Слайд 2
Structure of the Course
Oral scientific and technical communication
Written scientific and technical communication

Слайд 3
What is your motivation to attend these lessons?
Have you ever had any experience
in written/oral scientific/technical communication?
If yes, tell us a little bit about it.

Слайд 4
Oral vs. written communication
Aims: to inform or persuade?
Style: formal or semi-formal?
Structure?

Слайд 5
Oral scientific and technical communication

Слайд 6
Presentation is like a sweet

Слайд 7
2. Form of the presentation
1. Contents of the speech

Слайд 8
Contents of the speech
Deep ideas
Choice of information
Structure
Logics

Слайд 9
Слайд 10
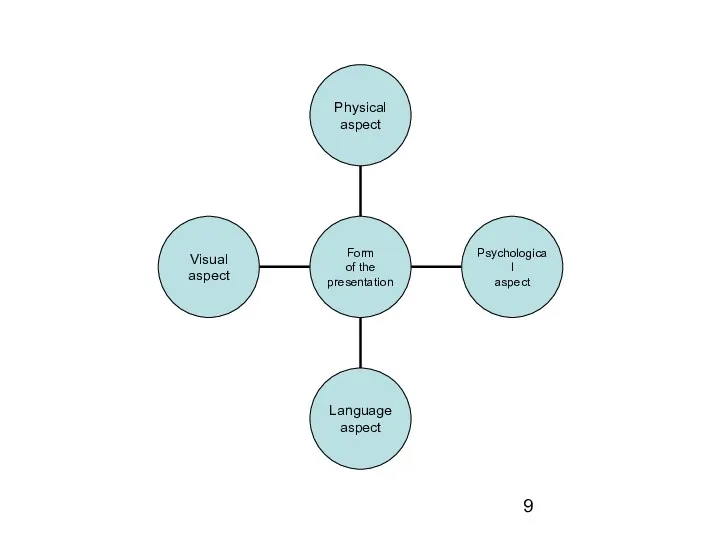
Form of the presentation
Physical aspect:
muscular relaxation
breath
body language (gestures, postures, and movement)
articulation

Слайд 11
Form of the presentation
Psychological aspect:
anxiety management
making contact with the audience
appropriate answers to the
questions

Слайд 12
Form of the presentation
Language aspect:
correct use of grammar structures, words and expressions, correct
pronunciation etc.
rhetorical techniques

Слайд 13
Form of the presentation
Visual aspect:
contents and design of slides

Слайд 14
Speech anxiety (stage fright)
speaker–audience opposition
fear of rejection
excitement paralyzing fear

Слайд 15
Ways of relaxation
breath exercises
physical exercises

Слайд 16
Breath is the key to life

Слайд 17
Breath exercises
Ex. 1
As you inhale, draw your shoulders and elbows back. Hold your
breath for 2 sec., then exhale abruptly.

Слайд 18
Breath exercises
Ex. 2
Inhale energetically for 4 sec., straining all your muscles. Then exhale
and relax all the muscles for 4-6 sec.

Слайд 19
Breath exercises
Ex. 3
Place a hand on your lower belly. Inhale deeply into your
lower belly. Feel the hand rising as your belly fills. Don’t let your chest and shoulders rise.

Слайд 20
Breath exercises
Ex. 4
Sit down on a chair and bend over so that your
body would lie on your laps. Inhale slowly – your body will rise; exhale pronouncing “pf-f-f”.

Слайд 21
Breath exercises
Ex. 5
Inhale into your lower belly. Puff out your cheeks. Blow the
air out of your cheeks through the narrow hole in your mouth. Do it slowly and with noise.

Слайд 22
Muscular relaxation
Ex. 1
This exercise can be done in standing, lying or sitting position.
Strain every muscle of your body for 5 sec. Then relax completely for the next 5 sec.

Слайд 23
Muscular relaxation
Ex. 2
Adopt an uncomfortable pose. Try to feel the place where there
is a painful point in your body. Use only your mind to relax this muscle without changing your position.

Слайд 24
Слайд 25
Know your audience
Who are these people?
What do they expect from your presentation?
What
do they already know?
What don’t they know yet?
What information will be useful for them? What information will be redundant?

