Содержание
- 2. Zavin gajera(group leader) ch-07 Jaydeep rangani ch-10 Ninma chandu ch-09 Nadan shah ch-12 Subham ch-11 GROUP-2
- 3. Introduction Types of building Design load/building load Common building components Introduction building bye-laws Topic:construction
- 4. Two types of building Based upon occupancy Based on structure Types of building
- 5. Building include based upon occupany. Residential building Educational building Institutional building Assembly building Business building Mercantile
- 6. Based on structure 1.Load bearing structure It has lod bearing walls which receive the loads and
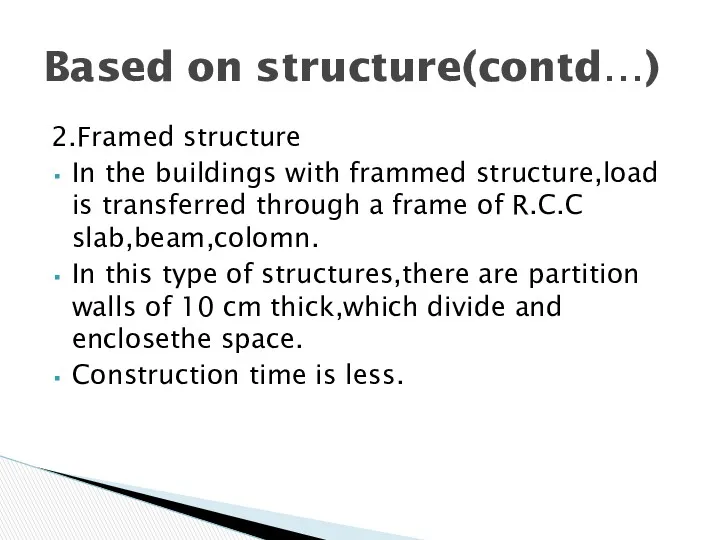
- 7. Based on structure(contd…)
- 8. 2.Framed structure In the buildings with frammed structure,load is transferred through a frame of R.C.C slab,beam,colomn.
- 9. Based on structure(contd…)
