Содержание
- 2. Social Contract Theory By SOCIAL CONTRACT – people within a given area agreed to give up
- 3. Force Theory
- 4. Force Theory State was born of force One person/small group claimed control over an area and
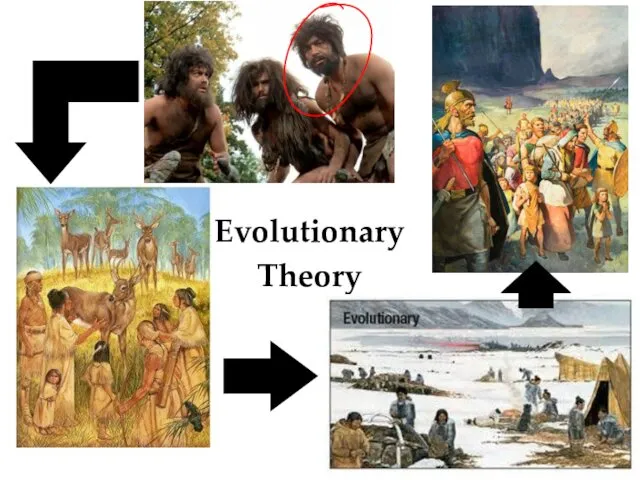
- 5. Evolutionary Theory
- 6. Evolutionary Theory State developed NATURALLY out of the early family Primitive family (one person was the
- 7. Divine Right Theory
- 8. Divine Right Theory From 15th – 18th century, this was widely accepted in much of Western
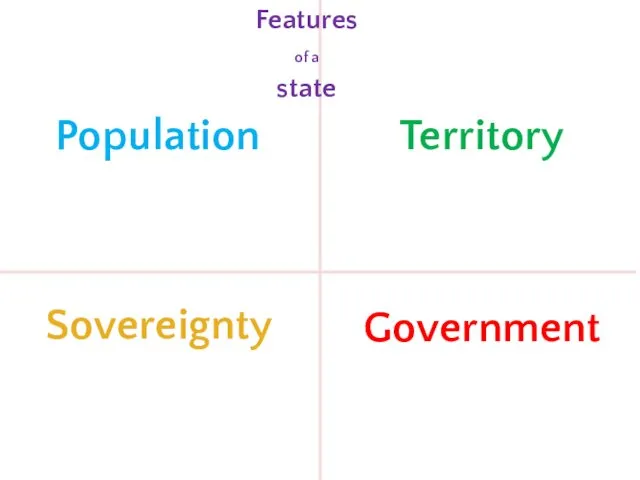
- 9. Features of a state
- 10. Population Territory Sovereignty Government Features of a state
- 11. When we are talking about the state… Definition: is a body of people, living in a
- 12. The state –Defined by 4 Things (1) Population Definition: the group of people who are the
- 13. The state –Defined by 4 Things (1) Population The population of a state also has a
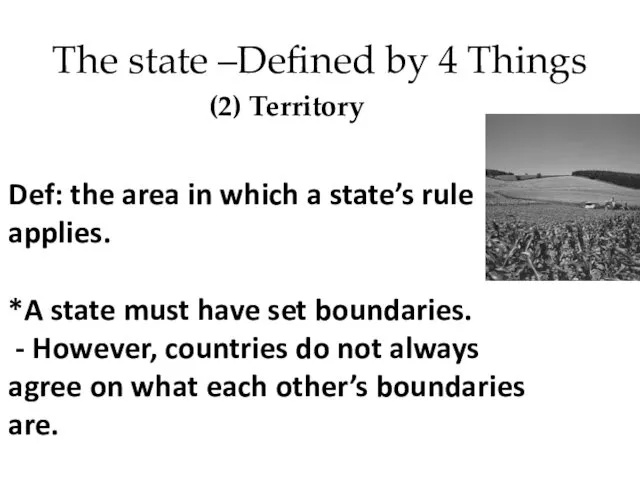
- 14. The state –Defined by 4 Things (2) Territory Def: the area in which a state’s rule
- 15. The state –Defined by 4 Things (2) Territory **Boundaries can change over time. - Sometimes they
- 16. The state –Defined by 4 Things (3) Sovereignty Def: the ability to rule absolutely within a
- 17. The state –Defined by 4 Things (3) Sovereignty cont. In our world today, the world’s states
- 18. The state –Defined by 4 Things (4) Government Def: the organization inside a state that controls
- 19. Civil society a ‘political community’, a society governed by law, under the authority of a state.
