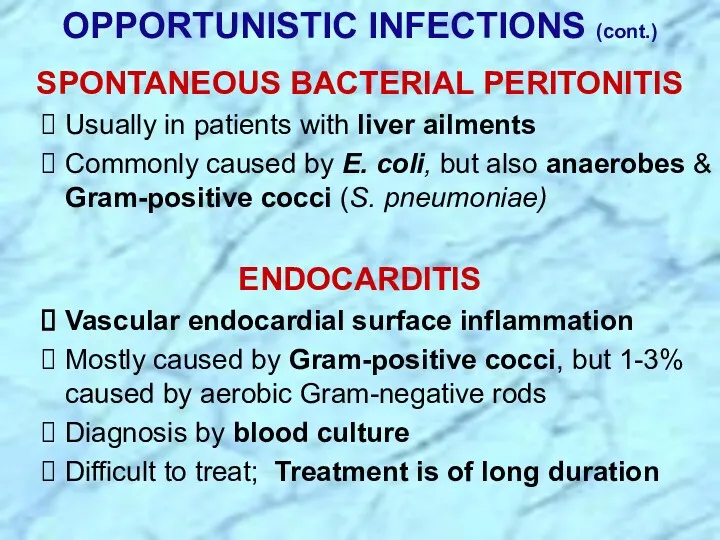
- 7. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL PERITONITIS Usually in patients with liver ailments Commonly caused by E.
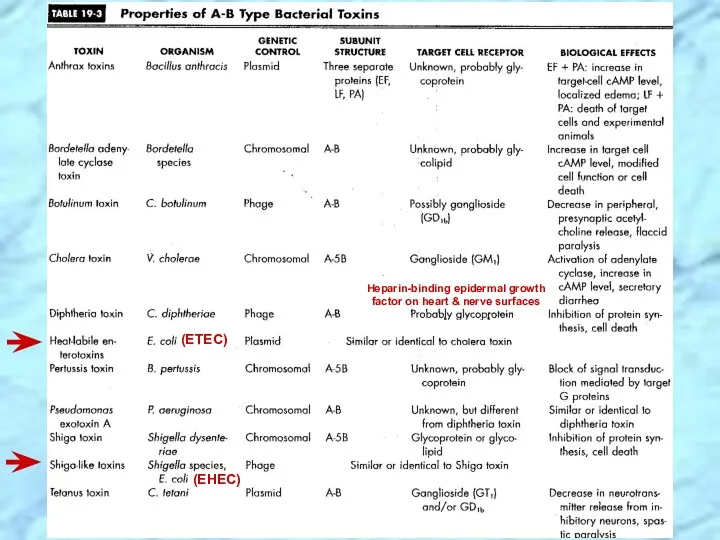
- 8. Common Virulence Factors Endotoxin Capsule Antigenic phase variation Sequestration of growth factors Resistance to serum killing
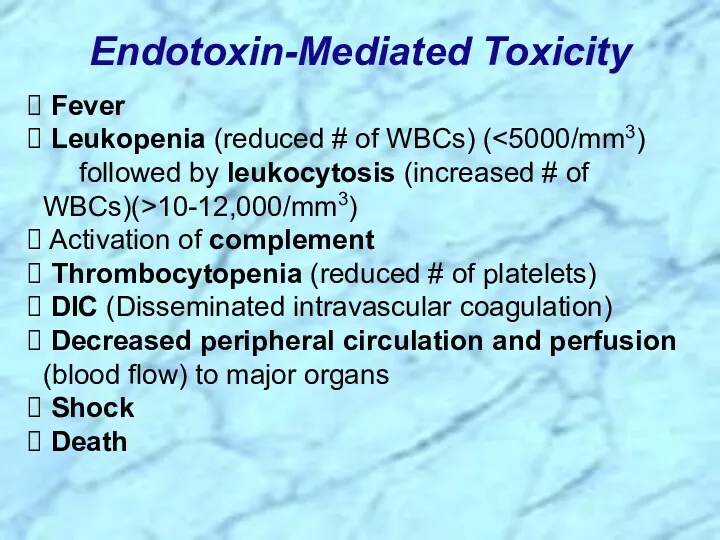
- 9. Fever Leukopenia (reduced # of WBCs) ( 10-12,000/mm3) Activation of complement Thrombocytopenia (reduced # of platelets)
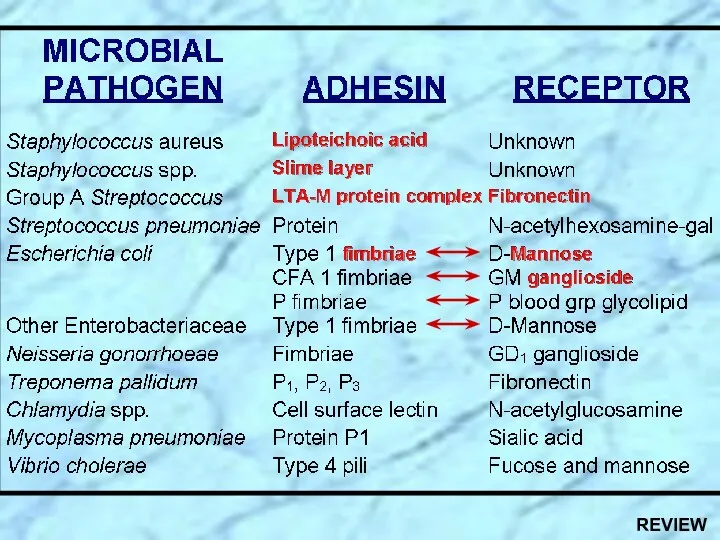
- 10. See Handout on Enterobacteriaceae General Information
- 11. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections
- 12. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections (cont.)
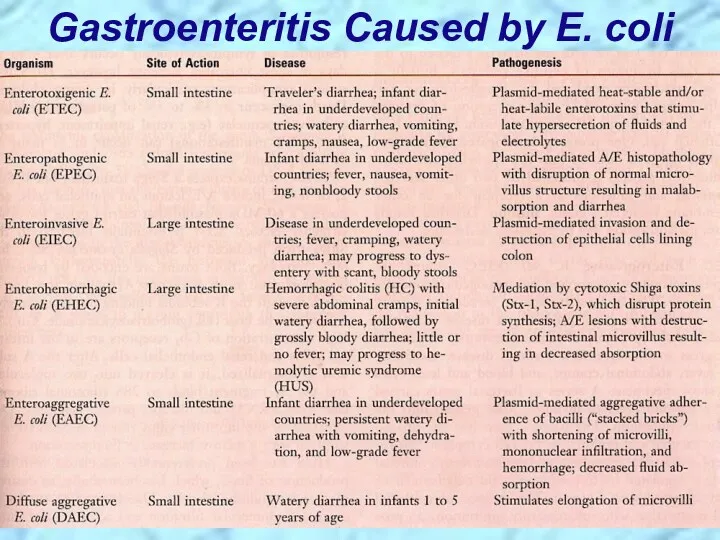
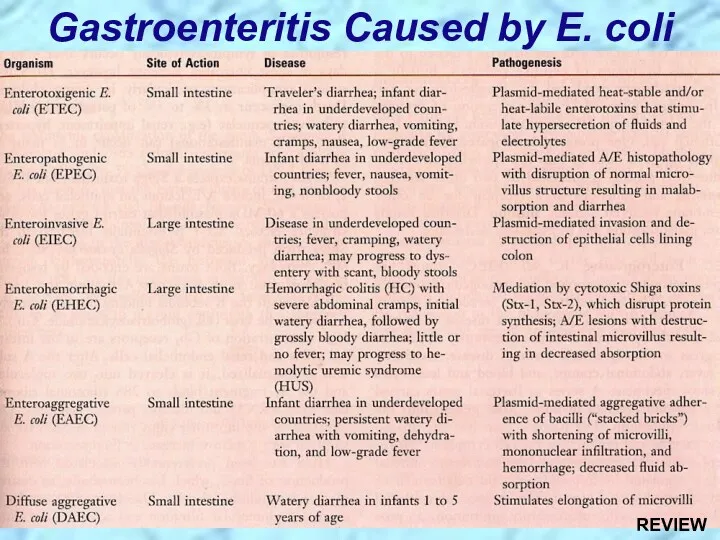
- 13. Gastroenteritis Caused by E. coli
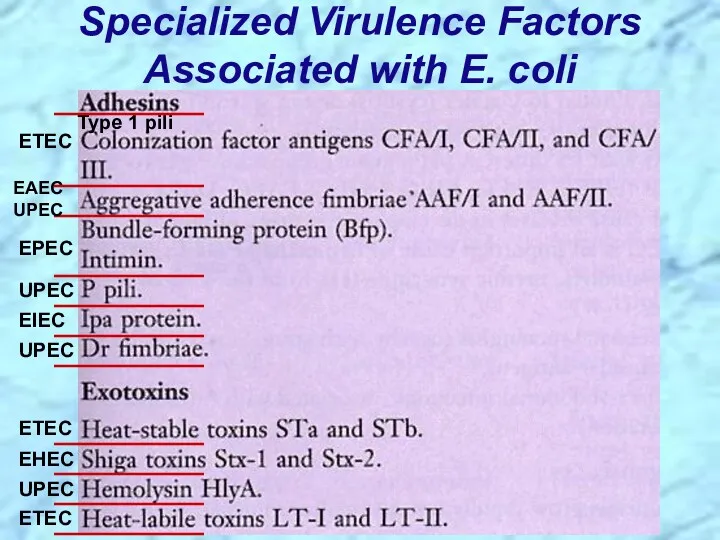
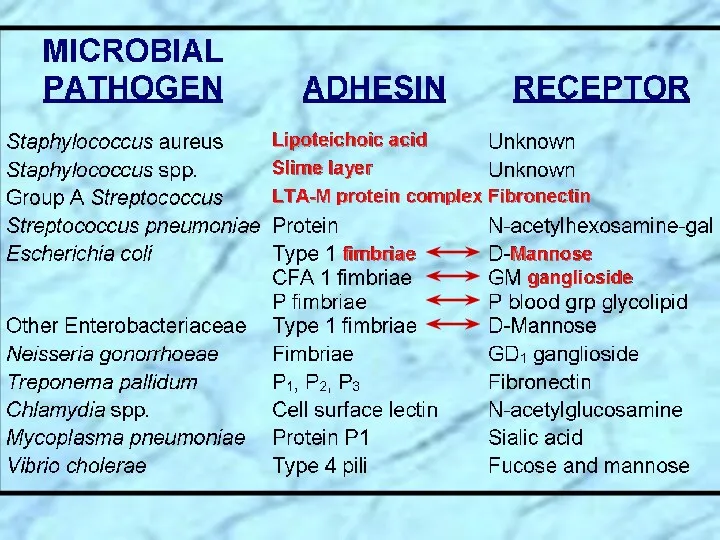
- 14. Specialized Virulence Factors Associated with E. coli EAEC UPEC EPEC ETEC Type 1 pili UPEC UPEC
