Содержание
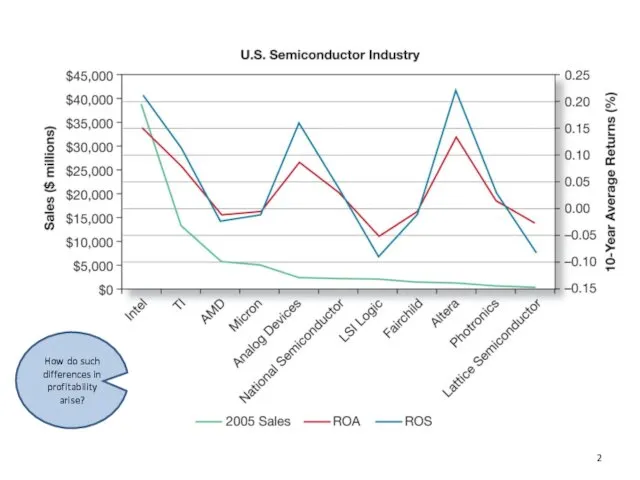
- 2. How do such differences in profitability arise?
- 3. Resource-Based View of the Firm Why some firms outperform others? Endowment of strategic resources that are
- 4. Resource-Based View of the Firm Tangible resources – relatively easy to identify Financial – firm’s cash,
- 5. Resource-Based View of the Firm Intangible resources – embedded in unique routines and practices Human –
- 6. Resource-Based View of the Firm Organizational capabilities – competencies/skills that a firm employs to transform inputs
- 7. QUESTION Gillette combines several technologies to attain unparalleled success in the wet shaving industry. This is
- 8. Resource-Based View of the Firm Two Critical Assumptions of RBV: Resource Heterogeneity: different firms have different
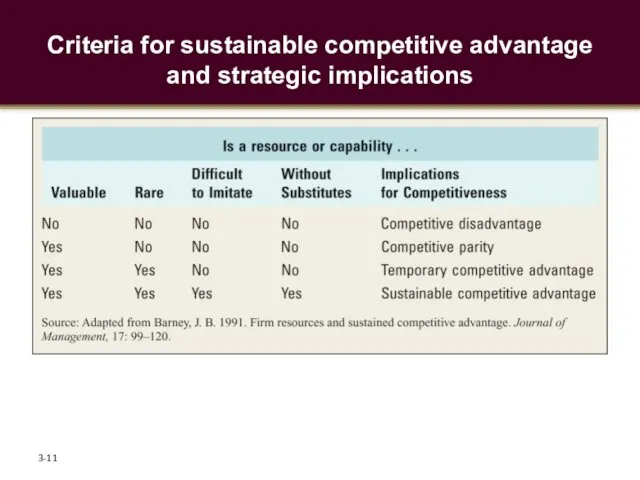
- 9. Firm Resources and Sustainable Competitive Advantages Four Key Attributes of Resources Is the resource valuable? Enable
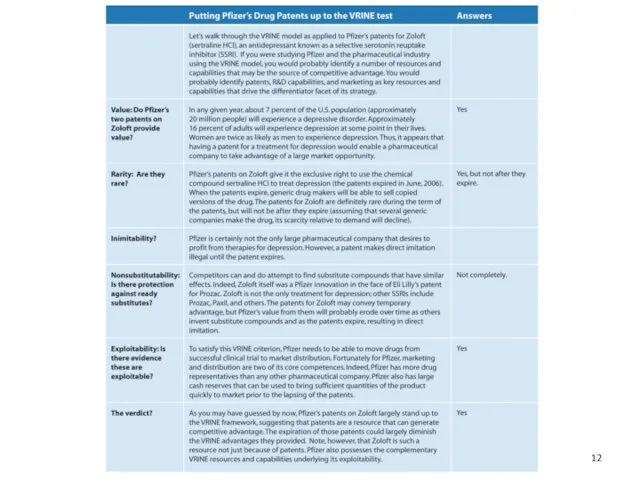
- 10. Firm Resources and Sustainable Competitive Advantages Can the resource be imitated easily? Physical uniqueness (a beautiful
- 11. Criteria for sustainable competitive advantage and strategic implications 3-
- 13. Resources of Manchester United Manchester United is one of the world's most popular sports franchises, and
- 14. Questions According to text, how well did Manchester United play in 2013-14? How has this affected
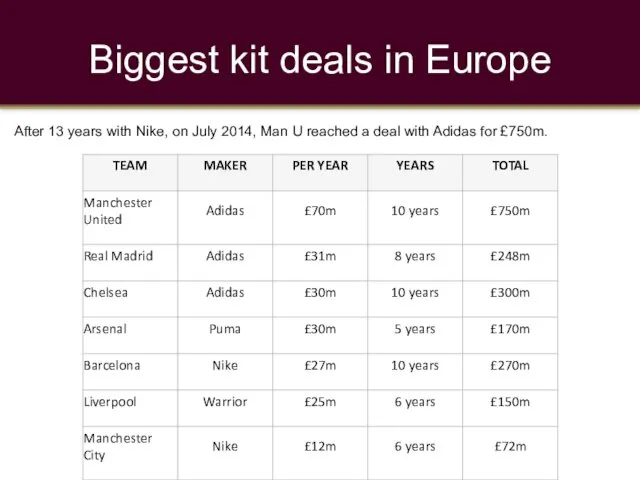
- 15. Biggest kit deals in Europe After 13 years with Nike, on July 2014, Man U reached
- 16. Value-Chain Analysis Value-chain analysis a strategic analysis of an organization that uses value creating activities. View
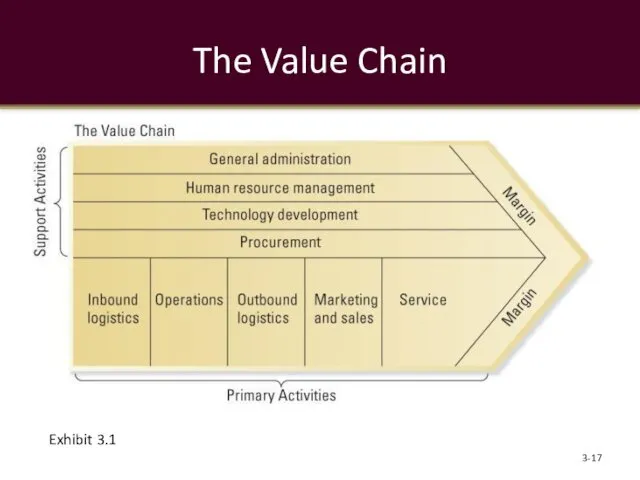
- 17. The Value Chain 3- Exhibit 3.1
