The pathology, syndromology, nosology of the exogenous intoxication register. Infections and intoxications mental disorders презентация
Содержание
- 2. Exogenous psychoses лат. exogenus – out, outside Exogenous psychoses are a group of mental disorders with
- 3. Exogenous reaction type (K. Bonhoeffer, 1910) the brain can react to a variety of external damaging
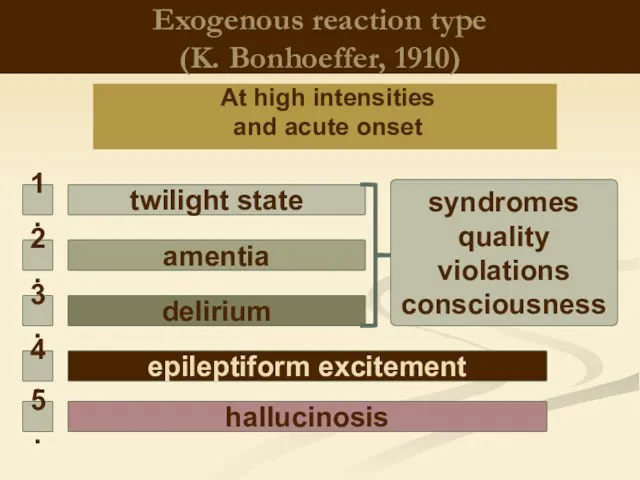
- 4. Exogenous reaction type (K. Bonhoeffer, 1910) At high intensities and acute onset delirium amentia twilight state
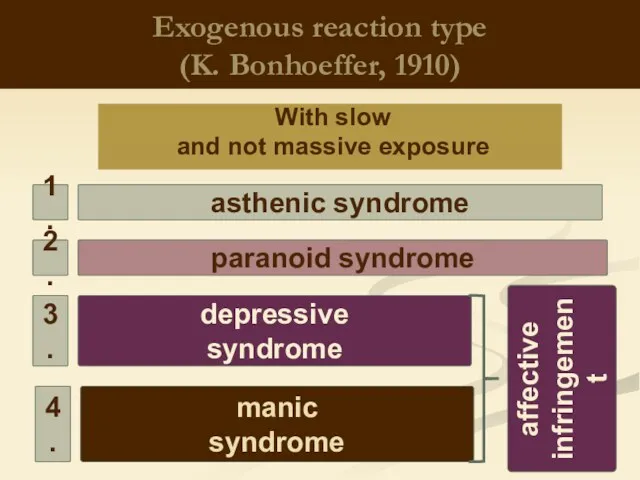
- 5. Exogenous reaction type (K. Bonhoeffer, 1910) With slow and not massive exposure depressive syndrome paranoid syndrome
- 6. Exogenous reaction type (K. Bonhoeffer, 1910) Atypical syndromes hallucinatory-delusional syndrome mood disorder (dysphoria, euphoria) emotional weakness
- 7. Exogenous reaction type (Modern view) asthenic syndrome syndromes of impaired consciousness (qualitative, quantitative) Syndromes of disorders
- 8. Asthenic syndrome
- 9. Anxiety disorders of organic nature
- 10. Psychoorganic syndrome
- 11. Emotional disorders
- 12. Hallucinatory-paranoid syndrome
- 13. COMA
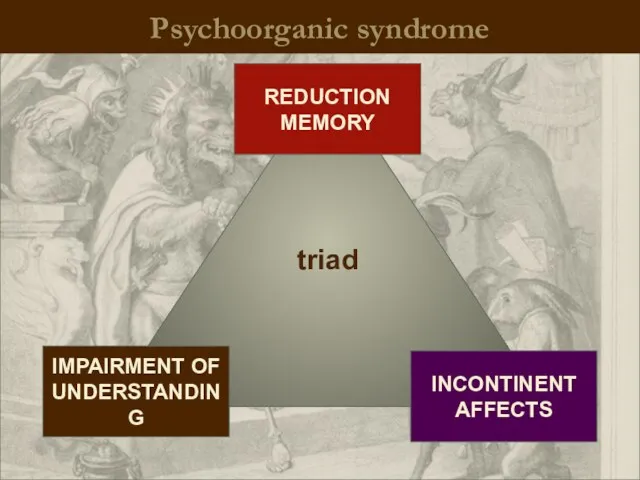
- 14. Psychoorganic syndrome triad IMPAIRMENT OF UNDERSTANDING REDUCTION MEMORY INCONTINENT AFFECTS
- 15. Diagnostic options psychoorganic syndrome ICD-10 Organic neurosis-like disorders - organic emotionally labile disorder (asthenic), organic anxiety
- 16. The types of psychoorganic syndrome depending on emotional disorders leading symptom Cerebro - asthenia accompanied by
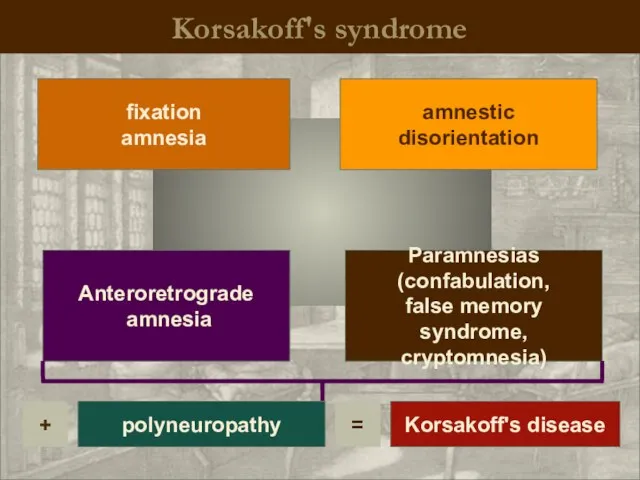
- 17. Korsakoff's syndrome Paramnesias (confabulation, false memory syndrome, cryptomnesia) fixation amnesia Anteroretrograde amnesia amnestic disorientation polyneuropathy +
- 18. INFECTIOUS PSYCHOSES - intoxication bacterial toxins, decay products of proteins TOXIC PSYCHOSES - intoxication exogenous substances
- 19. Clinical picture of toxic psychsis symptoms of quality and quantitative disturbance of consciousness asthenic syndrome hallucinatory-delusional
- 20. TOXIC PSYCHOSIS
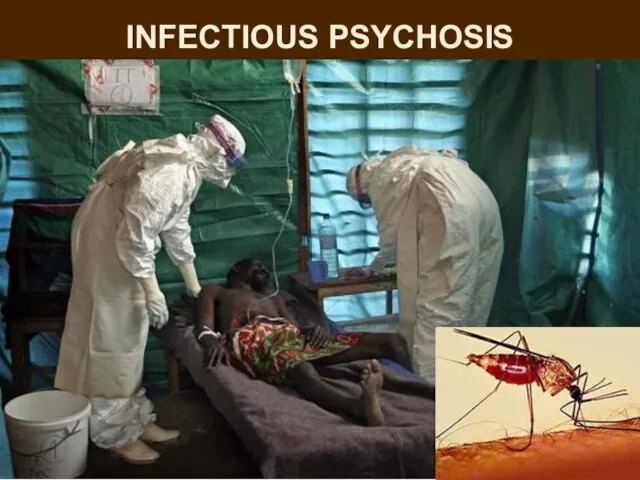
- 21. INFECTIOUS PSYCHOSIS
- 22. Delirium
- 23. Oneiroid
- 24. INFECTIOUS PSYCHOSES Symptomatic - arise in common infectious diseases as a result of intoxication Intracranial -
- 25. SYMPTOMATIC INFECTIOUS PSYCHOSES ACUTE (acute infectious diseases) - Occur as a complication of the underlying disease