- 20. Is THAT a STATE? Is the Republic of Kazakhstan just one big state? Does it have
- 21. THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN? A state can’t have less than 30,000 people.
- 22. Monaco has only 27,000 people! THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 23. The boundaries of a territory can change. THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 24. Can you name the three ways that boundaries change? THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN? War Negotiation
- 25. Sovereignty means that you have to check with someone above you. THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 26. Just the opposite! Sovereignty means there is NO ONE above you! THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
- 27. Government only exists to keep order and provide security. THUMBS UP or THUMBS DOWN?
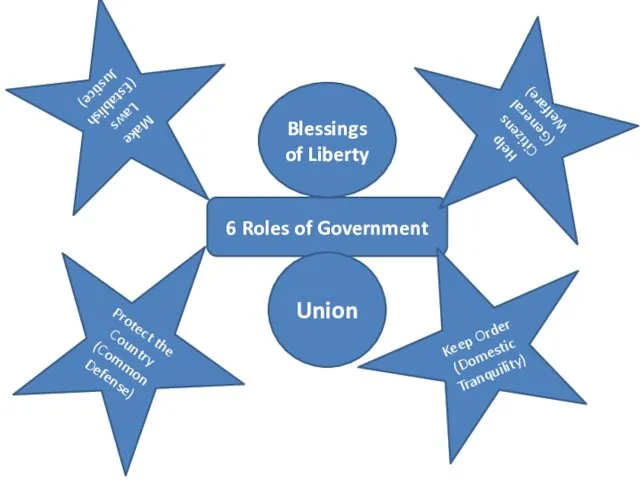
- 28. 6 Roles of Government Make Laws (Establish Justice) Protect the Country (Common Defense) Keep Order (Domestic
- 29. The 50 states that make up the USA are not considered independent “states.” THUMBS UP or
- 31. Скачать презентацию
























 Общество как сложная динамичная система
Общество как сложная динамичная система Статусы и социальные роли личности
Статусы и социальные роли личности Модель оцінки потреб дитини та її сім’ї
Модель оцінки потреб дитини та її сім’ї Родовые понятия и методологические основания социологии Эмиля Дюркгейма в цитатах
Родовые понятия и методологические основания социологии Эмиля Дюркгейма в цитатах Моя семья
Моя семья конспект урока обществознания в 10 классе Политические режимы
конспект урока обществознания в 10 классе Политические режимы Социальная структура общества. (8 класс)
Социальная структура общества. (8 класс) Источники права.
Источники права. Семейные ценности и традиции. 5 класс
Семейные ценности и традиции. 5 класс Федеральные проекты, входящие в национальный проект до 2024г
Федеральные проекты, входящие в национальный проект до 2024г Молодежный парламент при Земском Собрании Нытвенского муниципального района Пермского края
Молодежный парламент при Земском Собрании Нытвенского муниципального района Пермского края Негізгі ұғымдар және статистиканың категориялары
Негізгі ұғымдар және статистиканың категориялары Социальная реклама Дорога не прощает ошибок
Социальная реклама Дорога не прощает ошибок Структура социальной власти в малой группе. Типология стилей руководства
Структура социальной власти в малой группе. Типология стилей руководства познай самого себя
познай самого себя Презентация Право в понятиях и определениях для уч-ся 9 классов
Презентация Право в понятиях и определениях для уч-ся 9 классов Развитие территориального общественного самоуправления в Архангельской области
Развитие территориального общественного самоуправления в Архангельской области Право на труд. Трудовые правоотношения
Право на труд. Трудовые правоотношения Права и свободы человека и гражданина РФ (презентация)
Права и свободы человека и гражданина РФ (презентация) Роль государства в экономике.
Роль государства в экономике. Политические партии в политической системе общества
Политические партии в политической системе общества Близкие соседи
Близкие соседи Социальная работа как деятельность
Социальная работа как деятельность Независимый благотворительный культурный фонд Творческий союз поддержки творческой молодежи и ветеранов, мастеров искусств
Независимый благотворительный культурный фонд Творческий союз поддержки творческой молодежи и ветеранов, мастеров искусств Проект Помощь детям
Проект Помощь детям Целевая аудитория ВЖИК
Целевая аудитория ВЖИК Технология социальной работы с малообеспеченной семьей
Технология социальной работы с малообеспеченной семьей Досуг и отдых
Досуг и отдых