Содержание
- 2. Definition оf motivation Motivation is Qualities Of Motivation Process of motivation Six c’s of motivation Basic
- 3. Definition of motivation: * The driving force within individuals by which they attempt to achieve some
- 4. Motivation is… Complex Psychological Physical Unique to each and every person Context sensitive Not fully understood
- 5. Qualities of Motivation: Energizes behavior Directs behavior Enable persistence towards a goal Exists in varying details
- 6. MOTIVATION AS A PROCESS: It is a process by which a person’s efforts are energized, directed
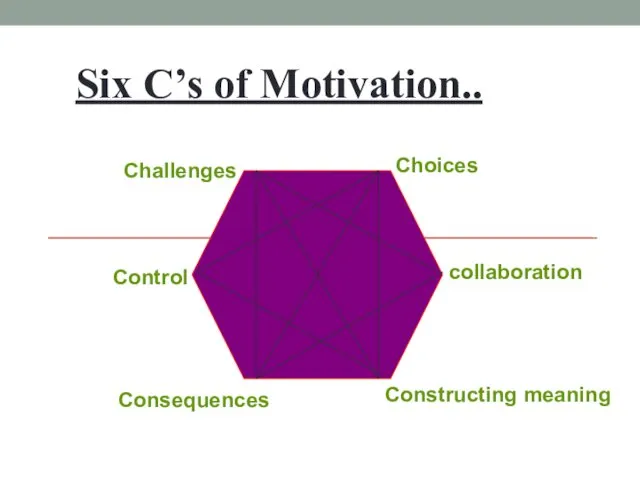
- 7. Six C’s of Motivation.. Choices collaboration Constructing meaning Consequences Control Challenges
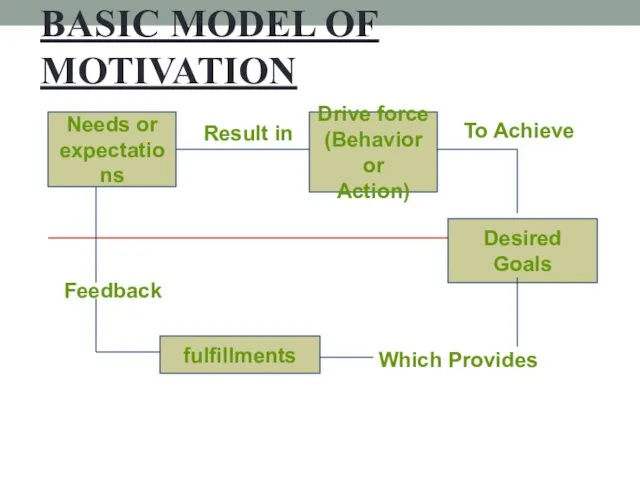
- 8. BASIC MODEL OF MOTIVATION Needs or expectations Result in Drive force (Behavior or Action) To Achieve
- 9. Early Theories of Motivation: Content Theories: Emphasis on what motivates individuals. Maslow’s need Hierarchy Macgregor's Theories
- 10. Process Theories of Motivation: Emphasis on actual process of motivation. Three needs Theory ( McClelland) Goal-setting
- 11. Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs theory Needs were categories as five levels of lower-higher-order needs. *Individual must
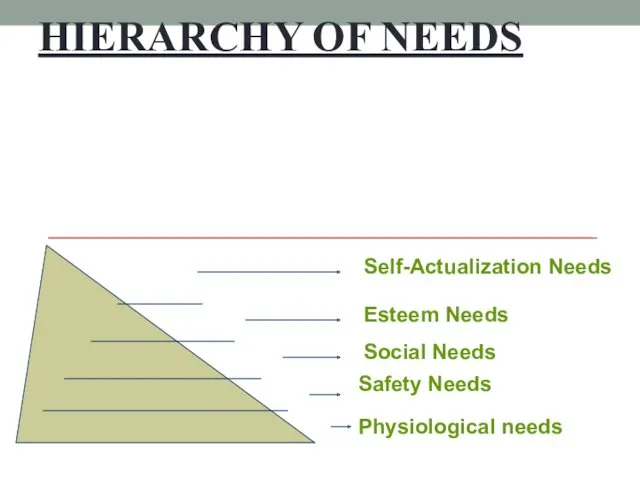
- 12. HIERARCHY OF NEEDS Physiological needs Safety Needs Social Needs Esteem Needs Self-Actualization Needs
- 13. McGregor’s Theory X and Y Theory X Assume that workers have little ambition, dislike work, avoid
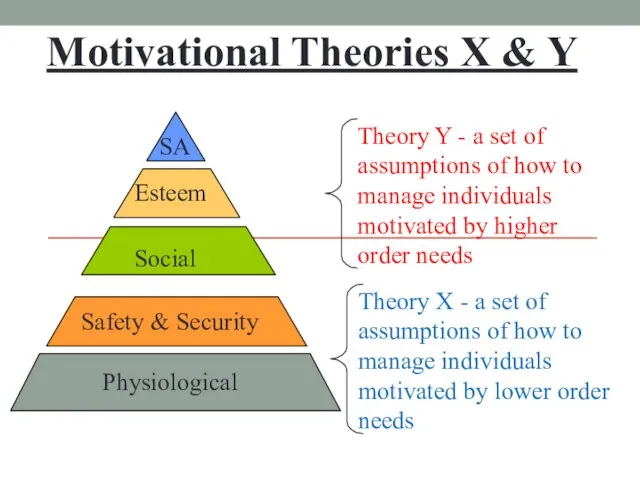
- 14. Motivational Theories X & Y Social
- 15. McClelland’s Need Theory: Need for Achievement Need for Achievement The desire to excel and succeed