- 26. DELIRIUM
- 27. INFECTIOUS DELIIUM dynamic variants An initial delirium - preceded by symptoms of somatic disorders and occurs
- 28. PROTRACED SYMPTOMATIC INFECTIOUS PSYCHOSES asthenic-depressive syndrome in the form of sadness, anxiety or apathetic depression, which
- 29. Infectious intracranial psychoses Neuroinfections PRIMARY INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF THE BRAIN (epidemic, Japanese encephalitis, parainfectious encephalitis -
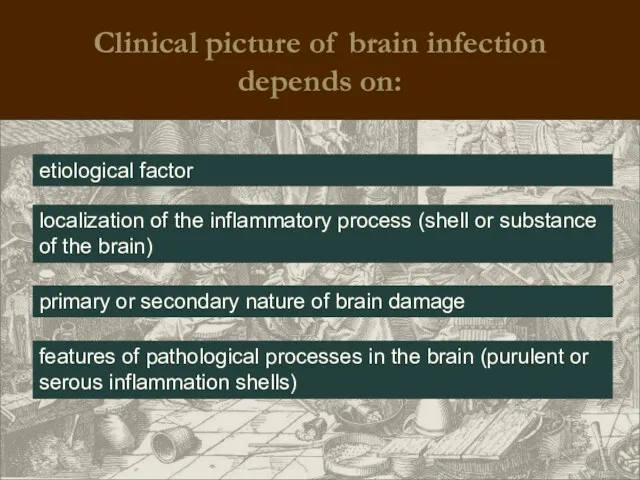
- 30. Clinical picture of brain infection depends on: etiological factor localization of the inflammatory process (shell or
- 31. Mental disorders in primary infectious diseases of the brain Acute encephalitis any period is accompanied by
- 32. "Preferably" syndrome in tubercular psychosis (K.A. Wangenheim) asthenic confusion paranoid-asthenic syndrome manic-depressive syndrome manic-asthenic syndrome
- 33. “Preferred” syndrome in pyogenic infection (K. A. Wangenheim) amnestic syndrome disinhibition amentia, asthenic confusion catatonic-oneiroid syndrome
- 34. "Preferably" rheumatic syndromes in psychosis (KA Wangenheim) dementia pseudoparalytic syndrome disinhibition dream-like state, dream-like stupor catatonic-oneiroid
- 35. NEUROSYPHILIS (Secondary syphilis) – defeat by Treponema pallidum membranes and blood vessels of the brain parenchyma:
- 36. PHASES of NEUROSYPHILIS I – syphilitic neurasthenia III - Clinic due to disorders of cerebral circulation
- 37. Cerebral syphilis (Tertiary syphilis) Paralysis progressiva, dementia paralytica Paralysis (Illness A. L. Bayle, 1822) – Treponema
- 38. stage of total dementia - paralytic syndrome - total dementia with euphoria, complacency, a sharp decline
- 39. FORMS OF CEREBRAL SYPHILIS simple expansive depressive-hypochondriac hallucinatory-paranoid Lissauer’s paralysis taboparesis
- 40. Expansive form Unknown patient
- 41. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!
- 43. Скачать презентацию

































 Клетки иммунной системы. Цитокины
Клетки иммунной системы. Цитокины Особенности ухода медицинской сестры в послеоперационном периоде после операции на брюшной полости
Особенности ухода медицинской сестры в послеоперационном периоде после операции на брюшной полости Реализация региональных проектов национального проекта Здравоохранение в Липецкой области