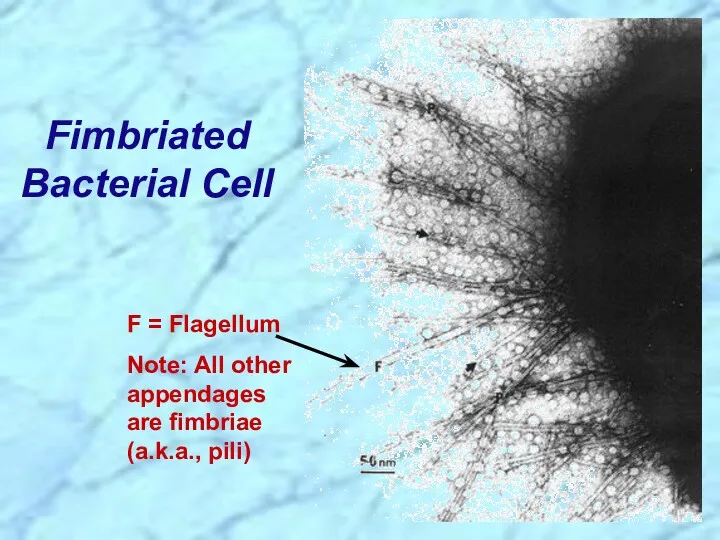
- 15. Fimbriated Bacterial Cell F = Flagellum Note: All other appendages are fimbriae (a.k.a., pili)
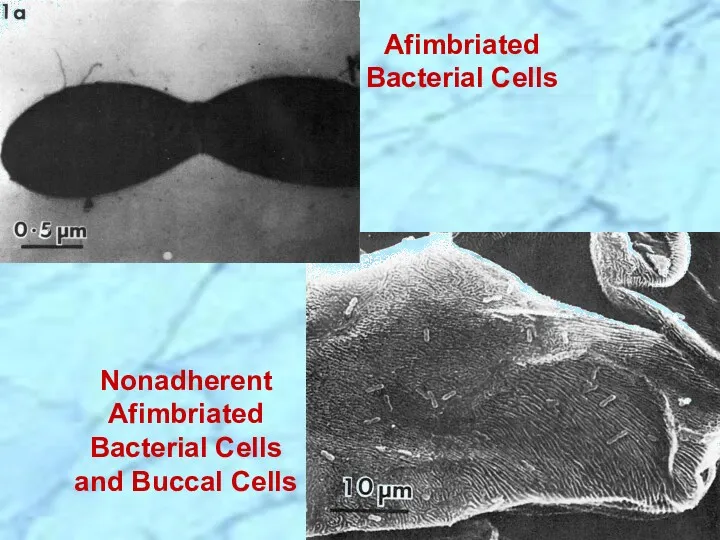
- 16. Afimbriated Bacterial Cells Nonadherent Afimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells
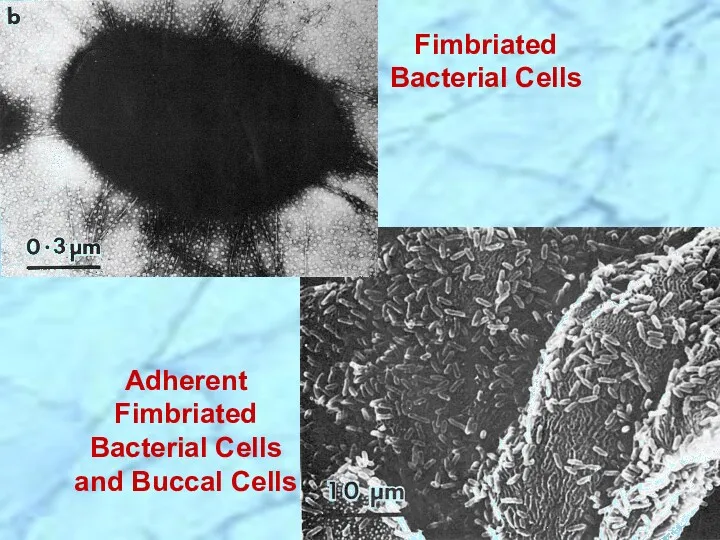
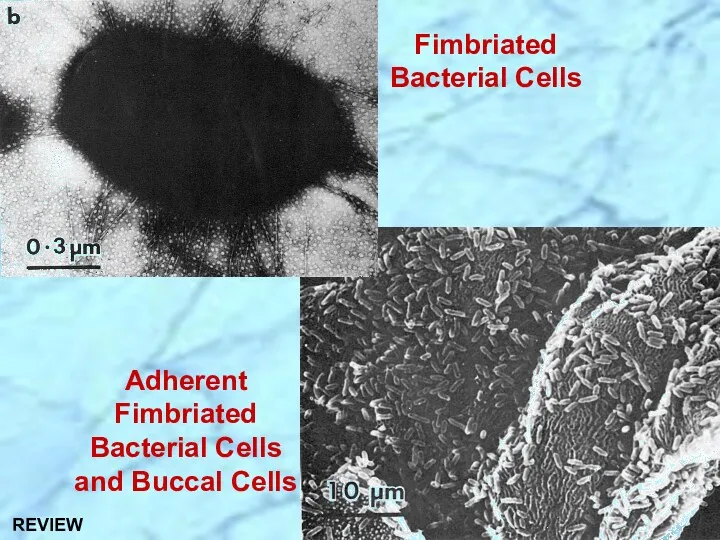
- 17. Adherent Fimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells Fimbriated Bacterial Cells
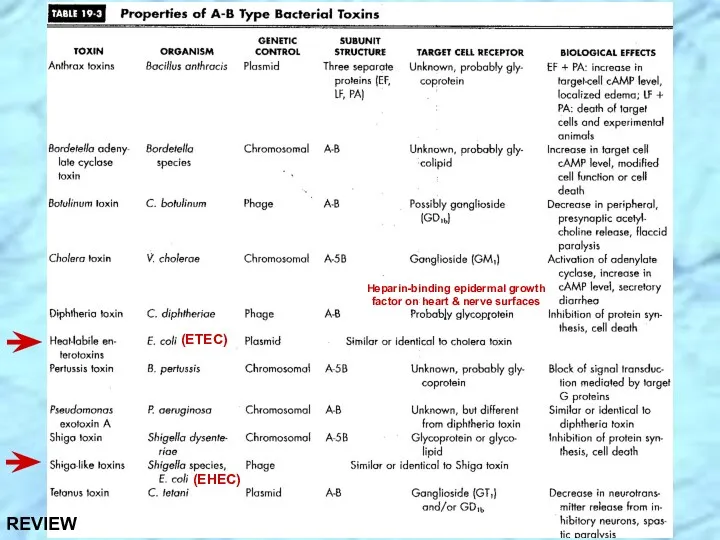
- 19. (ETEC) (EHEC)
- 21. REVIEW
- 22. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS PNEUMONIA ABDOMINAL SEPSIS MENINGITIS SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL
- 23. Common Virulence Factors Endotoxin Capsule Antigenic phase variation Sequestration of growth factors Resistance to serum killing
- 24. REVIEW See Handout on Enterobacteriaceae General Information
- 25. Fever Leukopenia (reduced # of WBCs) ( 10-12,000/mm3) Activation of complement Thrombocytopenia (reduced # of platelets)
