Содержание
- 2. What is a Strategy? Examples of Corporate Strategy in 2009 GM files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy
- 3. Tasks Involved in Strategic Management Defining business and stating a mission Setting measurable objectives Crafting a
- 4. Developing a Mission & Objectives An organization’s Mission Reflects management’s vision of what the organization seeks
- 5. Examples of Types of Objectives Financial Increase earnings growth from 10 to 15% per year Boost
- 6. What Does a Strategy Include? How to satisfy customers How to grow the business Organic growth
- 7. What is a Strategic Plan A strategic plan maps Where the organization is headed Short and
- 8. Implementing Strategy Implementing a strategy involves Creating fits between the way things are done and what
- 9. Evaluating Performance The tasks of strategic management are not one-time only exercises because Times and conditions
- 10. A Situation Analysis A situation analysis identifies strategic options and opportunities A situation analysis involves External
- 11. SWOT Internal Factors Strengths Weaknesses E x F Opportunities t a e c r t Threats
- 12. Five Forces Model Rivalry among sellers Substitute Products Buyers Potential Entrants Suppliers Kelley Summer 2009 GM
- 13. Analysis of Competitive Forces The analysis is designed to identify the main sources of competitive forces
- 14. Environmental Scanning A way to monitor and interpret social, political, economic, ecological and technological events in
- 15. Assessing Competitive Positions: Strategic Groups A Strategic Group consists of those rival firms with similar competitive
- 16. Competitor Analysis An organization’s strategy is affected by Current strategies of competitors Actions competitors are likely
- 17. Key Industry Success Factors Key success factors spell the difference between Profit and loss Competitive success
- 18. Competitive Strategy Kelley Summer 2009 GM 105 Strategic Management
- 19. Competitive Strategy A competitive strategy consists of moves to Attract customers Withstand competitive pressures Strengthen an
- 20. Overall Low-Cost Leadership Strategy Strive to be the overall low-cost provider in an industry How to
- 21. Overall Low-Cost Leadership Strategy Kelley Summer 2009 GM 105 Strategic Management
- 22. When Does an Overall Low-Cost Strategy Work the Best When price competition is a dominant competitive
- 23. When Doesn’t a Overall Low-Cost Strategy Work When technological breakthroughs open cost reductions for competitors, negating
- 24. Broad Differentiation Strategies Striving to build customer loyalty by differentiating an organization’s products from competitors’ products
- 25. Broad Differentiation Strategies Where to look for differentiation opportunities Supply chain Research and development Production activities
- 26. Pitfalls of a Broad Differentiation Strategy Trying to differentiate on an unimportant product feature that doesn’t
- 27. Best-Cost Provider Strategy Striving to give customers more value for the money by combining an emphasis
- 28. Advantages of Best-Cost Provider Strategy Competitive advantage comes from matching close competitors on key product attributes
- 29. Focus Strategies Focus strategy based on low-cost Concentrate on a narrow customer segment beating the competition
- 30. What Makes a Niche Attractive? Large enough to be profitable Good growth potential Not critical to
- 31. Strengths and Risks of Focus Strategies Strengths Competitors don’t have the motivation to meet specialized needs
- 32. From Single-Business to Diversification Stage 1 - Single-business serves a local or regional market Stage 2
- 33. The Growth Matrix Products Present New M a Present r k e New t s Market