Реализация региональных проектов национального проекта Здравоохранение в Липецкой области Врожденный сифилис
Врожденный сифилис Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях системы крови и кроветворных органов у детей. Анемии. Лейкоз
Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях системы крови и кроветворных органов у детей. Анемии. Лейкоз Болезни зубов (пульпит и кариес)
Болезни зубов (пульпит и кариес) Анаэробная инфекция
Анаэробная инфекция Антисептика
Антисептика Балалардағы ерін мен тіл аурулары. Клиникасы, нақтамасы, емі. Лекция 8
Балалардағы ерін мен тіл аурулары. Клиникасы, нақтамасы, емі. Лекция 8 Синаптотропные средства фармакология холинотропных и адренотропных препаратов
Синаптотропные средства фармакология холинотропных и адренотропных препаратов Группы крови. Переливание крови
Группы крови. Переливание крови Проблема здоровья людей: глобальный аспект
Проблема здоровья людей: глобальный аспект Ғылыми зерттеулердегі науқастардың рөлі. Науқастардың құқығы
Ғылыми зерттеулердегі науқастардың рөлі. Науқастардың құқығы Формирование аптечки первой помощи для путешествий
Формирование аптечки первой помощи для путешествий ПВБ. Семиотика мочевыделительной системы
ПВБ. Семиотика мочевыделительной системы Репродуктивне здоров’я молоді
Репродуктивне здоров’я молоді Технологии выполнения простых медицинских услуг
Технологии выполнения простых медицинских услуг Рентгеновская и позитронная томография
Рентгеновская и позитронная томография Атеросклероз. Внешние признаки атеросклероза
Атеросклероз. Внешние признаки атеросклероза Кір. Краснуха
Кір. Краснуха Сочетание рентгеновских синдромов патологии легких. Рентгенопульмонология
Сочетание рентгеновских синдромов патологии легких. Рентгенопульмонология Гострий апендицит у дітей
Гострий апендицит у дітей Перевязочный материал
Перевязочный материал Исследование минерализата в клинической фармации
Исследование минерализата в клинической фармации Фармакодинамика. Фармакологические эффекты, локализация и механизмы действия лекарственных средств
Фармакодинамика. Фармакологические эффекты, локализация и механизмы действия лекарственных средств Инструменты для лапароскопической хирургии
Инструменты для лапароскопической хирургии Желтухи у новорожденных
Желтухи у новорожденных Частная травматология. Повреждения тупыми предметами
Частная травматология. Повреждения тупыми предметами