Содержание
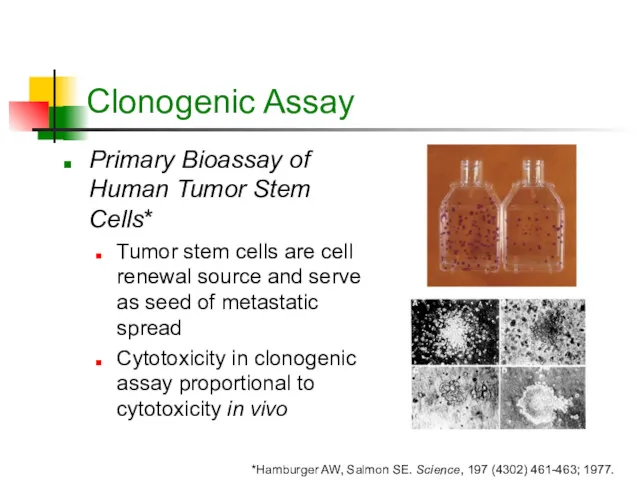
- 2. Clonogenic Assay Primary Bioassay of Human Tumor Stem Cells* Tumor stem cells are cell renewal source
- 3. Tritiated Thymidine Incorporation 3H-TdR measures cells in S-phase Quantifies cell number as cpm
- 4. Historical in vitro Assays Clonogenic Assay Labor intensive Not readily amenable to high throughput 3H-TdR Limitations
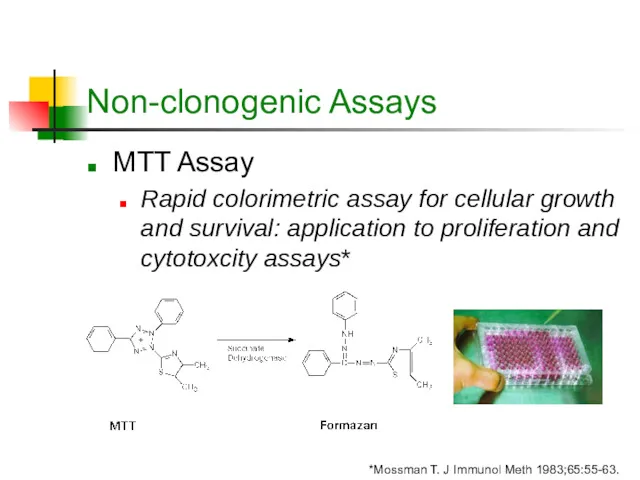
- 5. Non-clonogenic Assays MTT Assay Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and
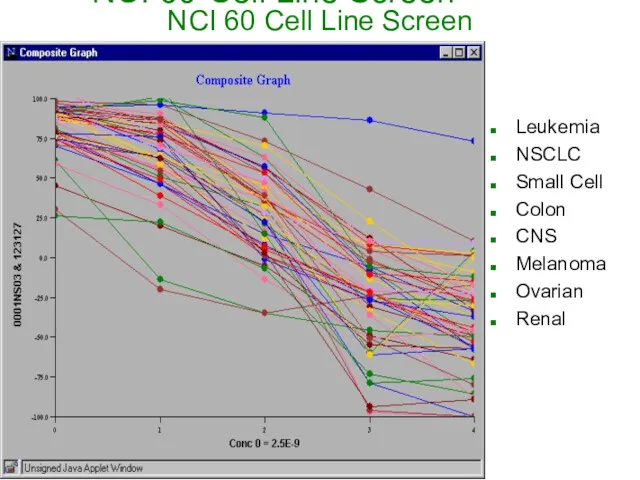
- 6. NCI 60-Cell Line Screen Leukemia NSCLC Small Cell Colon CNS Melanoma Ovarian Renal NCI 60 Cell
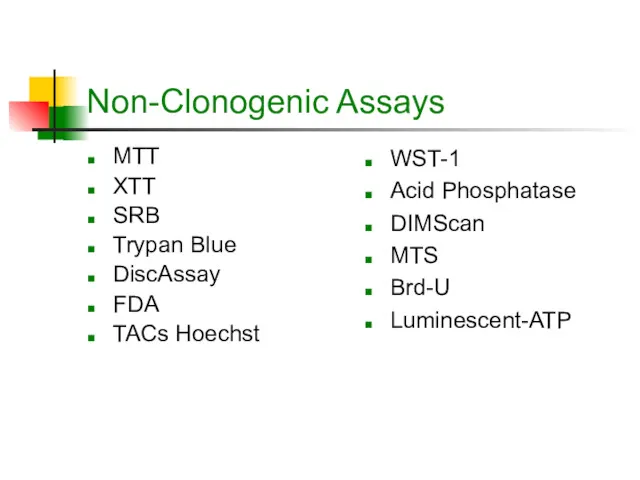
- 7. Non-Clonogenic Assays MTT XTT SRB Trypan Blue DiscAssay FDA TACs Hoechst WST-1 Acid Phosphatase DIMScan MTS
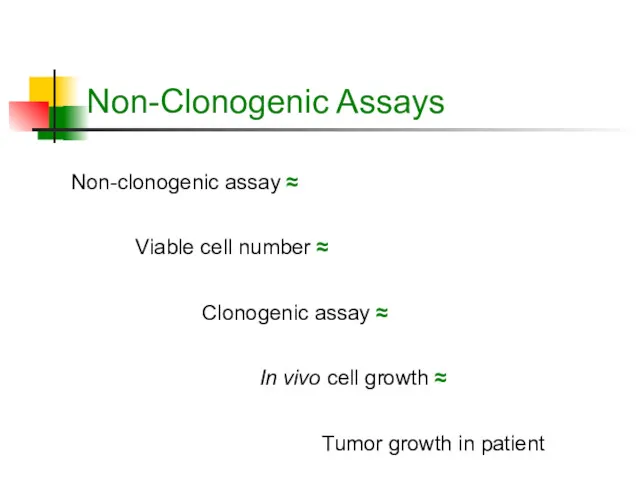
- 8. Non-Clonogenic Assays Non-clonogenic assay ≈ Clonogenic assay ≈ Viable cell number ≈ In vivo cell growth
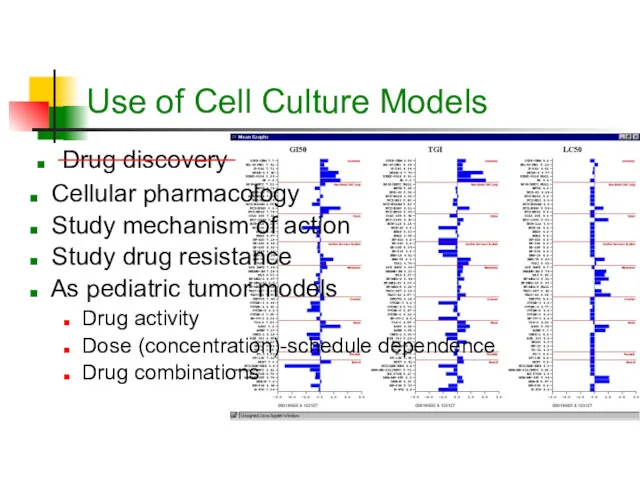
- 9. Use of Cell Culture Models Drug discovery Cellular pharmacology Study mechanism of action Study drug resistance
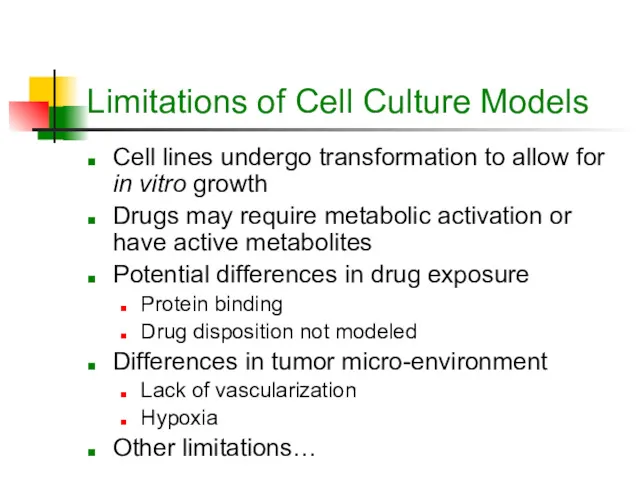
- 10. Limitations of Cell Culture Models Cell lines undergo transformation to allow for in vitro growth Drugs
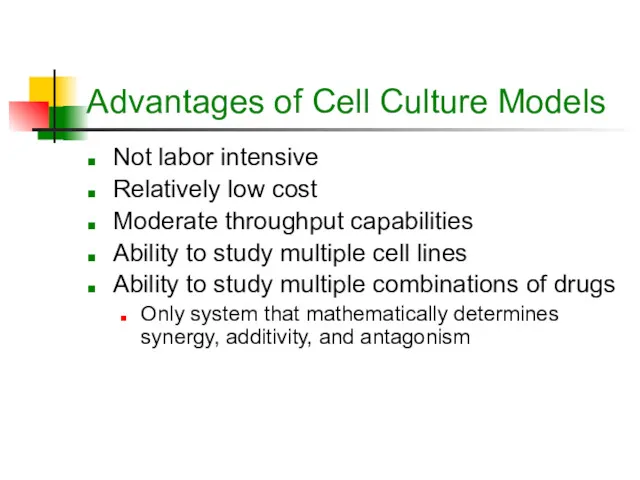
- 11. Advantages of Cell Culture Models Not labor intensive Relatively low cost Moderate throughput capabilities Ability to