- 26. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections REVIEW
- 27. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections (cont.) REVIEW
- 28. Gastroenteritis Caused by E. coli REVIEW
- 29. Fimbriated Bacterial Cell F = Flagellum Note: All other appendages are fimbriae (a.k.a., pili) REVIEW
- 30. Afimbriated Bacterial Cells Nonadherent Afimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells REVIEW
- 31. Adherent Fimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells Fimbriated Bacterial Cells REVIEW
- 32. REVIEW
- 33. (ETEC) (EHEC) REVIEW
- 35. Скачать презентацию

















 Бронхиальді астма диагностикасы және дифференциалды диагностикасы
Бронхиальді астма диагностикасы және дифференциалды диагностикасы Консультация по проведению ГИА в педиатрии. Порядок оказания медицинской помощи
Консультация по проведению ГИА в педиатрии. Порядок оказания медицинской помощи Первая помощь при острой сердечной недостаточности
Первая помощь при острой сердечной недостаточности Гастриты острые и хронические
Гастриты острые и хронические Симптоматична неплідність у жуйних
Симптоматична неплідність у жуйних Спортивное питание для разных видов боевых искусств: ММА, вольная борьба, сумо
Спортивное питание для разных видов боевых искусств: ММА, вольная борьба, сумо Основные средства повышения работоспособности и восстановления организма спортсменов после физических нагрузок
Основные средства повышения работоспособности и восстановления организма спортсменов после физических нагрузок Кислоты. Классификация. Патологическая физиология и анатомия отравления. Судебно-медицинское значение
Кислоты. Классификация. Патологическая физиология и анатомия отравления. Судебно-медицинское значение Болезни, обусловленные воздействием физических факторов производственной среды
Болезни, обусловленные воздействием физических факторов производственной среды Урология детского возраста
Урология детского возраста Болезнь Паркинсона
Болезнь Паркинсона Неотложная помощь при гипертоническом кризе
Неотложная помощь при гипертоническом кризе Морфофункциональная характеристика спинного мозга
Морфофункциональная характеристика спинного мозга Дәнекер тіннің диффузды аурулары
Дәнекер тіннің диффузды аурулары Лекарственные средства антидепрессанты
Лекарственные средства антидепрессанты Косыночные повязки
Косыночные повязки Күйік
Күйік Артериальная гипертензия
Артериальная гипертензия Острая кишечная непроходимость
Острая кишечная непроходимость Раны и раневой процесс
Раны и раневой процесс Шовный материал в хирургии
Шовный материал в хирургии Артериальная гипертензия у детей
Артериальная гипертензия у детей Патология периода новорожденности
Патология периода новорожденности Операции на грудной клетке
Операции на грудной клетке Питание и красота
Питание и красота Логопедический массаж с детьми с различными нарушениями. Дифференцированные приемы работы
Логопедический массаж с детьми с различными нарушениями. Дифференцированные приемы работы Варикоцеле. Расширение вен семенного канатика
Варикоцеле. Расширение вен семенного канатика Filling’s material: permanent & temporary. Active and passive voice
Filling’s material: permanent & temporary. Active and passive voice