Слайд 2
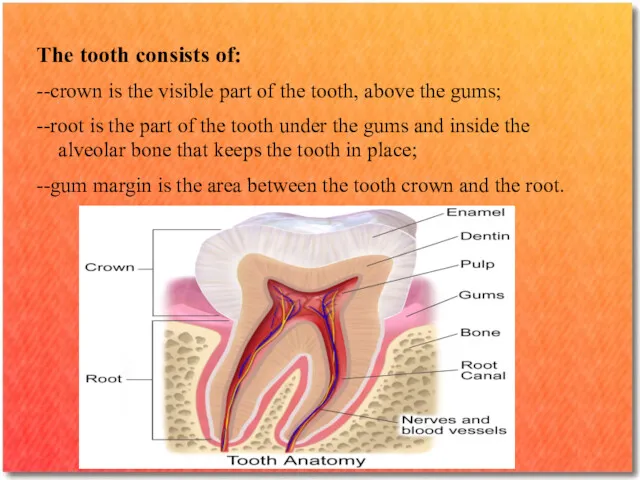
The tooth consists of:
--crown is the visible part of the
tooth, above the gums;
--root is the part of the tooth under the gums and inside the alveolar bone that keeps the tooth in place;
--gum margin is the area between the tooth crown and the root.
Слайд 3
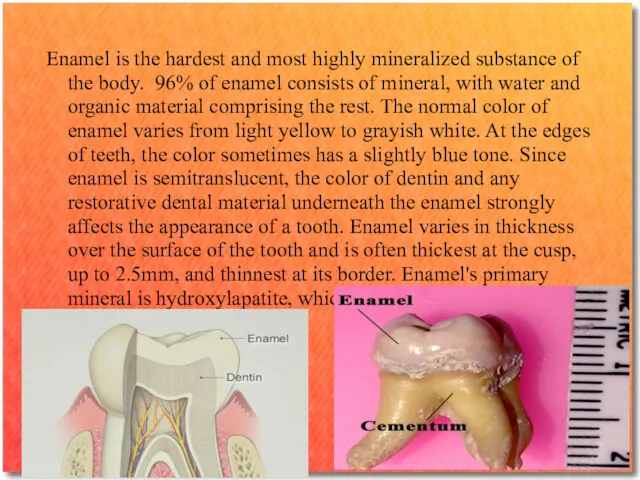
Enamel is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance of the
body. 96% of enamel consists of mineral, with water and organic material comprising the rest. The normal color of enamel varies from light yellow to grayish white. At the edges of teeth, the color sometimes has a slightly blue tone. Since enamel is semitranslucent, the color of dentin and any restorative dental material underneath the enamel strongly affects the appearance of a tooth. Enamel varies in thickness over the surface of the tooth and is often thickest at the cusp, up to 2.5mm, and thinnest at its border. Enamel's primary mineral is hydroxylapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate.
Слайд 4
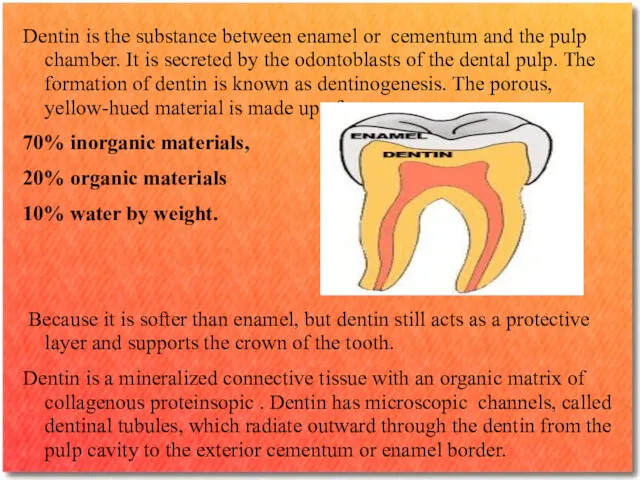
Dentin is the substance between enamel or cementum and the pulp
chamber. It is secreted by the odontoblasts of the dental pulp. The formation of dentin is known as dentinogenesis. The porous, yellow-hued material is made up of
70% inorganic materials,
20% organic materials
10% water by weight.
Because it is softer than enamel, but dentin still acts as a protective layer and supports the crown of the tooth.
Dentin is a mineralized connective tissue with an organic matrix of collagenous proteinsopic . Dentin has microscopic channels, called dentinal tubules, which radiate outward through the dentin from the pulp cavity to the exterior cementum or enamel border.
Слайд 5

