Содержание
- 2. Introduction (09.11) Basic concepts (09.18) Fire and explosion (09.25) Explosion prevention, sources of ignition (10.02) Overpressure
- 3. Budapesti Műszaki és Gazdaságtudományi Egyetem Szerves Kémia és Technológia Tanszék Industrial Safety Webpage: http://oct.bme.hu/safety name: safety
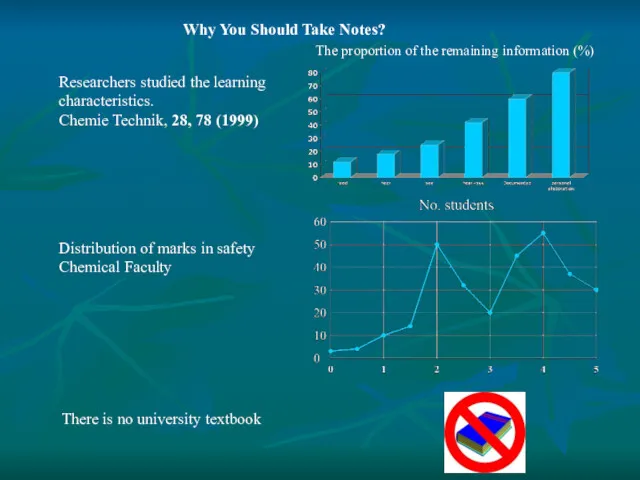
- 4. Why You Should Take Notes? Researchers studied the learning characteristics. Chemie Technik, 28, 78 (1999) Distribution
- 5. Basic concepts SAFETY ENGINEERING safety (safe work at workspace) security (asset protection, protection against sabotage) 1.
- 6. Basic concepts 2. HEALTH AT WORK PREVENTION OF OCCUPATIONAL HARM (DISEASE) Characteristics: Sustained, regular effect (years,
- 7. Basic concepts OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH (OSH) – Organized activity aimed at ensuring the physical integrity
- 8. The burning down of a cold storage house in Zalaegerszeg, Hungary (2004) Incident ? broad economic
- 9. Why dangerous the chemical plant? Chemical plant hazard – distribution of accidents Transportation, traffic 45 -
- 10. A HIERARCHY OF PROTECTION Organizational measures - prohibitions, regulations - education Personal protective equipment usage depends
- 11. A HIERARCHY OF PROTECTION Safe technology, preventive protection –Dangerous technologies are taken to abroad - Changing
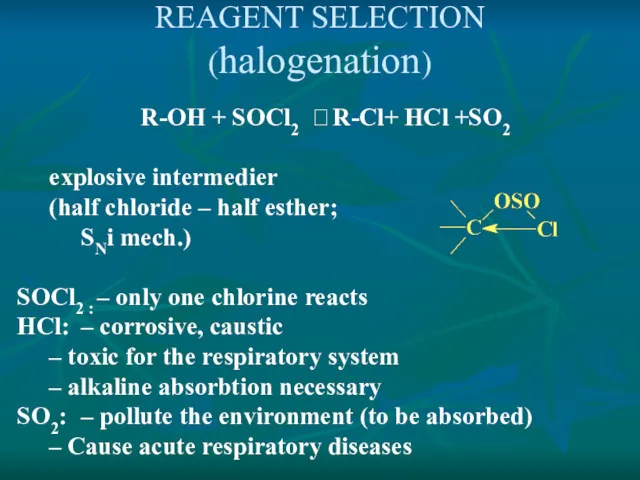
- 12. REAGENT SELECTION (halogenation) R-OH + SOCl2 ? R-Cl+ HCl +SO2 explosive intermedier (half chloride – half
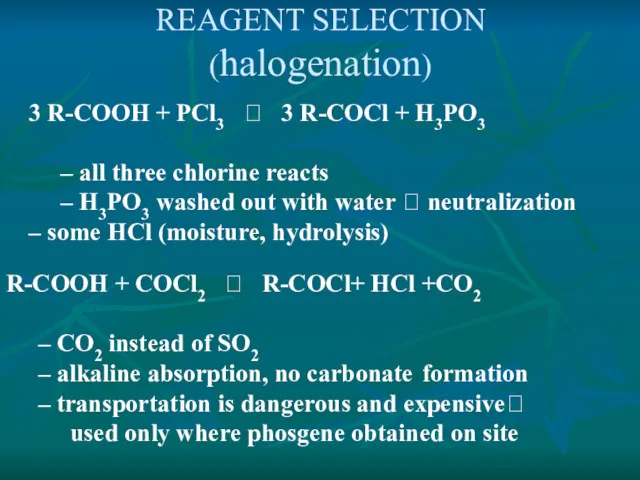
- 13. REAGENT SELECTION (halogenation) 3 R-COOH + PCl3 ? 3 R-COCl + H3PO3 – all three chlorine
- 14. REAGENT SELECTION (Alkylation of amines) R-NH2 + R’Br ? R-NH-R’+ HBr R’Br has vesicant effect HBr
- 15. Film reactor instead of tank reactor: - well-cooled, well-stirred - small amount of material, few kilograms
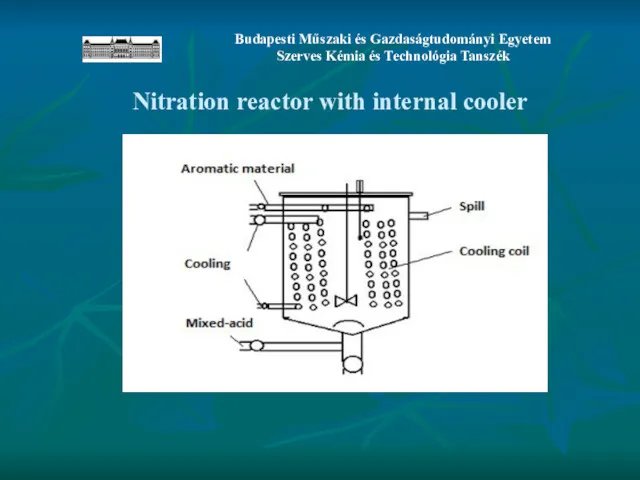
- 16. Nitration reactor with internal cooler
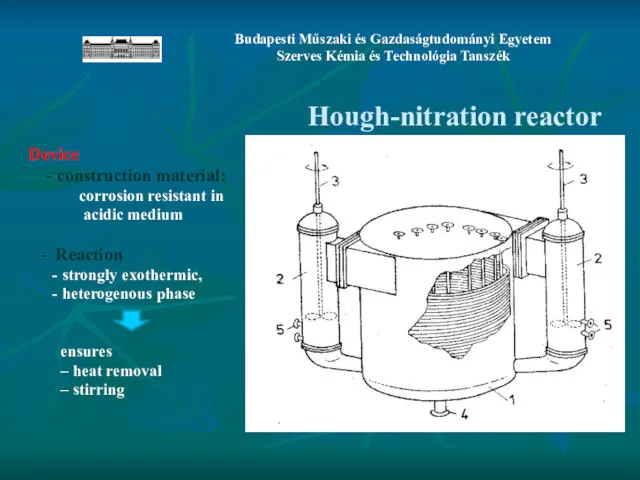
- 17. Hough-nitration reactor Device - construction material: corrosion resistant in acidic medium - Reaction - strongly exothermic,
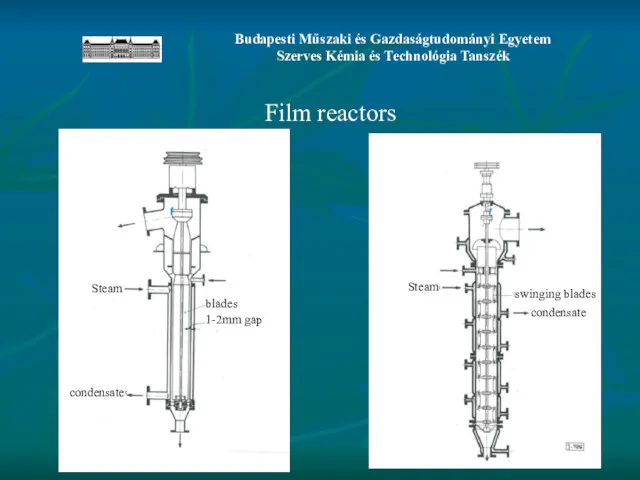
- 18. Film reactors Steam Steam condensate condensate swinging blades blades 1-2mm gap
- 19. UNIT REPLACEMENT(nitration) Aim of nitration in the practice: nitration fully complete economic issues (the nitric acid
- 21. Скачать презентацию












 Своя игра. Вред курения, алкоголя, наркотиков
Своя игра. Вред курения, алкоголя, наркотиков Жұмыс орнының метеорологиялық жағдайы