- 12. Example: Determination of Synergy Problems with the “addition” method Drug A 25% cell kill Drug B
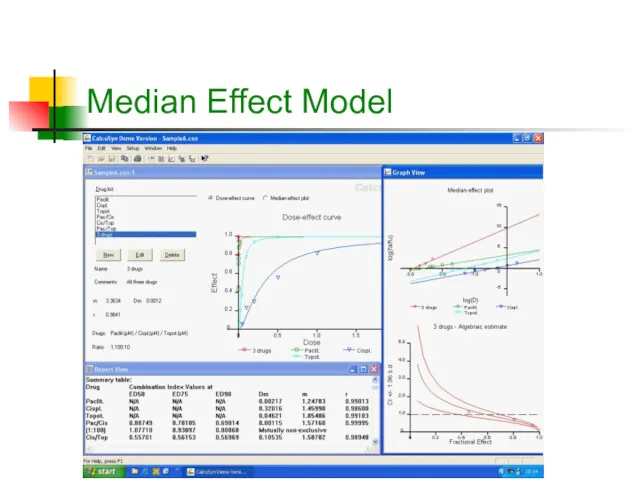
- 13. Median Effect Model
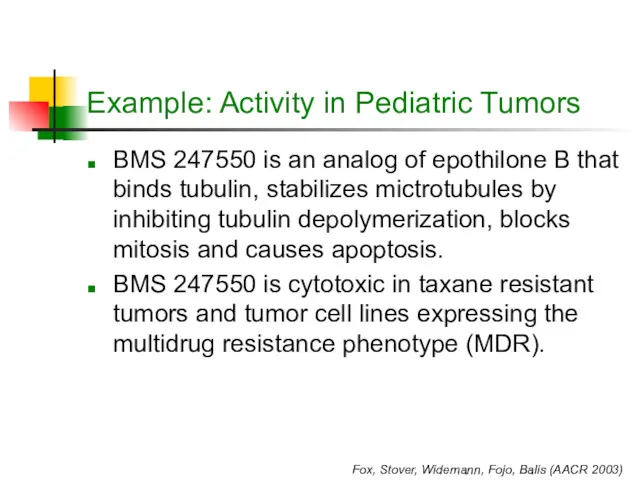
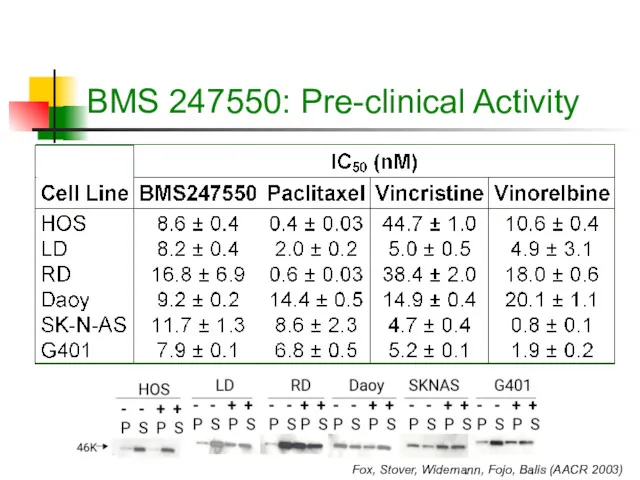
- 14. Example: Activity in Pediatric Tumors BMS 247550 is an analog of epothilone B that binds tubulin,
- 15. BMS 247550: Pre-clinical Activity Fox, Stover, Widemann, Fojo, Balis (AACR 2003)
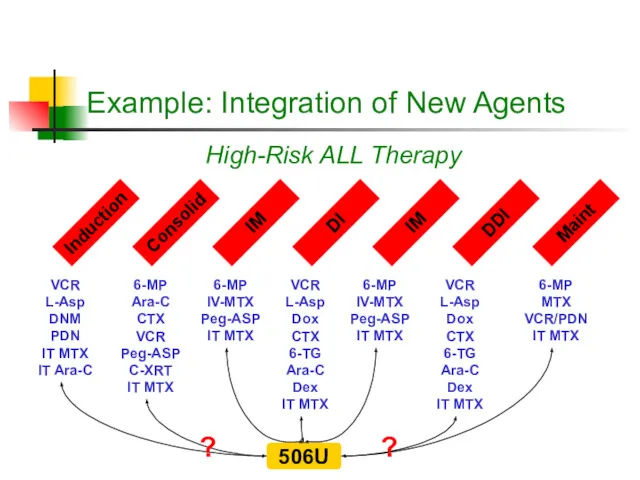
- 16. Example: Integration of New Agents
- 17. Asparaginase + 506U Nelarabine --> Asn [-] Asn [-] --> Nelarabine % Survival Jayaprakash, Adamson, Lampkin,
- 18. Perspectives on Cell Culture Models In vitro models are a cost efficient method to search for
- 20. Скачать презентацию

![Asparaginase + 506U Nelarabine --> Asn [-] Asn [-] -->](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/147698/slide-16.jpg)

 КОСМОС Интерактивная игра
КОСМОС Интерактивная игра Портрет современного педагога
Портрет современного педагога Организация педагогического процесса по дополнительному образованию декоративно-прикладного творчества . Кружок Флористика
Организация педагогического процесса по дополнительному образованию декоративно-прикладного творчества . Кружок Флористика Теоретические и методические основы социально-коммуникативного развития дошкольников
Теоретические и методические основы социально-коммуникативного развития дошкольников Профилактика суицида среди подростков
