Содержание
- 2. Definition Tissues -- groups of cells organised to perform one or more functions.
- 3. Please, note and write down: 4 basic types of tissues: Epithelial (Epithelium) Connective Muscular Nervous
- 4. Please, note and write down: There are two main types of Epithelial Tissue: 1. Covering and
- 5. Please, note and write down: Covering and lining epithelia lie on the free surface: - cover
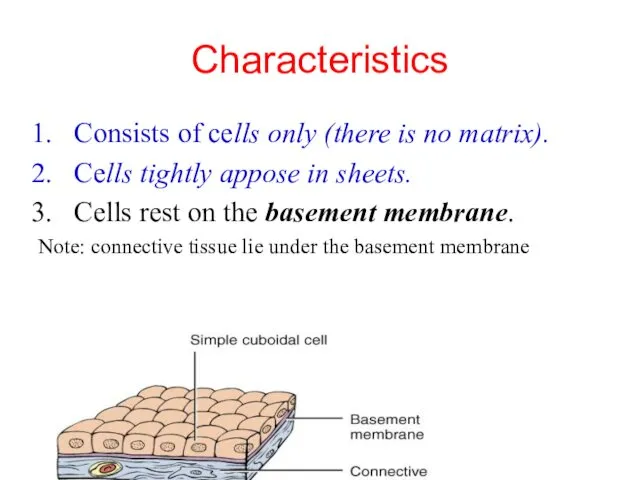
- 6. Characteristics Consists of cells only (there is no matrix). Cells tightly appose in sheets. Cells rest
- 7. Importance : Epithelium create a selective barrier between the organism and its external environment: any substances
- 8. Please, note and write down: Two types of surface epithelia: epithelium is simple, when it is
- 9. Maine functions protection diffusion or absorption or excretion = exchange
- 10. Another functions transport (along free surface) secretion sensation.
- 11. Characteristics. 3. polarity - cells have 2 surfaces : the apical or free surface - towards