- 34. Market Penetration Use when markets are not saturated with an organization’s products Use when the usage
- 35. Product Development Use when the organization has successful products that are in the maturity stage of
- 36. Market Development Use when channels of distribution are available, reliable and inexpensive Use when the organization
- 37. Diversification Use when entering new industries Acquire an existing company in the target industry Start a
- 38. Start a New Company Use when ample time exists to enter by starting from scratch Use
- 39. Joint Ventures Use when it is too risky to go it alone Use when pooling competencies
- 40. Linking the Budget to Strategy Implementation of a strategy requires Enough resources to support the strategy
- 41. Implementing Best Practices & Continuous Improvement Implementing a strategy involves adopting “best practices” Best practices means:
- 42. Instituting Best Practices & Continuous Improvement Quality improvement programs are linked to Defect-free manufacture Superior product
- 43. Formal Reporting of Strategy-Critical Information Accurate & timely information is essential to guide action Prompt feedback
- 44. Formal Reporting of Strategy-Critical Information Information systems should cover Customer data Operations data Employee data Financial
- 46. Скачать презентацию
 Делопроизводство. Деловое письмо
Делопроизводство. Деловое письмо Сущность менеджмента
Сущность менеджмента Мозговой штурм (25)
Мозговой штурм (25) Кадрларды таңдау
Кадрларды таңдау Управление финансовыми рисками. Основы теории риск-менеджмента
Управление финансовыми рисками. Основы теории риск-менеджмента Планування розвитку управлінських інформаційних систем. Управління інформаційними системами в організації
Планування розвитку управлінських інформаційних систем. Управління інформаційними системами в організації Сучасні підходи до оцінки ризиків інформаційних технологій. Управління ризиками ІТ
Сучасні підходи до оцінки ризиків інформаційних технологій. Управління ризиками ІТ Жеке құрам бойынша ереже
Жеке құрам бойынша ереже Проектирование операционной системы предприятия
Проектирование операционной системы предприятия Система государственного управления охраной труда в РФ
Система государственного управления охраной труда в РФ Складская логистика
Складская логистика Модели менеджмента
Модели менеджмента Основы профессиональной этики
Основы профессиональной этики Формирование дел организации. (Тема 2)
Формирование дел организации. (Тема 2) Основные этапы отбора персонала
Основные этапы отбора персонала Карьерное консультирование в контексте организации
Карьерное консультирование в контексте организации Теоретические основы системы корпоративного управления
Теоретические основы системы корпоративного управления Кадровый резерв
Кадровый резерв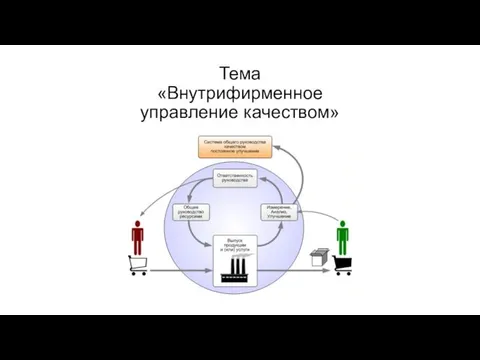 Внутрифирменное управление качеством
Внутрифирменное управление качеством Организационная структура таможенных органов
Организационная структура таможенных органов Планирование численности персонала. (Тема 5)
Планирование численности персонала. (Тема 5) Подходы в менеджменте. Система управления. Закономерности и принципы управления
Подходы в менеджменте. Система управления. Закономерности и принципы управления SNW-талдау
SNW-талдау Бизнес-модель или почему у вас должны купить?
Бизнес-модель или почему у вас должны купить?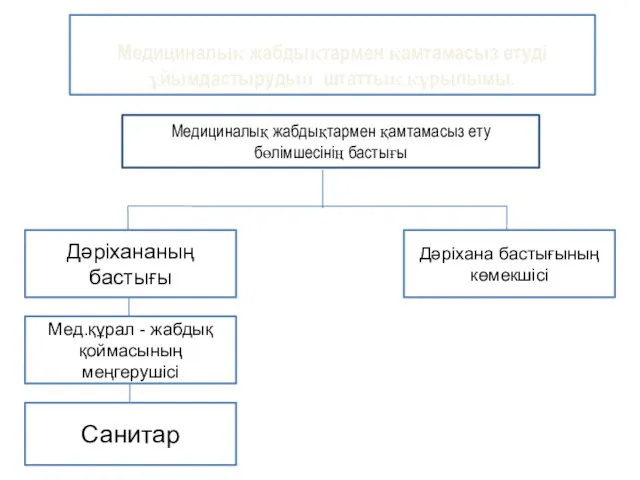 Медициналық жабдықтармен қамтамасыз ету бөлімшесінің бастығы
Медициналық жабдықтармен қамтамасыз ету бөлімшесінің бастығы Квалиметрия как наука и ее роль в управлении качеством
Квалиметрия как наука и ее роль в управлении качеством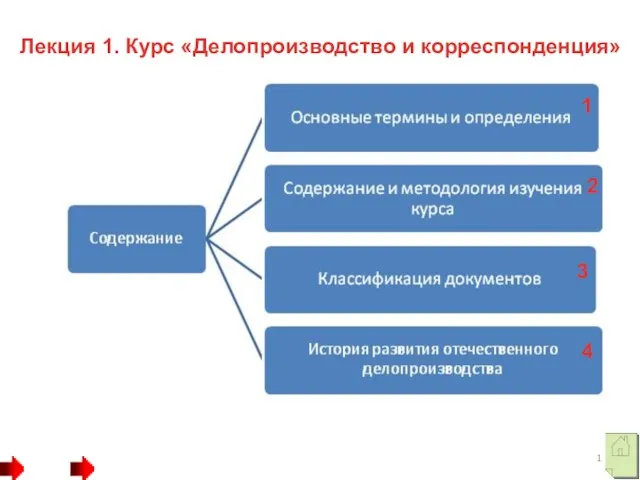 Делопроизводство и корреспонденция
Делопроизводство и корреспонденция Основы работы с MS Project
Основы работы с MS Project