- 18. Value-Chain Analysis Primary activities contribute to the physical creation of the product or service, its sale
- 19. Value-Chain Analysis Support activities activities of the value chain that either add value by themselves or
- 20. QUESTION In assessing its primary activities, an airline would examine: A. Employee training programs B. Baggage
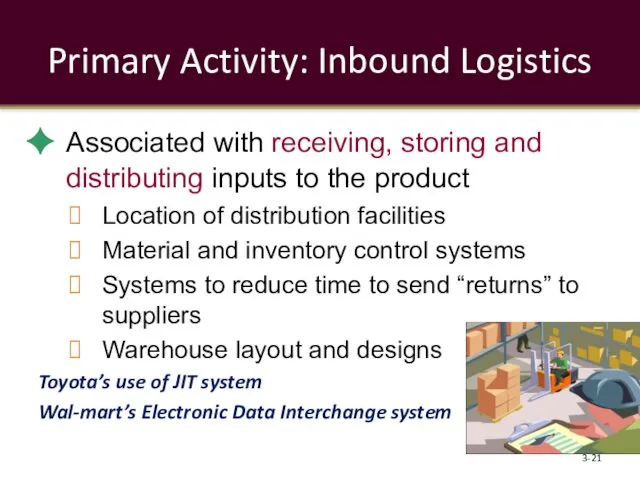
- 21. Primary Activity: Inbound Logistics Associated with receiving, storing and distributing inputs to the product Location of
- 22. Primary Activity: Operations Associated with transforming inputs into the final product form Efficient plant operations Incorporation
- 23. How Does Automation Affect Cost Structure? 3- Harley-Davidson Then and Now
- 24. Primary Activity: Outbound Logistics Associated with collecting, storing, and distributing the product or service to buyers
- 25. Primary Activity: Marketing and Sales Associated with purchases of products and services by end users and
- 26. Primary Activity: Service Associated with providing service to enhance or maintain the value of the product
- 27. Support Activity: Procurement Function of purchasing inputs used in the firm’s value chain Procurement of raw
- 28. Support Activity: Human Resource Management Activities involved in the recruiting, hiring, training, development, and compensation of
- 29. Support Activity: Technology Development Related to a wide range of activities and those embodied in processes
- 30. Support Activity: General Administration Typically supports the entire value chain and not individual activities Ability of
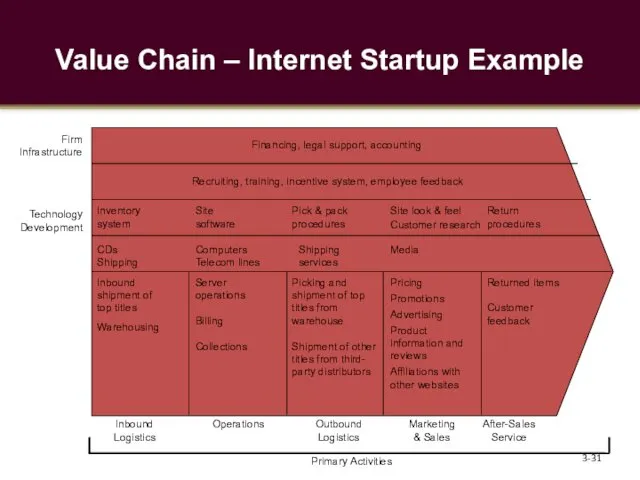
- 31. Value Chain – Internet Startup Example 3- Inbound shipment of top titles Warehousing Server operations Billing
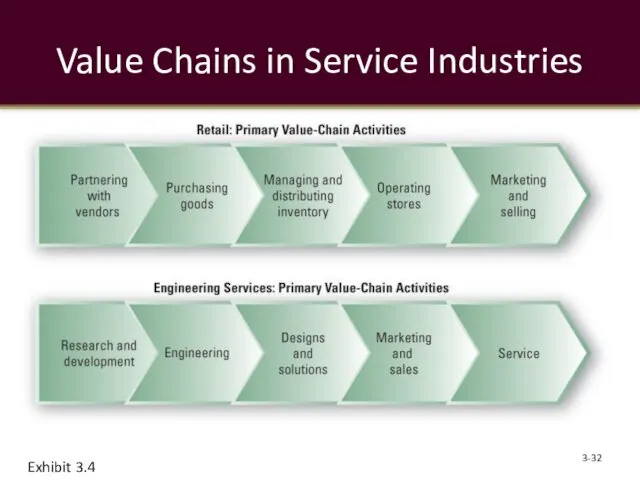
- 32. Value Chains in Service Industries 3- Exhibit 3.4
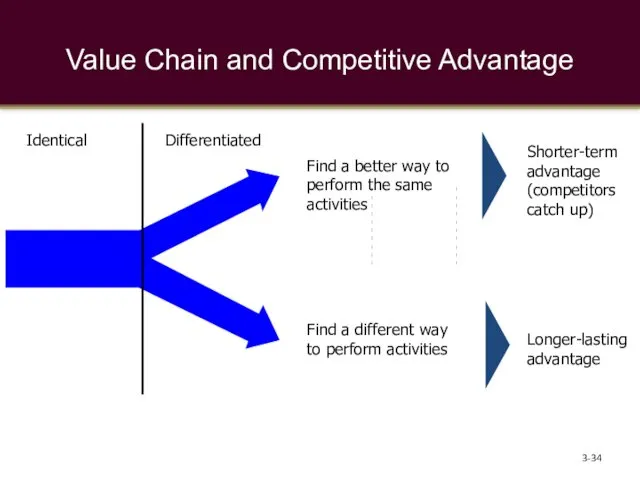