Жұмыс орнының метеорологиялық жағдайы Правила дорожного движения для велосипедистов
Правила дорожного движения для велосипедистов Памятка о безопасности при лесных пожарах
Памятка о безопасности при лесных пожарах Теледидар бейнелерін алу қағидасы
Теледидар бейнелерін алу қағидасы Безопасное лето
Безопасное лето Природные опасности
Природные опасности Пожары в жилых и общественных зданиях, их причины и последствия
Пожары в жилых и общественных зданиях, их причины и последствия Рациональное питание. Гигиена питания
Рациональное питание. Гигиена питания Тактичні можливості пожежно-рятувальних підрозділів при подачі води перекачуванням
Тактичні можливості пожежно-рятувальних підрозділів при подачі води перекачуванням Жол қозғалысына қатысушылардың міндеттері
Жол қозғалысына қатысушылардың міндеттері Разведение костра
Разведение костра Мобильный телефон - наш враг
Мобильный телефон - наш враг Светофор наш друг и помощник
Светофор наш друг и помощник Личная гигиена в процессе занятий физическими упражнениями
Личная гигиена в процессе занятий физическими упражнениями Классификация ЧС метеорологического характера
Классификация ЧС метеорологического характера Тест для учащихся начальной школы по теме Безопасность Интернет
Тест для учащихся начальной школы по теме Безопасность Интернет Обеспечение пожарной безопасности производственных и бытовых объектов
Обеспечение пожарной безопасности производственных и бытовых объектов Противопожарный инструктаж и пожарно-технический минимум
Противопожарный инструктаж и пожарно-технический минимум Презентация по ОБЖ для учащихся 7-х классов Анатомо-физиологические особенности человека в подростковом возрасте
Презентация по ОБЖ для учащихся 7-х классов Анатомо-физиологические особенности человека в подростковом возрасте Басты байлық - денсаулық
Басты байлық - денсаулық Вулканы, извержения вулканов, расположение вулканов на Земле. (7 класс)
Вулканы, извержения вулканов, расположение вулканов на Земле. (7 класс) Організація охорони праці на підприємстві. Тема 4
Організація охорони праці на підприємстві. Тема 4 Специальная обработка
Специальная обработка Санитарно-эпидемиологические требования к перевозке железнодорожным транспортом организованных групп детей
Санитарно-эпидемиологические требования к перевозке железнодорожным транспортом организованных групп детей Действия работников организаций при пожаре
Действия работников организаций при пожаре Важность гигиены
Важность гигиены Безопасное лето. Памятка на летние каникулы
Безопасное лето. Памятка на летние каникулы