Содержание
- 2. Plan of the lecture 1. Definition of urinary tract infections in children 2. Risk factors and
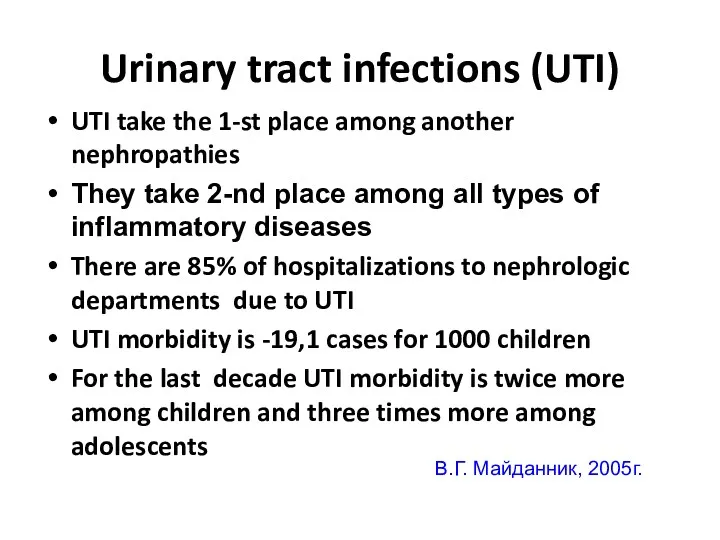
- 3. Urinary tract infections (UTI) UTI take the 1-st place among another nephropathies They take 2-nd place
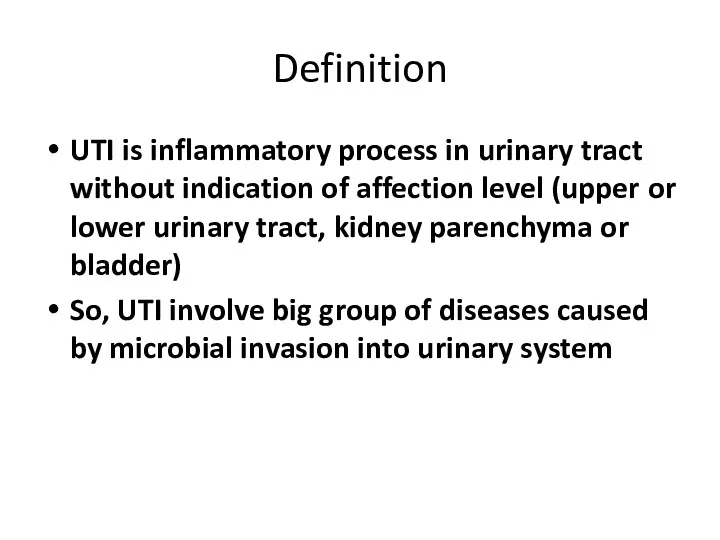
- 4. Definition UTI is inflammatory process in urinary tract without indication of affection level (upper or lower
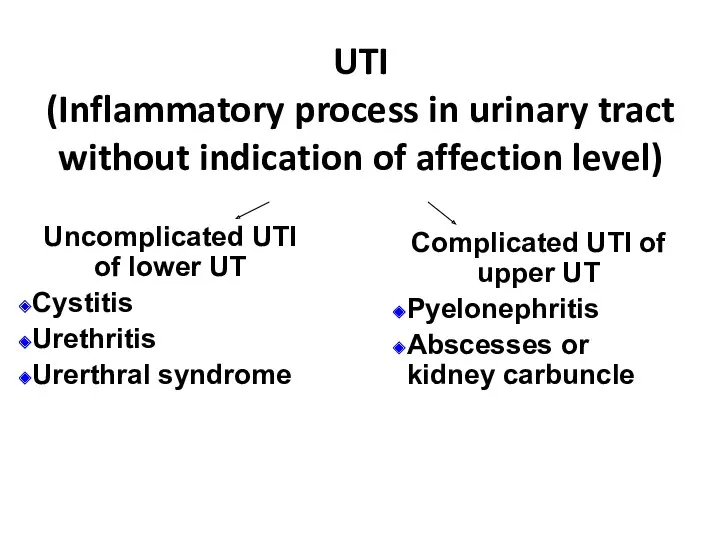
- 5. UTI (Inflammatory process in urinary tract without indication of affection level) Uncomplicated UTI of lower UT
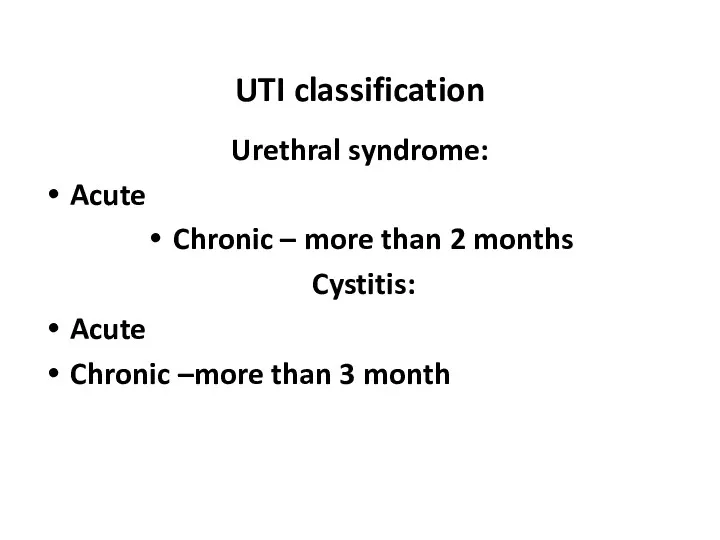
- 6. UTI classification Urethral syndrome: Acute Chronic – more than 2 months Cystitis: Acute Chronic –more than
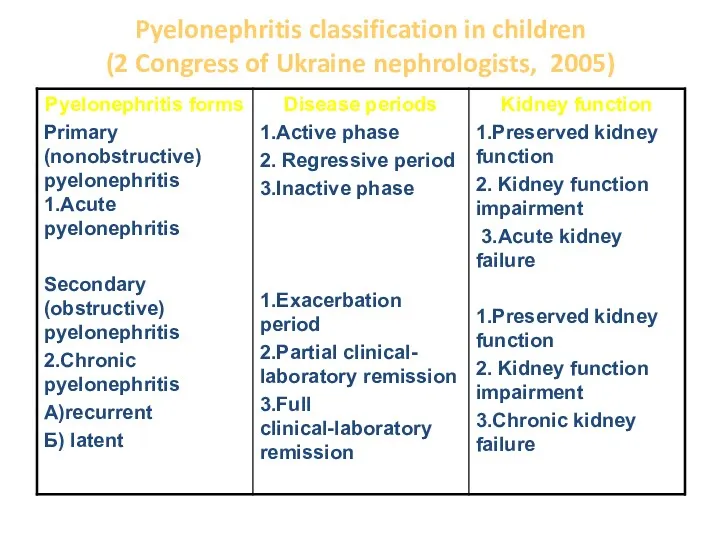
- 7. Pyelonephritis classification in children (2 Congress of Ukraine nephrologists, 2005)
- 8. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is presence of bacteria in urine in diagnostic titer without clinical manifestation and is
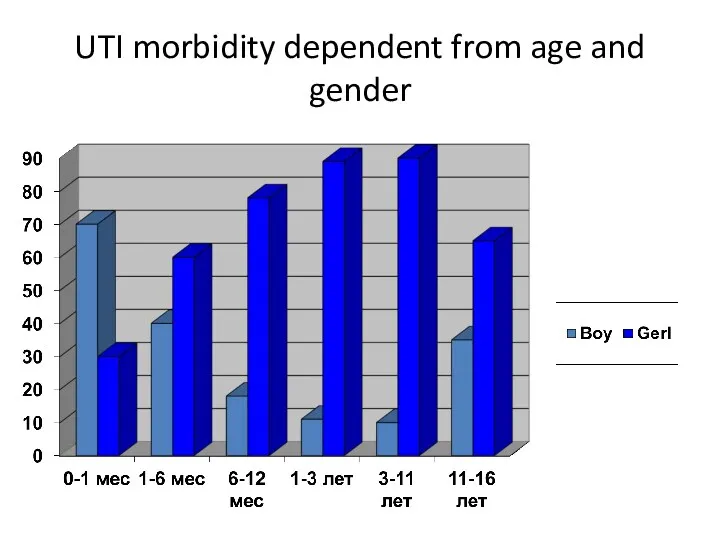
- 9. UTI morbidity dependent from age and gender
- 10. Risk factors of UTI: Pyelonephritis in pregnant women Chronic infectious focuses especially urogenital in mothers Inflammatory