- 33. Value Chain and Competitive Advantage 3-
- 34. Value Chain and Competitive Advantage 3- Identical Differentiated Find a different way to perform activities Find
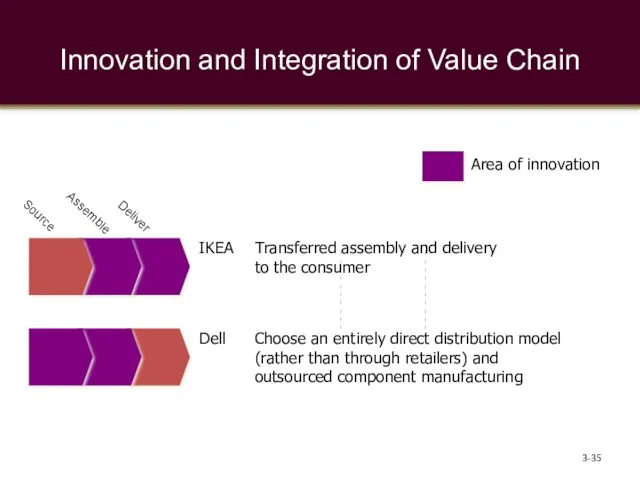
- 35. Innovation and Integration of Value Chain 3- Transferred assembly and delivery to the consumer Choose an
- 36. Key Takeaways 3-
- 37. Evaluating Firm Performance Financial ratio analysis Balance sheet Income statement Historical comparison Comparison with industry norms
- 38. Financial Ratio Analysis Five types of financial ratios Short-term solvency or liquidity Long-term solvency measures Asset
- 40. Скачать презентацию

























 Стратегические и тактические планы в системе менеджмента
Стратегические и тактические планы в системе менеджмента Организация инфраструктуры производства
Организация инфраструктуры производства Менеджмент качества физкультурно-оздоровительных и спортивных услуг: методы определения качества услуг
Менеджмент качества физкультурно-оздоровительных и спортивных услуг: методы определения качества услуг Мотивационное управление. (Тема 14)
Мотивационное управление. (Тема 14) Поняття інноваційного менеджменту
Поняття інноваційного менеджменту Менеджмент. Ускоренная программа обучения - специально для выпускников СПО
Менеджмент. Ускоренная программа обучения - специально для выпускников СПО Организация молодежных проектов
Организация молодежных проектов Автоматизация и обеспечение безопасности основного бизнес-процесса в ООО Дежурная аптека
Автоматизация и обеспечение безопасности основного бизнес-процесса в ООО Дежурная аптека Общая характеристика управления организацией
Общая характеристика управления организацией Сущность менеджмента
Сущность менеджмента Современные теории мотивации
Современные теории мотивации История развития и возникновения стратегического управления