- 16. McClelland’s Need Theory: Need for Power Need for Power – The need to influence the behavior
- 17. McClelland’s Need Theory: Need for Affiliation Need for Affiliation – The desire for interpersonal relationship
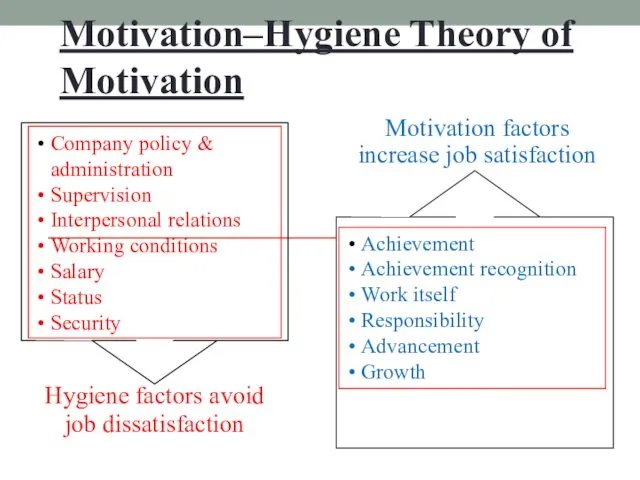
- 18. Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory Job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction are created by different factors. Hygiene factors- Extrinsic
- 19. Motivation–Hygiene Theory of Motivation
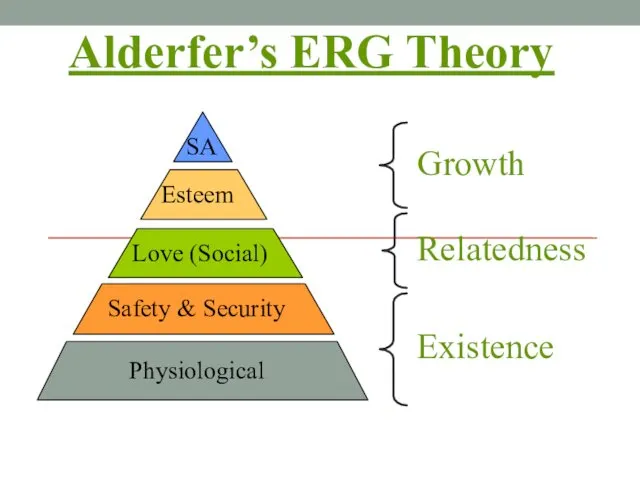
- 20. Alderfer’s ERG Theory Existence Relatedness Growth
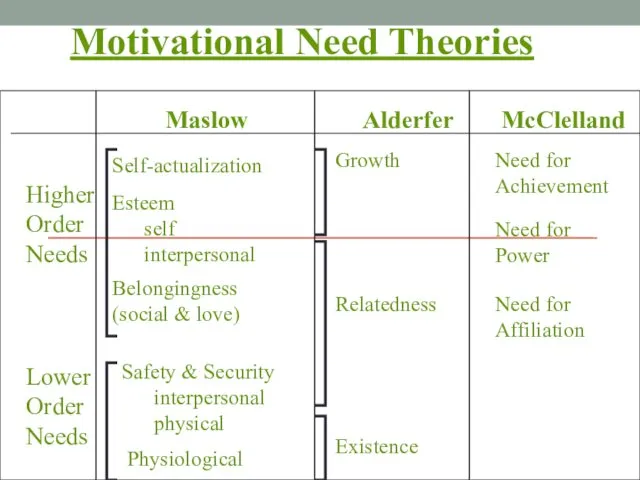
- 21. Self-actualization Motivational Need Theories Maslow Alderfer McClelland Higher Order Needs Lower Order Needs Esteem self interpersonal
- 22. Case Study The manager of A.B.C.Ltd. Realized that the level of moral and motivation of their
- 24. Скачать презентацию














 Самосовершенствование личности
Самосовершенствование личности Выступление на педагогическом совете по теме: Психологические особенности учащихся разных возрастных групп
Выступление на педагогическом совете по теме: Психологические особенности учащихся разных возрастных групп 10 шагов к построению команды
10 шагов к построению команды Планирование работы. Ведение учетно-отчетной документации педагога-психолога
Планирование работы. Ведение учетно-отчетной документации педагога-психолога Адаптация пятиклассников к обучению в средней школе
Адаптация пятиклассников к обучению в средней школе История психоаналитического движения
История психоаналитического движения Психологія управління як наука
Психологія управління як наука Введение в методологию научного исследования
Введение в методологию научного исследования Социальная идентичность, образ Я –концепции