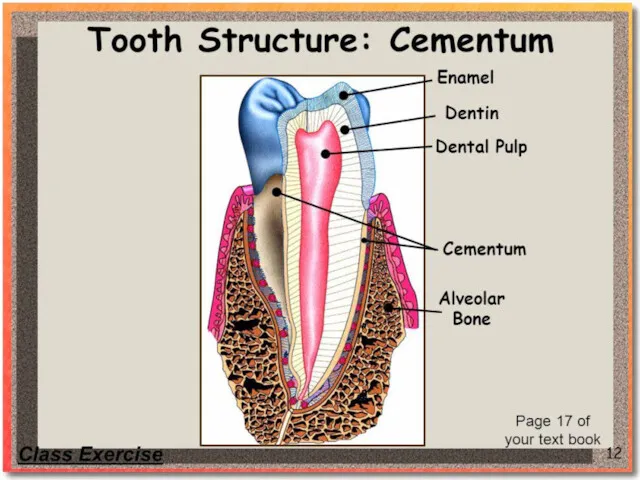
Cementum is a specialized bone like substance covering the root of
a tooth. It is approximately
45% inorganic material (mainly hydroxyapatite),
33% organic material (mainly collagen)
22% water.
Cementum is excreted by cementoblasts within the root of the tooth and is thickest at the root apex. Its coloration is yellowish. The principal role of cementum is to serve as a medium by which the periodontal ligaments can attach to the tooth for stability. At the cementoenamel junction, the cementum is acellular due to its lack of cellular components, and this acellular type covers at least ⅔ of the root. The more permeable form of cementum, cellular cementum, covers about ⅓ of the root apex.
Слайд 6
Слайд 7

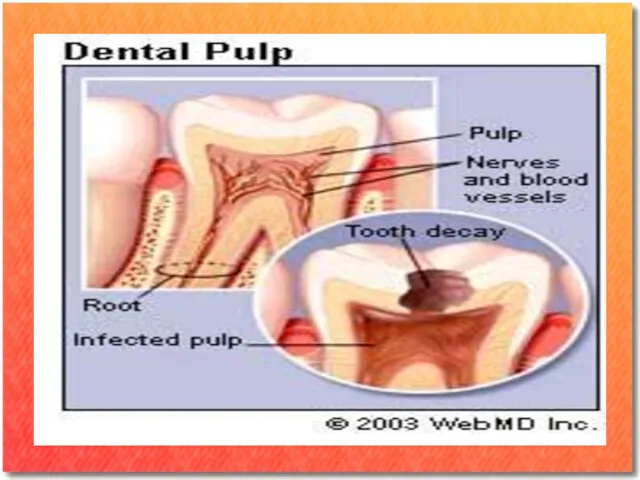
The dental pulp is the central part of the tooth filled
with soft connective tissue. This tissue contains blood vessels and nerves that enter the tooth from a hole at the apex of the root. Along the border between the dentin and the pulp are odontoblasts, which initiate the formation of dentin.
Cells in the pulp include :
--fibroblasts,
--preodontoblasts,
--macrophages
--T- lymphocytes.
The pulp is commonly called "the nerve" of the tooth.
Слайд 8
Слайд 9

Систематизация грамматического материала: модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты.
Слайд 10

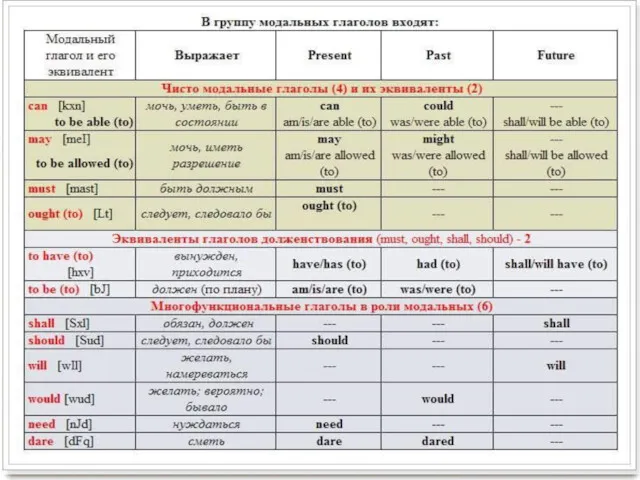
Modal verbs
can, could,
must, should,
ought to, may,
might, will,
would, shall - are modal auxiliary verbs that express ability, necessity, obligation, duty, request, permission, advice, desire, probability, possibility, etc. Modal verbs express the speaker's attitude to the action indicated by the main verb.
Слайд 11