Слайд 26

Слайд 27
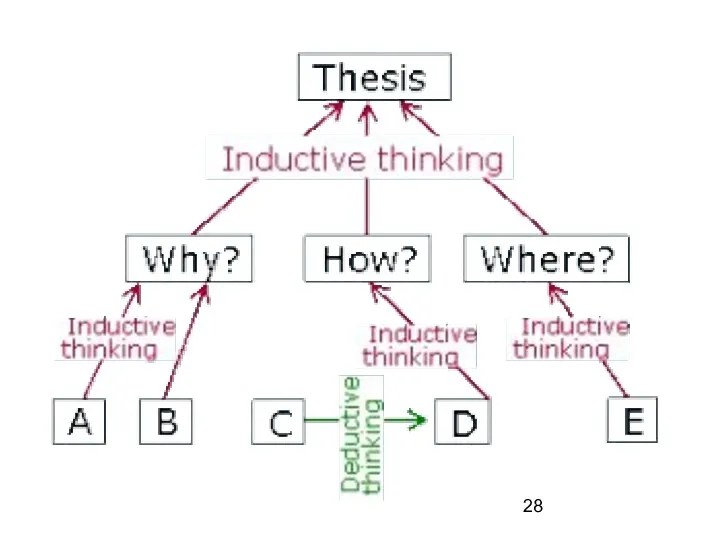
The Pyramid Principle
Multilevel system (the lower the level, the more details it has)
Executive
summary as the peak of the pyramid
Supporting arguments
Inductive reasoning
Deductive reasoning

Слайд 28
Слайд 29

Слайд 30
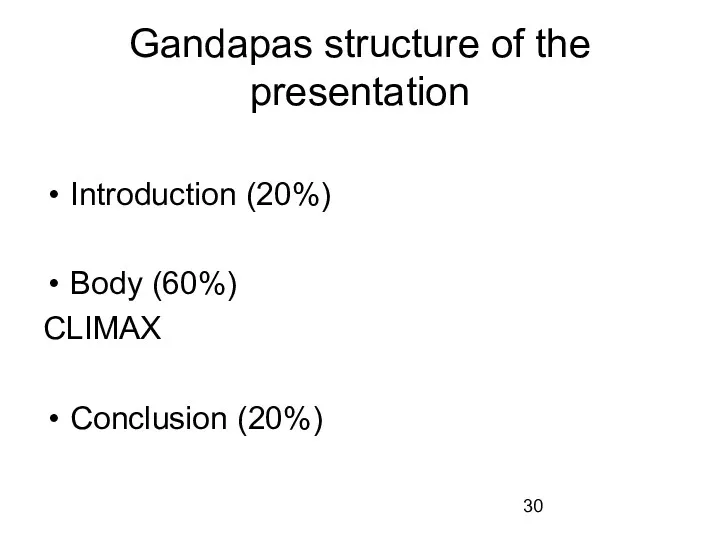
Gandapas structure of the presentation
Introduction (20%)
Body (60%)
CLIMAX
Conclusion (20%)
Слайд 31
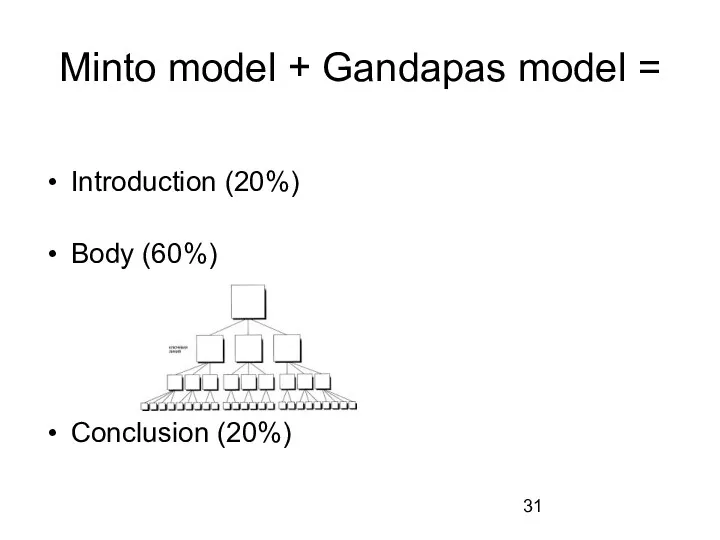
Minto model + Gandapas model =
Introduction (20%)
Body (60%)
Conclusion (20%)
Слайд 32
vk.com/communication_2017

Слайд 33
Credit Requirements
12 ninety-minute lessons attended
1 prepared presentation
1 text written at home

Слайд 34
Introduction
Self-presentation
Structure of the presentation
Question(s)
Joke
Interesting fact connected with the topic
Story connected with the topic
Expression
of feelings
Compliment to the audience
Using of “in-group/out-group” principle

Слайд 35
Conclusion
Summary of the presentation
Prospects
Question(s)
Joke
Story connected with the topic
Expression of feelings
Compliment to the
audience
Using of “in-group/out-group” principle
Aphorism
Appeal

Слайд 36
Logical Aspect of Presentation

Слайд 37

Слайд 38
Logos
appeal to logical reasoning ability of speakers, the message by which you attempt
to reason with your audience

Слайд 39
Logos
facts
case studies
statistics
experiments
logical reasoning
analogies

Слайд 40
Pathos
appeal to beliefs and feelings

Слайд 41
Ethos
the speaker’s character, credibility, and authority

Слайд 42
Ethos
trustworthiness
expert testimony
reliable sources
fairness

Слайд 43

Слайд 44

Слайд 45
Argument Structure
A premise (or premiss) of an argument is something that is put
forward as a truth, but which is not proven.
A conclusion (or claim) is the statement with which you want the other person to agree.
Inferences are further statements between the conclusion and the premises which translate the premises into the conclusion.