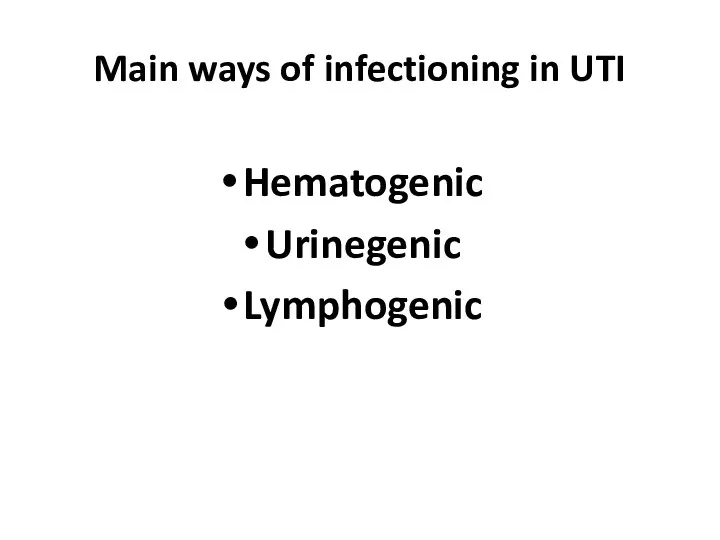
- 11. Main ways of infectioning in UTI Hematogenic Urinegenic Lymphogenic
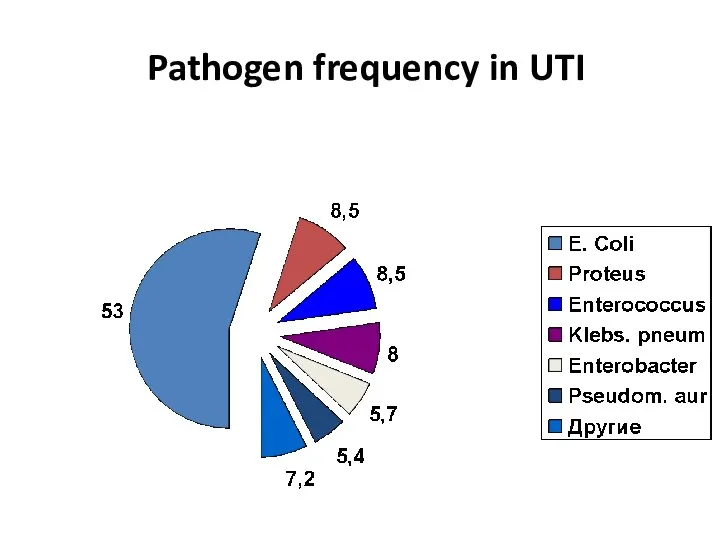
- 12. Pathogen frequency in UTI
- 13. Predisposing factors Vesicoureteric reflux Obstructive uropathy Neurogenic bladder Trauma of lumbosacral region Malnutrition Immunosuppressive therapy
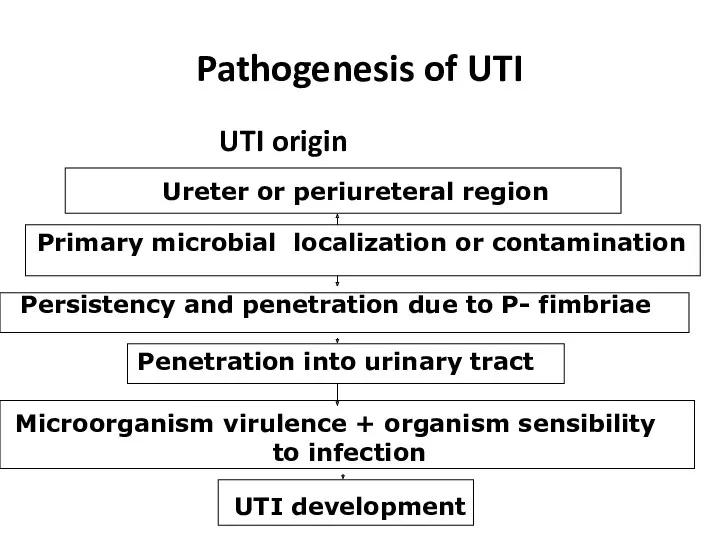
- 14. Pathogenesis of UTI UTI origin Ureter or periureteral region Primary microbial localization or contamination Persistency and
- 15. Pyelonephritis pathogenesis In ascendant way of infectioning due to vesicle-urethral reflux microorganisms enter upper UT epithelium
- 16. Phases of pyelonephritis pathogenesis: Initial, connected with microorganism adhesion Primary alteration and nonspecific answer Specific or
- 17. Main differentiative features of upper and lower UTI clinical signs In upper UTI inflammatory reaction will
- 18. To confirm UTI diagnostic titer of bacteria count in urine is: > 104 bacteria/ml taken as
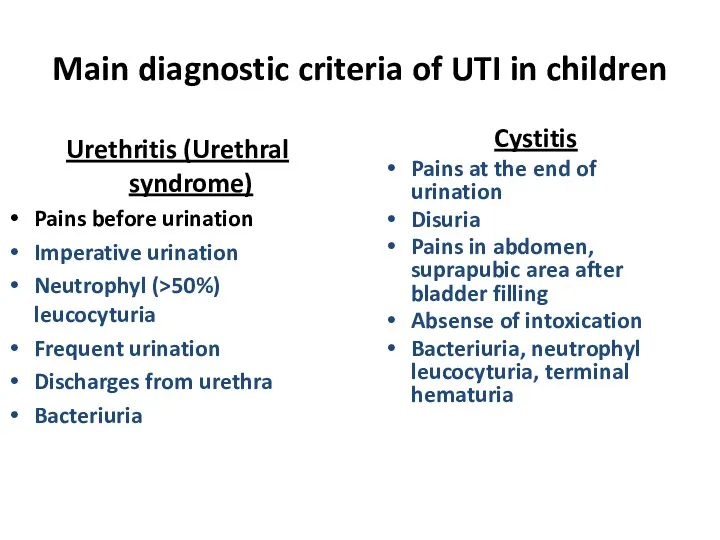
- 19. Main diagnostic criteria of UTI in children Urethritis (Urethral syndrome) Pains before urination Imperative urination Neutrophyl