- 10. Designloads/buildingload Various loads are taken into account while designing the foundation of a structure loads coming
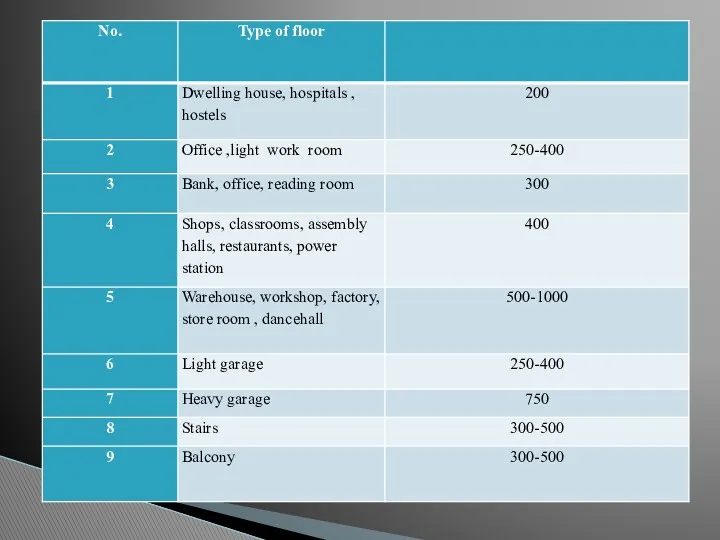
- 11. Live load: Live load consists of moving or variable load due to people or occupants, their
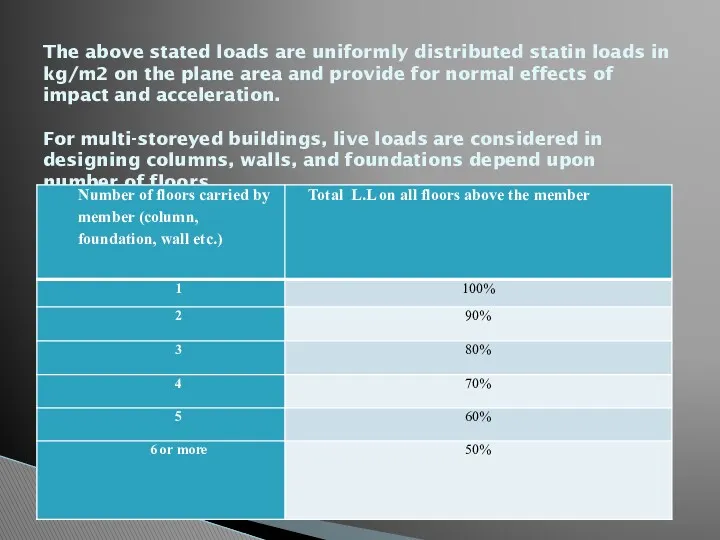
- 13. The above stated loads are uniformly distributed statin loads in kg/m2 on the plane area and
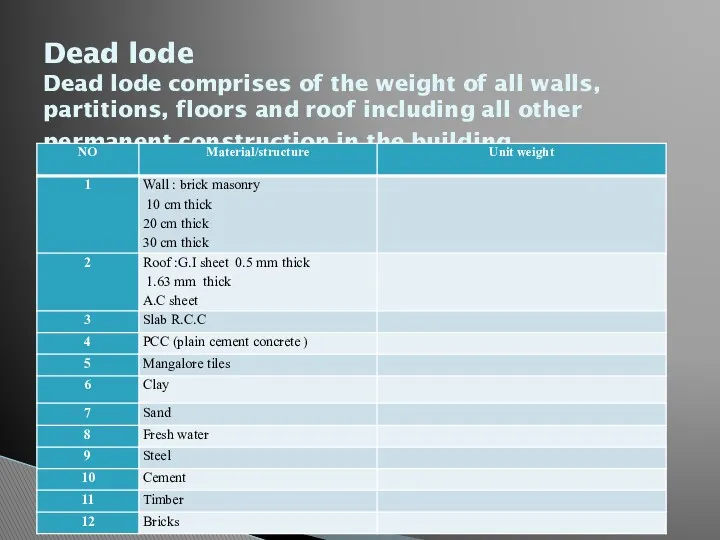
- 14. Dead lode Dead lode comprises of the weight of all walls, partitions, floors and roof including
- 15. Wind load It is considered as basic wind pressure which is an equivalents static pressure in
- 16. Snow load Actual load due to snow will depend up to the shape of the roofs
- 17. Earthquake forces An earthquake produces waves in every possible direction below ground. As per intensity or