Modal verbs do not have the future tense form. The future
is expressed by the present tense forms with the help of the context and adverbs of time referring to the future. (With the exception of the modal verbs WILL, WOULD, of course, which express the future.)
Can I go there tomorrow? – Yes, you can.
Могу я пойти туда завтра? – Да, можете.
Can they go there now? – No, they can't.
Могут они пойти туда сейчас? – Нет, не могут.
Слайд 12

Modal verbs take the infinitive without the particle "to". (The modal
verb OUGHT TO consists of two parts: "ought" and "to".) There are several infinitive forms in English.
to do – active infinitive / simple infinitive
делать – активный инфинитив / простой инфинитив
to be doing – continuous infinitive
делать – продолженный инфинитив
to have done – perfect infinitive
сделать – перфектный инфинитив
to have been doing – perfect continuous infinitive
сделать – перфектный продолженный инфинитив
to be done – passive infinitive
быть сделанным – пассивный инфинитив
to have been done – perfect passive infinitive
Слайд 13

Слайд 14

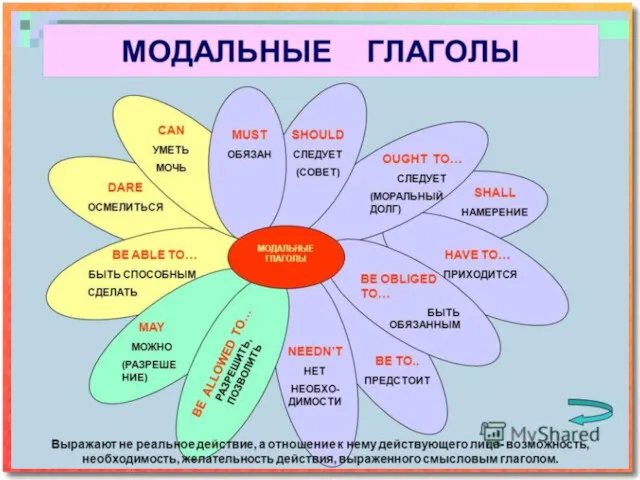
Эквиваленты модальных глаголов
Английские модальные глаголы не способны передавать все значения, заложенные
в описании ситуации по-русски:
Он сможет помочь тебе завтра. - Future - нет английской формы
Он должен был приехать вчера. - Past - нет английской формы
Поэтому в английском языке и существуют эквиваленты модальных глаголов
Слайд 15

В составе всех без исключения эквивалентов используются глаголы to be и
to have.
В предложении они могут стоять в любом времени (Past / Present / Future) и принимать любую из известных нам форм.
Эквиваленты используются не только вместо несуществующих форм модальных глаголов, но могут также употребляться вместо самих модальных глаголов; т.е. и в тех случаях, когда для данной ситуации форма модального глагола существует.
Эквиваленты тоже требуют после себя только форму Infinitive, но уже обязательно с частицей to.
Слайд 16
Слайд 17
