Слайд 46
Premises
There may be two or more premises in any argument.
If you are making
an argument, you should be ready to defend any of your own premises.
If you want to attack another person's argument, you can challenge the truth of their premises.

Слайд 47
Types of Logical Proofs
Argument from sign
Argument from induction
Argument from cause
Argument from deduction
Argument from
historical, literal, or figurative analogy
Argument from definition
Argument from statistics

Слайд 48
Argument from Sign
Certain
e.g. Fever is a sign of illness.
Probable
e.g. The
growing problem of obesity in America is a sign that a growing number of Americans are eating high calorie diets ...

Слайд 49
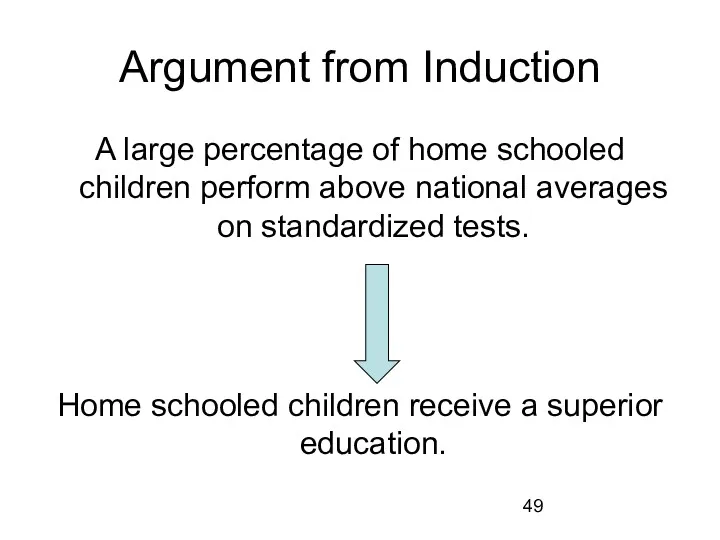
Argument from Induction
A large percentage of home schooled children perform above national averages
on standardized tests.
Home schooled children receive a superior education.
Слайд 50
Argument from Cause
Children are violent as a result of playing violent video games.

Слайд 51
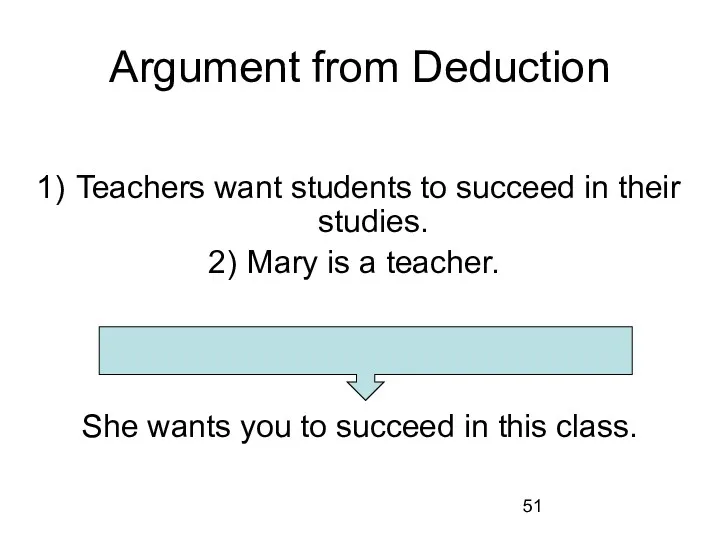
Argument from Deduction
Teachers want students to succeed in their studies.
Mary is a
teacher.
She wants you to succeed in this class.
Слайд 52
Argument from Analogy
e.g., if we use a comparison between Stalin and Putin to
analyze current events or predict future events in Russia

Слайд 53
Argument from Definition
The interpretation of what constitutes “life” will have a significant bearing
on the treatment of embryos for the purposes of stem cell research.

Слайд 54
Argument from Statistics
The USA should end draft registration because it costs $27.5 million
dollars per year.