История развития и возникновения стратегического управления Анализ целевой аудитории
Анализ целевой аудитории Управління інноваційною діяльністю
Управління інноваційною діяльністю Совершенствование структуры управления водопроводно-канализационным хозяйством и обеспечение реализации программы чистая вода
Совершенствование структуры управления водопроводно-канализационным хозяйством и обеспечение реализации программы чистая вода Самооценка. Методика самооценки по критериям функциональной модели оценки менеджмента
Самооценка. Методика самооценки по критериям функциональной модели оценки менеджмента Классификация уровней менеджеров. Функции, выполняемые менеджерами
Классификация уровней менеджеров. Функции, выполняемые менеджерами SWOT-анализ
SWOT-анализ Руководство, как функция менеджмента в спорте. (Лекция 3)
Руководство, как функция менеджмента в спорте. (Лекция 3) Теория X и Y МакГрегора
Теория X и Y МакГрегора Business Etiquette in China
Business Etiquette in China Управление временем. Тайм-менеджмент. Основы
Управление временем. Тайм-менеджмент. Основы Инновационный менеджмент. Инновации и инновационная деятельность
Инновационный менеджмент. Инновации и инновационная деятельность Риск и неопределенность как важнейшее условие современного государственного управления
Риск и неопределенность как важнейшее условие современного государственного управления Шаг 2: Анализ структуры компании. Взаимосвязь бизнес – процессов и показателей
Шаг 2: Анализ структуры компании. Взаимосвязь бизнес – процессов и показателей Методы анализа. Содержание методов. (Тема 3)
Методы анализа. Содержание методов. (Тема 3) Разработка программы повышения лояльности линейных руководителей
Разработка программы повышения лояльности линейных руководителей Качество. Управление качеством
Качество. Управление качеством