 Қызыл иектің ультраструктурасы, қызыл иек сайы,қызыл иек сұйықтығы
Қызыл иектің ультраструктурасы, қызыл иек сайы,қызыл иек сұйықтығы Трансплантация легких
Трансплантация легких Ультразвуковая диагностика заболеваний селезенки и регионарных лимфатических узлов
Ультразвуковая диагностика заболеваний селезенки и регионарных лимфатических узлов Основы безопасности питания
Основы безопасности питания Острый живот в гинекологии
Острый живот в гинекологии Фізіологічна класифікація та характеристика фізичних вправ
Фізіологічна класифікація та характеристика фізичних вправ Фармацевтична опіка при симптоматичному лікуванні болю у горлі, кашлю, лихоманки
Фармацевтична опіка при симптоматичному лікуванні болю у горлі, кашлю, лихоманки Анестезия севофлураном у детей
Анестезия севофлураном у детей Аптечная организация
Аптечная организация Pulmonary tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis Державна санітарно-епідеміологічна експертиза, як елемент соціально-гігієнічного моніторингу. Основні положення та організація
Державна санітарно-епідеміологічна експертиза, як елемент соціально-гігієнічного моніторингу. Основні положення та організація Диетическое питание
Диетическое питание Іштің жабық жарақаты
Іштің жабық жарақаты Жаңа туған нәрест елердің иммунитет інде иммуноглобулиндердің атқаратын ролі
Жаңа туған нәрест елердің иммунитет інде иммуноглобулиндердің атқаратын ролі Созылмалы аурулары бар науқастардың тістерін жұлу ерекшеліктері
Созылмалы аурулары бар науқастардың тістерін жұлу ерекшеліктері Тұқым қуалауға бейімделген аурулар
Тұқым қуалауға бейімделген аурулар Протозоология
Протозоология Основы кинезитерапии. Понятие о лечебной физической культуре
Основы кинезитерапии. Понятие о лечебной физической культуре Непрерывное медицинское образование
Непрерывное медицинское образование Анаэробная инфекция
Анаэробная инфекция Хранение и транспортирование товаров медицинского назначения на всех этапах товародвижения
Хранение и транспортирование товаров медицинского назначения на всех этапах товародвижения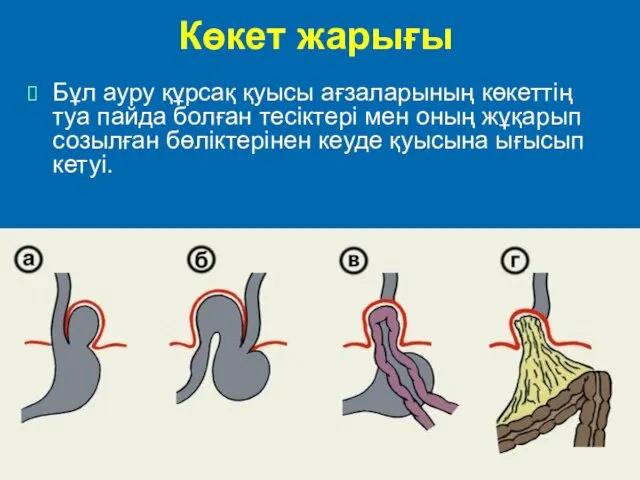 Көкет жарығы. Этиологиясы
Көкет жарығы. Этиологиясы Трансфузия компонентов крови
Трансфузия компонентов крови Общая характеристика учетной политики аптечной организации
Общая характеристика учетной политики аптечной организации Ядерная медицина
Ядерная медицина Equipment and instruments of dental clinic
Equipment and instruments of dental clinic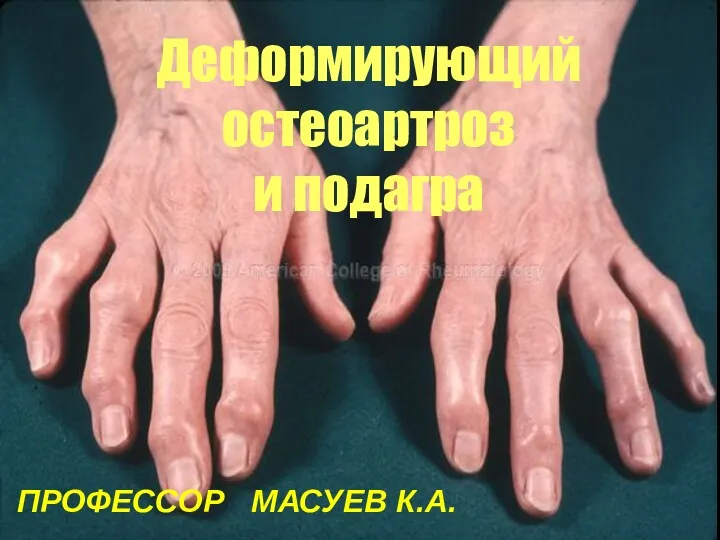 Остеоартроз: клиника, диагностика и современное лечение
Остеоартроз: клиника, диагностика и современное лечение Вреден ли фаст-фуд для нашего здоровья
Вреден ли фаст-фуд для нашего здоровья