- 18. Hydrostatic forces: The pressure generated by water is called as hydrostatic pressure. They act on the
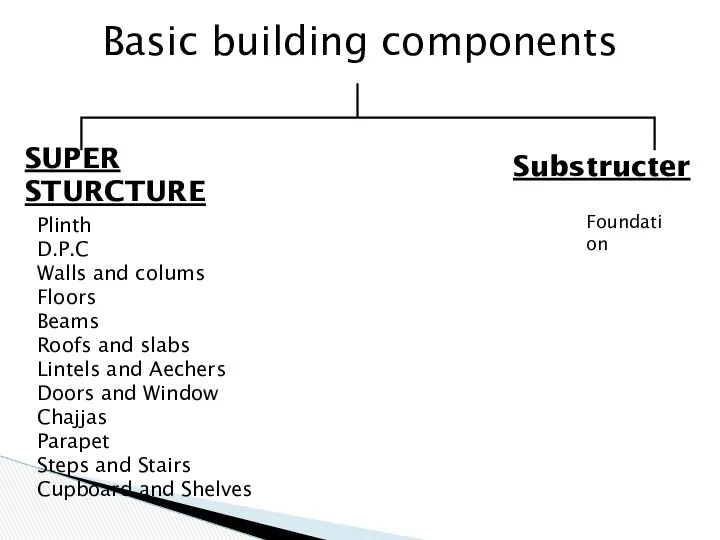
- 19. Basic building components SUPER STURCTURE Plinth D.P.C Walls and colums Floors Beams Roofs and slabs Lintels
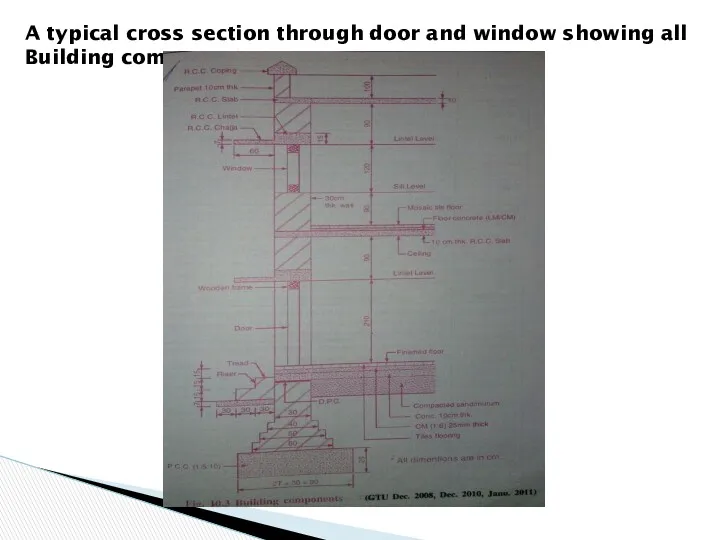
- 20. A typical cross section through door and window showing all Building components
- 21. Foundetion - It is a sturcture below the G.L . It is the lowest part of
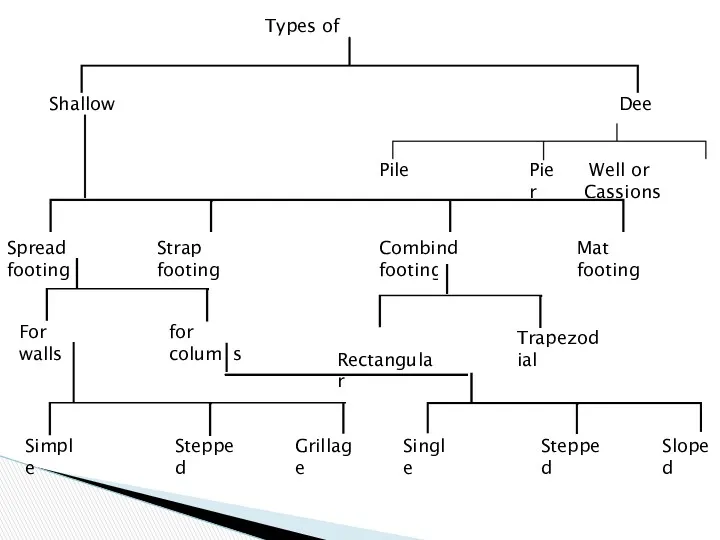
- 22. Types of Foundation Shallow Deep Pile Pier Well or Cassions Spread footing Strap footing Combind footing
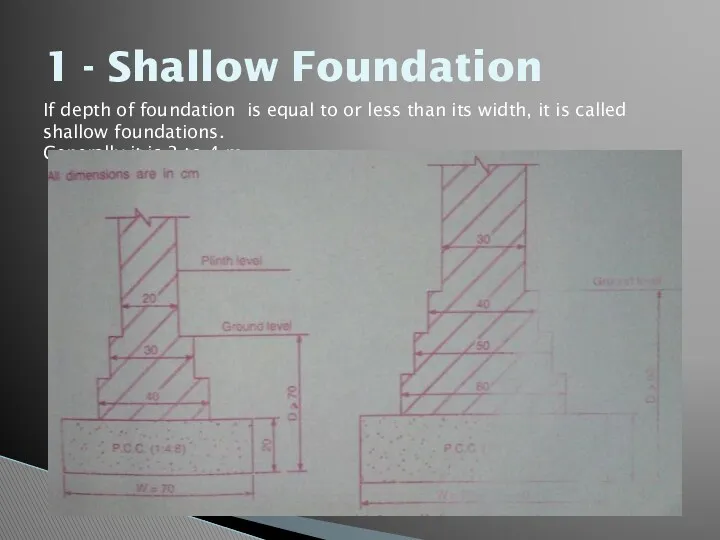
- 23. 1 - Shallow Foundation If depth of foundation is equal to or less than its width,
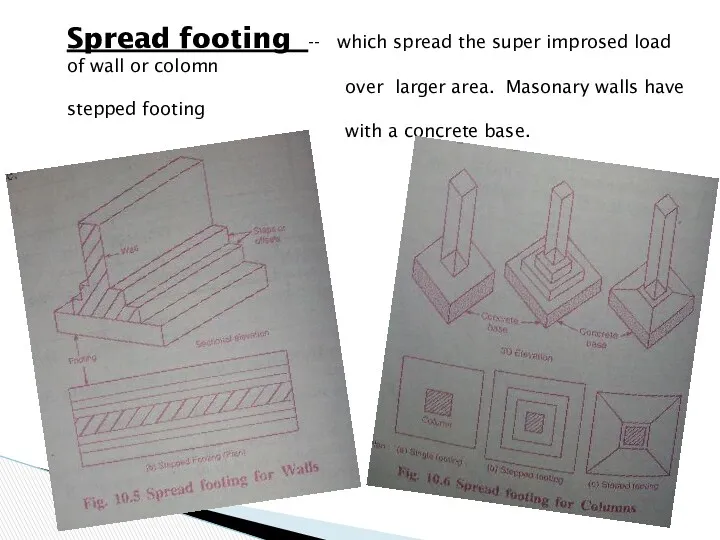
- 24. Spread footing -- which spread the super improsed load of wall or colomn over larger area.