Слайд 55
Types of Proof Connected with Ethos and Pathos
Argument from Authority
CLAIM: California will have
an earthquake.
SUPPORT: Professors and scientists say so.
Motivational Proofs
CLAIM: You should support this candidate.
SUPPORT: This candidate can help you get job security and safe neighborhoods.
Value proofs
CLAIM: The curriculum should be multicultural.
SUPPORT: A multicultural curriculum will contribute to equality and acceptance.

Слайд 56
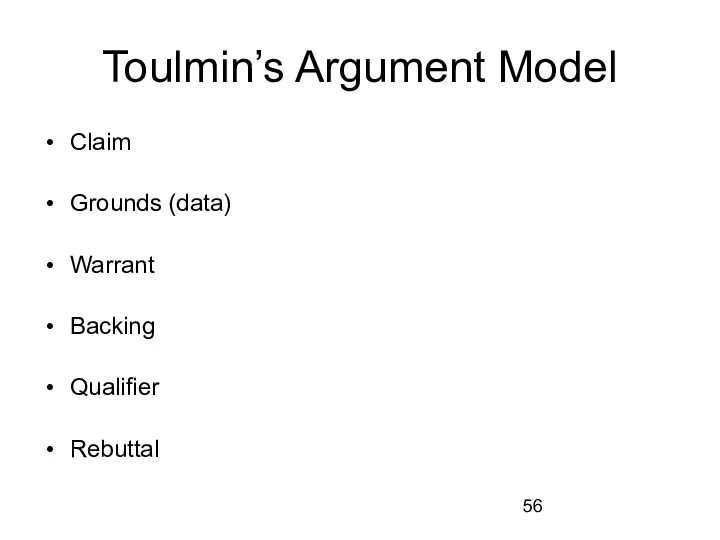
Toulmin’s Argument Model
Claim
Grounds (data)
Warrant
Backing
Qualifier
Rebuttal
Слайд 57
Toulmin’s Argument Model
Claim
You should use a hearing aid.
Grounds (data)
Over 70% of all people
over 65 years have a hearing difficulty.
Warrant
A hearing aid helps most people to hear better.
Backing
Hearing aids are available locally.
Qualifier
Hearing aids help most people.
Rebuttal
There is a support desk that deals with technical problems.

Слайд 58


























































 Профессия учитель начальных классов
Профессия учитель начальных классов Адаптация ребенка в детском саду
Адаптация ребенка в детском саду Вокальный кружок Веснушки МБДОУ Детский сад № 6
Вокальный кружок Веснушки МБДОУ Детский сад № 6 Профессия врач
Профессия врач Масленица. Игра-путешествие - младшая группа
Масленица. Игра-путешествие - младшая группа Зачем нужны автомобили, поезда
Зачем нужны автомобили, поезда Угадай мелодию ( музыку нужно скачать самим )
Угадай мелодию ( музыку нужно скачать самим ) Час общения, посвящённый профессиональному самоопределению.
Час общения, посвящённый профессиональному самоопределению. Схема работы над проектом
Схема работы над проектом Реставратор. История матрешки. Игра
Реставратор. История матрешки. Игра Архангельск-город воинской славы
Архангельск-город воинской славы педагогический совет Экспериментальная деятельность ОУ Диск
педагогический совет Экспериментальная деятельность ОУ Диск Презентация проекта Подарок маме
Презентация проекта Подарок маме Обучение иноязычному материалу: лексика и грамматика. Лекция 4
Обучение иноязычному материалу: лексика и грамматика. Лекция 4 Добро пожаловать в Бразилию!
Добро пожаловать в Бразилию! Использование элементов арт-диагностики во внеклассной работе
Использование элементов арт-диагностики во внеклассной работе Развитие познавательных процессов в дошкольном возрасте
Развитие познавательных процессов в дошкольном возрасте Угадай профессию. Игра
Угадай профессию. Игра Апрель - водолей
Апрель - водолей Достық және мен
Достық және мен Кто кого игра по ЗОЖ
Кто кого игра по ЗОЖ Цели и задачи лагеря. Логика развития лагерной смены
Цели и задачи лагеря. Логика развития лагерной смены “Правила дорожные – знать каждому положено.”
“Правила дорожные – знать каждому положено.” Родительское собрание 06.05.2019. 3-В класс
Родительское собрание 06.05.2019. 3-В класс Презентация Общие признаки птиц. 8 класс
Презентация Общие признаки птиц. 8 класс Системно-деятельностный подход. Требования к современному уроку, проектирование урока
Системно-деятельностный подход. Требования к современному уроку, проектирование урока Урок здоровья. Презентация.
Урок здоровья. Презентация. Образовательный проект Обучение правилам этикета как одно из условий социального развития воспитанников
Образовательный проект Обучение правилам этикета как одно из условий социального развития воспитанников