Социальная идентичность, образ Я –концепции Темперамент
Темперамент Страх - главный психологический враг
Страх - главный психологический враг 16 листопада - Міжнародний день толерантності
16 листопада - Міжнародний день толерантності Малая группа
Малая группа Адаптация детей первой младшей группы
Адаптация детей первой младшей группы Мудрые мысли о прощении и обиде
Мудрые мысли о прощении и обиде Жестокое обращение с детьми в семье родительское собрание
Жестокое обращение с детьми в семье родительское собрание Динамика некоторых социо-психологических и физиологических параметров после психоэмоционального напряжения у молодых людей
Динамика некоторых социо-психологических и физиологических параметров после психоэмоционального напряжения у молодых людей Karen Horney
Karen Horney Задержка психического развития
Задержка психического развития Типологические особенности высшей нервной деятельности первоклассников
Типологические особенности высшей нервной деятельности первоклассников Биологическая и психологическая подструктуры личности. Лекция 2
Биологическая и психологическая подструктуры личности. Лекция 2 Домашнее психологическое насилие над пожилыми людьми
Домашнее психологическое насилие над пожилыми людьми Мотивация учения школьников
Мотивация учения школьников Темперамент и профессия. Определение темперамента. Урок 2
Темперамент и профессия. Определение темперамента. Урок 2 Что такое речь
Что такое речь Види, типи і форми професійного спілкування
Види, типи і форми професійного спілкування Конфликты. Правила поведения в конфликтных ситуациях
Конфликты. Правила поведения в конфликтных ситуациях Влияние домашних животных на психику и поведение человека
Влияние домашних животных на психику и поведение человека