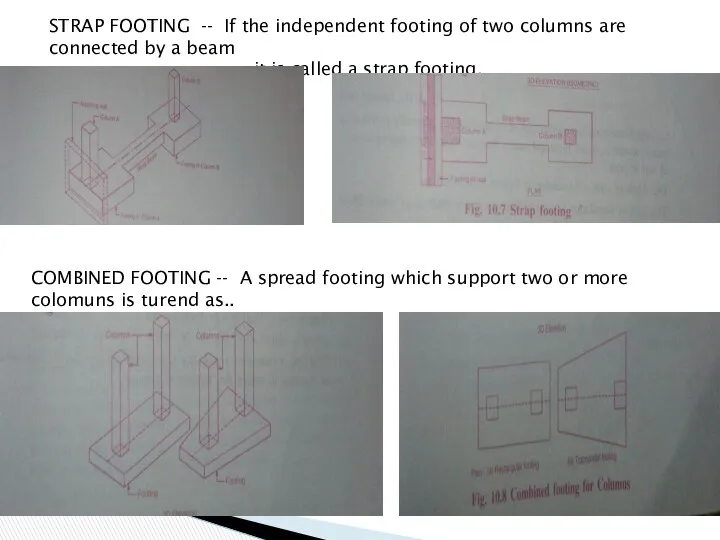
- 25. STRAP FOOTING -- If the independent footing of two columns are connected by a beam it
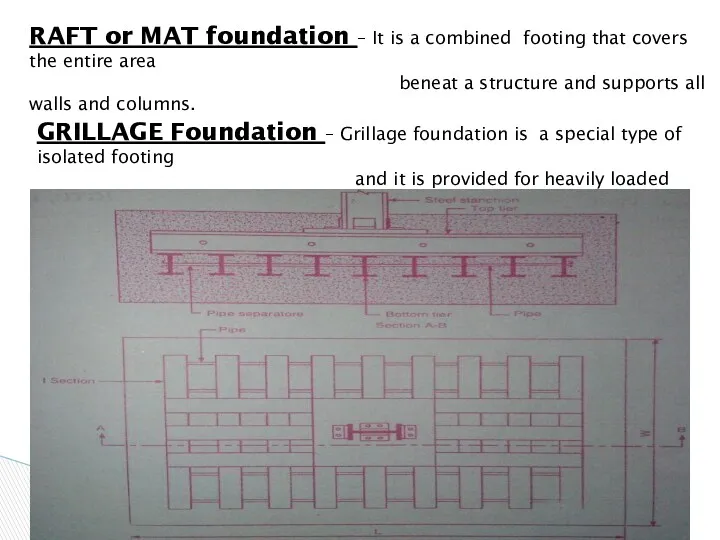
- 26. RAFT or MAT foundation – It is a combined footing that covers the entire area beneat
- 27. SUPER STRUCTURE Plinth Wall (i) Load bearing ( 20,30,40 cm) (ii) Non-load bearing (Partition wall –
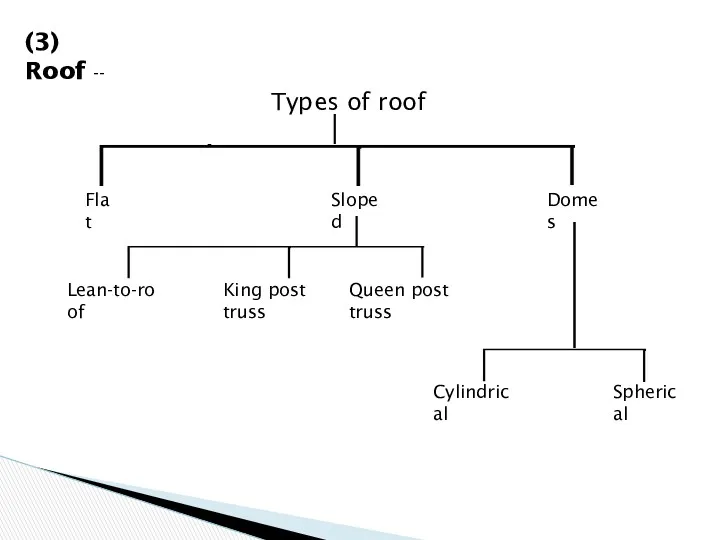
- 28. (3) Roof -- Types of roof Flat Sloped Domes Lean-to-roof King post truss Queen post truss
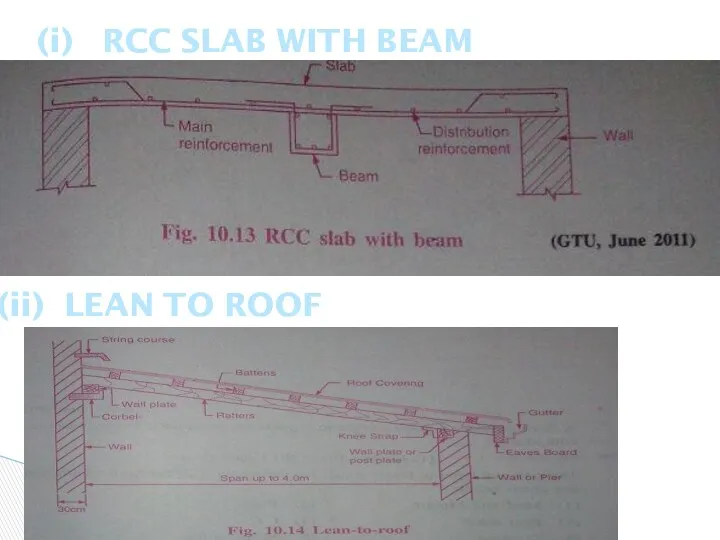
- 29. (i) RCC SLAB WITH BEAM (ii) LEAN TO ROOF
- 30. FLOOR -- A floor provides a plane surface to support the occupants, furniture and any equipment.
- 31. Doors & Window Types of Door (1) Battened and ledged door (2) Framed and panelled door
- 33. Скачать презентацию














 СЕМЬЯ И ОБЩЕОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ -ПАРТНЁРЫ В ВОСПИТАНИИ РЕБЁНКА.
СЕМЬЯ И ОБЩЕОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ -ПАРТНЁРЫ В ВОСПИТАНИИ РЕБЁНКА. Числит+сущ в Т.п
Числит+сущ в Т.п Самоанализ внеклассного мероприятия Моя любимая семья
Самоанализ внеклассного мероприятия Моя любимая семья RC Service Manual HD3033, HD3039, HD3036, HD3037, HD3077
RC Service Manual HD3033, HD3039, HD3036, HD3037, HD3077 Подвесной потолок
Подвесной потолок Инновационная экономика и технологическое предпринимательство
Инновационная экономика и технологическое предпринимательство Архитектура персонального компьютера
Архитектура персонального компьютера Жыныс қатынасынан жұғатын аурулар
Жыныс қатынасынан жұғатын аурулар Пауки-древнейшие обитатели нашей планеты
Пауки-древнейшие обитатели нашей планеты Бремя доказательства. Аргументы. Работа по экономическому праву