Профилактика суицида среди подростков Проблемы преемственности. ДОУ и начальная школа
Проблемы преемственности. ДОУ и начальная школа Презентация к урокам по развитию слуха и формированию произношения по рассказу Книга зимы в 5 классе школы I и II вида.
Презентация к урокам по развитию слуха и формированию произношения по рассказу Книга зимы в 5 классе школы I и II вида. Информационная карта инновационного опыта.
Информационная карта инновационного опыта. Система работы по формированию навыка фонемного анализа и синтеза
Система работы по формированию навыка фонемного анализа и синтеза Экологический проект Деревья вокруг нас. Старший дошкольный возраст
Экологический проект Деревья вокруг нас. Старший дошкольный возраст Жизнь и творчество М.Ю. Лермонтова
Жизнь и творчество М.Ю. Лермонтова Проект Методического кабинета ДОО
Проект Методического кабинета ДОО Классный час для 8 класса Формула успеха
Классный час для 8 класса Формула успеха Материалы для проведения устного счета во 2 классе школы I вида
Материалы для проведения устного счета во 2 классе школы I вида Функкції соціального педагога
Функкції соціального педагога Человек интересной судьбы. Наш учитель Карташов Е.П
Человек интересной судьбы. Наш учитель Карташов Е.П Лэпбук Все профессии нужны, все профессии важны
Лэпбук Все профессии нужны, все профессии важны Образ человека и его изображение. Полет в космос
Образ человека и его изображение. Полет в космос МБОУ Богатищевская СОШ Наша школьная страна
