Содержание
- 2. Corporate finance (narrow) The optimal capital structure (OF/TB) Composition debts (ST versus LT) Wich credit forms
- 3. 1. Optimal capital structure Miller-Modigliani Three theories: Target adjustment (more profits, more debts) Agency model (more
- 4. 2. Long versus short term Hedger LT credit needs with LT credits KT credit needs with
- 5. Hedger versus averter
- 6. 3. Credit forms Suppliers Bank credits LT Investment credits Leasing and financing Bank credits ST Overdraft
- 7. 3.1. Suppliers Policy = f (economic situation/sector/competitive position) Decision to take:: Credit period Credit insurance Credit
- 8. 3.2. Bank credits ST Overdraft (cash credit): Popular Cost = f (use) I = BI +
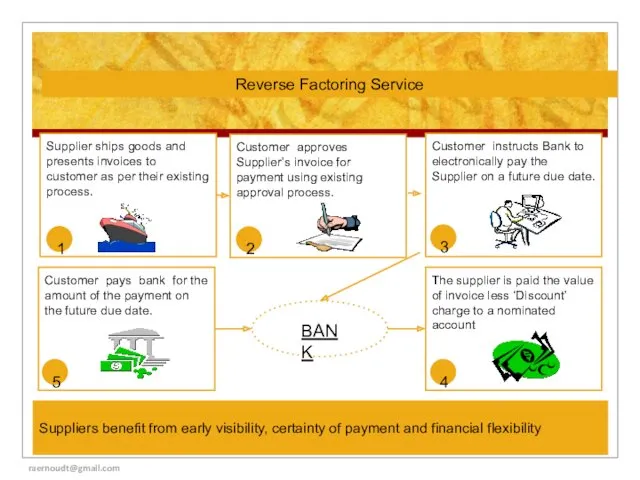
- 9. Customer approves Supplier’s invoice for payment using existing approval process. Customer instructs Bank to electronically pay
- 10. 3.3. Bank credits LT Investment credit Financing of investment Fixed pay back (or bullet) Interest payable
- 11. 4. Risk analysis Financial elements stable, permanent CF (= pbc) Optimal financial Structure : OF, OF/BT
- 12. 5. Guarantees Equal treatment principle Guarantee = priority on other debtors Notoriety: 25 to 35 %
- 13. 6. Risk analysis: model Total requested credits: Of which 1st Rang risk Of which 2nd Rang
- 15. Скачать презентацию











 Роль семьи в формировании межнациональной толерантности у детей старшего дошкольного возраста.
Роль семьи в формировании межнациональной толерантности у детей старшего дошкольного возраста. Разработка программы оптимального распределения энергии для диаграммы направленности антенной решетки
Разработка программы оптимального распределения энергии для диаграммы направленности антенной решетки А.С Пушкин Капитанская дочка
А.С Пушкин Капитанская дочка технология
технология Суточное осевое вращение Земли
Суточное осевое вращение Земли Право международной безопасности. Международное публичное право
Право международной безопасности. Международное публичное право Комплексный центр социального обслуживания населения г. Бородино. Сопровождение семей, имеющих детей-инвалидов
Комплексный центр социального обслуживания населения г. Бородино. Сопровождение семей, имеющих детей-инвалидов История адаптивного спорта для лиц с поражением слуха
История адаптивного спорта для лиц с поражением слуха Презентация игра Четвёртый лишний
Презентация игра Четвёртый лишний Профессиональный стресс. Проявление хронической усталости и психического выгорания
Профессиональный стресс. Проявление хронической усталости и психического выгорания Морская политика России
Морская политика России Презентация Наша жизнь
Презентация Наша жизнь Информационно - коммуникационные технологии в работе с детьми по экологическому воспитанию
Информационно - коммуникационные технологии в работе с детьми по экологическому воспитанию Запорная арматура. Классификация
Запорная арматура. Классификация Биологическое преобразование энергии: дыхание, фотосинтез, хемосинтез
Биологическое преобразование энергии: дыхание, фотосинтез, хемосинтез Интегральное исчисление функций нескольких переменных. Двойные интегралы
Интегральное исчисление функций нескольких переменных. Двойные интегралы подготовка_к_кр_дроби_и_смешанные_числа
подготовка_к_кр_дроби_и_смешанные_числа Фильтры грубой очистки фланцевые MVI серии FF.310. Технический паспорт
Фильтры грубой очистки фланцевые MVI серии FF.310. Технический паспорт Mark Twain
Mark Twain Мышление и культура в этнопсихологии. (Тема 4)
Мышление и культура в этнопсихологии. (Тема 4) Привычки успешных мам
Привычки успешных мам Основания. Состав оснований
Основания. Состав оснований Готовность к школьному обучению
Готовность к школьному обучению Система организации оказания медицинской помощи городскому населению
Система организации оказания медицинской помощи городскому населению ВКР: Имидж гостиничного предприятия (планирование, формирование, продвижение)
ВКР: Имидж гостиничного предприятия (планирование, формирование, продвижение) Издержки фирмы
Издержки фирмы Здравствуй, школа!
Здравствуй, школа! Диагностика острой ревматической лихорадки
Диагностика острой ревматической лихорадки