Бремя доказательства. Аргументы. Работа по экономическому праву Долг и совесть. 8 класс
Долг и совесть. 8 класс Светоотражающие наклейки на одежде
Светоотражающие наклейки на одежде Бақытжан Бейсалыүлы Каратаев
Бақытжан Бейсалыүлы Каратаев 20230925_kartochki
20230925_kartochki Новый Год
Новый Год 144 года Самарскому знамени
144 года Самарскому знамени Сочинение по картине И.Я. Билибина Иван-царевич и лягушка-квакушка
Сочинение по картине И.Я. Билибина Иван-царевич и лягушка-квакушка Самоуправление. Копилка старшего вожатого.
Самоуправление. Копилка старшего вожатого. Палестина - батьківщина християнства та іудаїзму
Палестина - батьківщина християнства та іудаїзму Основы журналистики
Основы журналистики Послеродовые гнойно-септические заболевания
Послеродовые гнойно-септические заболевания Анатомия + Хирургические доступы к Поджелудочной железе
Анатомия + Хирургические доступы к Поджелудочной железе Открываем Родину вместе (из опыта работы учителя начальных классов)
Открываем Родину вместе (из опыта работы учителя начальных классов) Развитие артикуляционной моторики у детей с тяжелыми нарушениями речи
Развитие артикуляционной моторики у детей с тяжелыми нарушениями речи Властивості складних систем. Біосфера. Основні положення В. І. Вернадського про біосферу
Властивості складних систем. Біосфера. Основні положення В. І. Вернадського про біосферу Искусство и духовная жизнь
Искусство и духовная жизнь Микронасосы. Принцип действия микронасосов
Микронасосы. Принцип действия микронасосов Организация и проведение мероприятий по воспроизводству лесов и лесоразведению
Организация и проведение мероприятий по воспроизводству лесов и лесоразведению