МБОУ Богатищевская СОШ Наша школьная страна Защита леса и зеленых насаждений города. Методическая разработка для учащихся 6-7 классов,
Защита леса и зеленых насаждений города. Методическая разработка для учащихся 6-7 классов, Реализация системно-деятельностного подхода на уроке окружающего мира
Реализация системно-деятельностного подхода на уроке окружающего мира Лоскутное шитьё. 5 класс
Лоскутное шитьё. 5 класс Профессия столяр
Профессия столяр Образовательный проект по патриотическому воспитанию школьников Мы помним, мы гордимся! Посвящается 70-летию Победы в Великой Отечественной войне
Образовательный проект по патриотическому воспитанию школьников Мы помним, мы гордимся! Посвящается 70-летию Победы в Великой Отечественной войне Презентация к родительскому собранию
Презентация к родительскому собранию Готовимся к школе. Занятие второе
Готовимся к школе. Занятие второе Методика обучения работе с бумагой и картоном. (1 класс)
Методика обучения работе с бумагой и картоном. (1 класс) История и традиции Нового года. Мероприятие с презентацией. (Слайд 23) (Слайд 41) Загадка: На ёлке всё, что хочешь, есть:Игрушек там – не перечесть.Конфеты, дождик и хлопушки,Гирлянды, звезды и верхушка.Среди блестящей мишурыСверкают к
История и традиции Нового года. Мероприятие с презентацией. (Слайд 23) (Слайд 41) Загадка: На ёлке всё, что хочешь, есть:Игрушек там – не перечесть.Конфеты, дождик и хлопушки,Гирлянды, звезды и верхушка.Среди блестящей мишурыСверкают к