- 20. Pyelonephritis Intoxicative syndrome (fever >38°С; frequently without visible cause, head ache, flaccidity) Painful syndrome (lumbal pains,
- 21. Pyelonephritis peculiarities in infants and toddlers Fever, flaccidity, irritation Can start with neurotoxicosis or intestine syndrome
- 22. Pyelonephritis peculiarities in schoolchildren and adolescents Fever, head ache, flaccidity, fatigability, shadows around eyes Abdomen pains
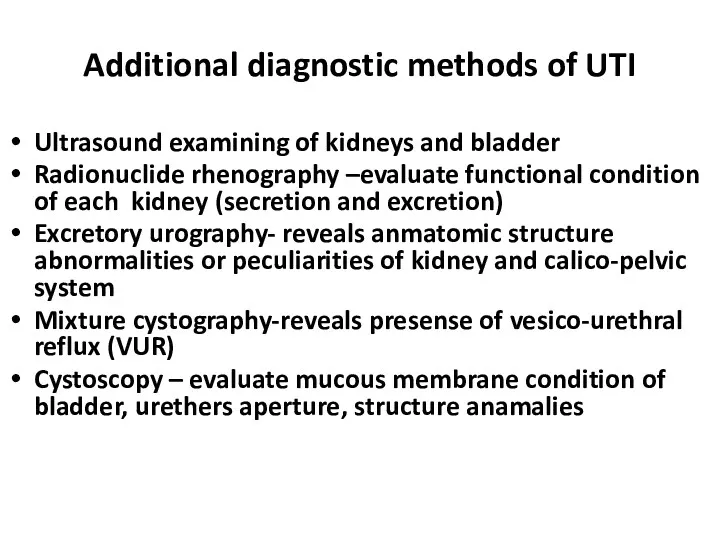
- 23. Additional diagnostic methods of UTI Ultrasound examining of kidneys and bladder Radionuclide rhenography –evaluate functional condition
- 24. UTI treatment Regimen – for period of intoxication is strict bed one Diet–special diet №5 according
- 25. Rational antibiotic treatment Antibiotic choice is performed according to causative bacteria sensibility; Antibiotic choice is performed
- 26. Antimicrobial treatment of urethritis (urethral syndrome) Antibiotics (amoxyclav or zinnat) or may be uroseptics like co-trimxozol,
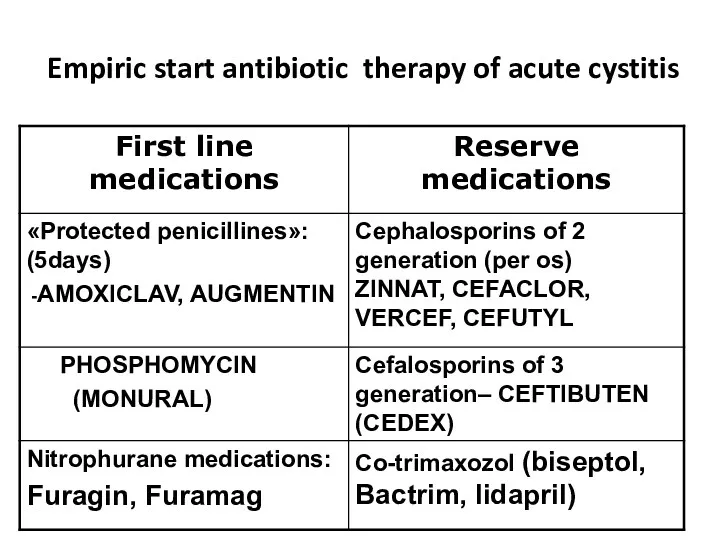
- 27. Empiric start antibiotic therapy of acute cystitis
- 28. «STEP» -therapy of Pyelonephritis Means usage of parenteral antibiotic usage during high inflammatory activity and after
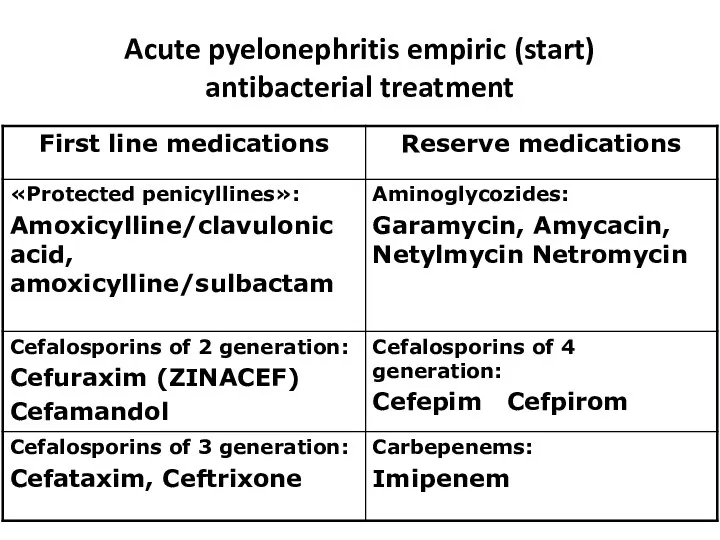
- 29. Acute pyelonephritis empiric (start) antibacterial treatment
- 30. Indications for combined antibacterial therapy in children with pyelonephritis Severe septic course of inflammatory process in
- 31. Antibiotic treatment duration in pyelonephritis Antimicrobial drugs must be used until full eradication of microbial agents
- 32. Antibiotic treatment duration in pyelonephritis If effect of treatment is absent 14 days later or if
- 33. Complications Apostematous nephritis (lots of abscesses in kidney) – is acute septic disease Carbuncle manifests with
- 34. Outpatient care After primary acute pyelonephritis children must get outpatient care for 3 years, in the
- 35. Urine examining must be performed : 2 – 3 weeks later after intercurrent disease When child
- 37. Скачать презентацию





















 Аффективные расстройства. Расстройства воли и влечений
Аффективные расстройства. Расстройства воли и влечений Метапневмовирусная инфекция птиц
Метапневмовирусная инфекция птиц Современные принципы антихеликобактерной терапии
Современные принципы антихеликобактерной терапии МӘМС арқылы денсаулық сақтау мекемесін таңдау
МӘМС арқылы денсаулық сақтау мекемесін таңдау Человек, как объект генетических исследований. Экскурс в историю генетики человека. Методы генетического анализа. (Лекция 10)
Человек, как объект генетических исследований. Экскурс в историю генетики человека. Методы генетического анализа. (Лекция 10) Тіс жарып шыққаннан кейін дамитын тісжегі емес ақаулар
Тіс жарып шыққаннан кейін дамитын тісжегі емес ақаулар Методы исследование уровня здоровья и физического состояния
Методы исследование уровня здоровья и физического состояния Техника транспортной иммобилизации верхней конечности
Техника транспортной иммобилизации верхней конечности Основные инфекционные болезни
Основные инфекционные болезни Принципы купирования острого инфаркта миокарда
Принципы купирования острого инфаркта миокарда Биологически активные добавки
Биологически активные добавки Лекарственные средства, влияющие на сердечно-сосудистую систему. Кардиотонические средства
Лекарственные средства, влияющие на сердечно-сосудистую систему. Кардиотонические средства Рак молочной железы
Рак молочной железы Бронхолитические средства
Бронхолитические средства Гангрены, пролежни, трофические язвы, свищи
Гангрены, пролежни, трофические язвы, свищи Опухоли мочевого пузыря
Опухоли мочевого пузыря Болезни системы кровообращения как медико-социальная проблема
Болезни системы кровообращения как медико-социальная проблема Хроническое заболевание атеросклероз
Хроническое заболевание атеросклероз Экономические, социальные и нравственные последствия, связанные с злоупотреблением психоактивными веществами
Экономические, социальные и нравственные последствия, связанные с злоупотреблением психоактивными веществами Ауру сезімінің физиологиясы
Ауру сезімінің физиологиясы Колоректальный рак
Колоректальный рак Патогенез лейкозів
Патогенез лейкозів Проблемы организации торакальной хирургии в России
Проблемы организации торакальной хирургии в России Кисломолочные продукты
Кисломолочные продукты Пороки развития позвоночника
Пороки развития позвоночника Синдром приобретенного иммунного дефицита (СПИД) и ВИЧ
Синдром приобретенного иммунного дефицита (СПИД) и ВИЧ Методы диагностики
Методы диагностики Кардиотоксичность при лечении онкологических заболеваний
Кардиотоксичность при лечении онкологических заболеваний