- 12. Shape of cells: Squamous. Cuboidal. Columnar.
- 13. !!! In case of stratified epithelia the second name describes the shape of the top layer
- 14. Please, note and write down: The morphology of the epithelium correlates with its function: - Epithelia
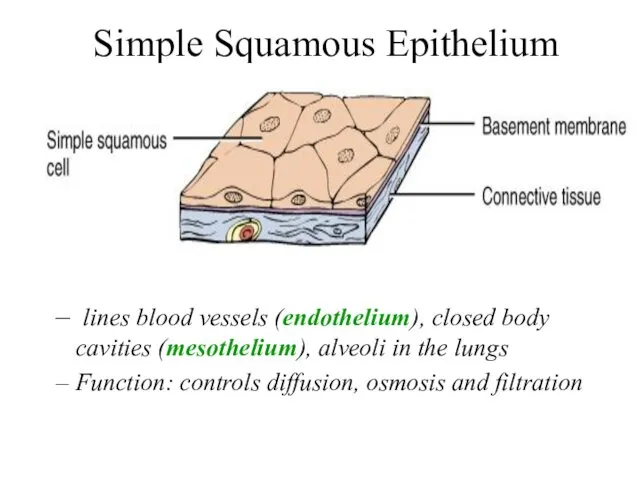
- 15. Simple Squamous Epithelium lines blood vessels (endothelium), closed body cavities (mesothelium), alveoli in the lungs Function:
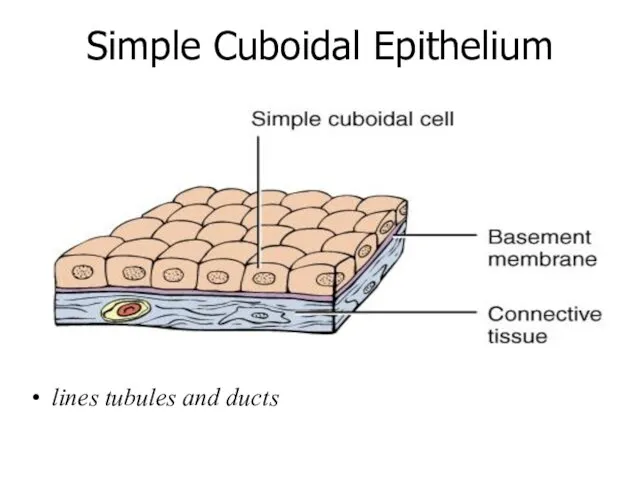
- 16. Simple Cuboidal Epithelium lines tubules and ducts
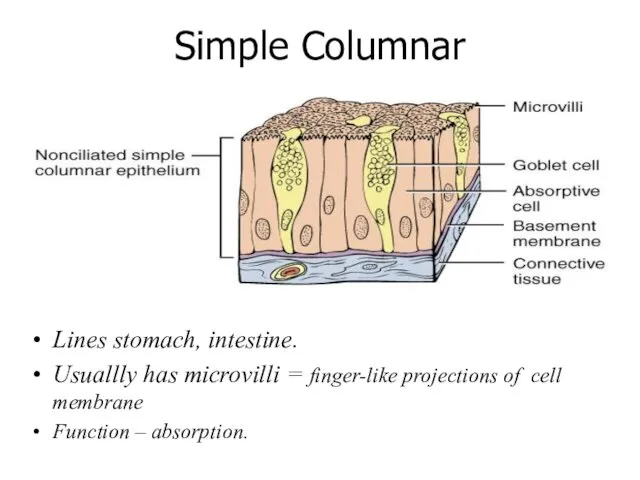
- 17. Simple Columnar Lines stomach, intestine. Usuallly has microvilli = finger-like projections of cell membrane Function –
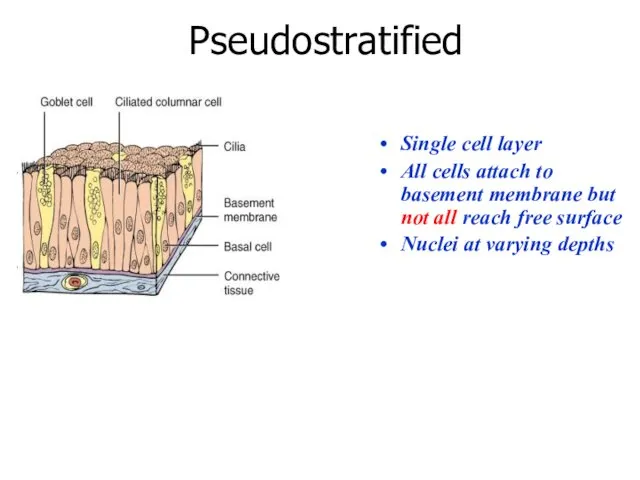
- 18. Pseudostratified Single cell layer All cells attach to basement membrane but not all reach free surface
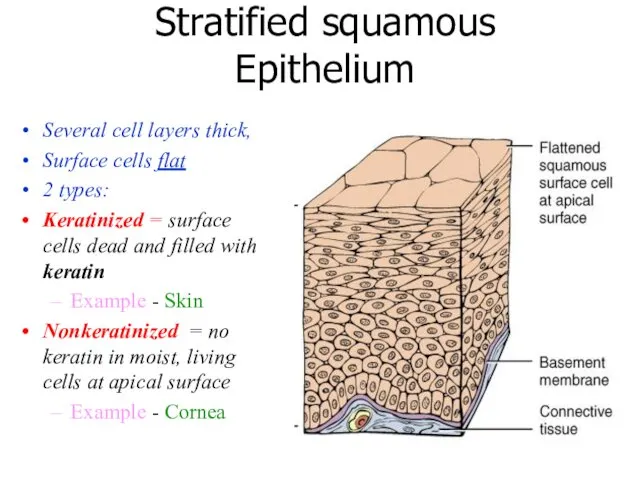
- 19. Stratified squamous Epithelium Several cell layers thick, Surface cells flat 2 types: Keratinized = surface cells
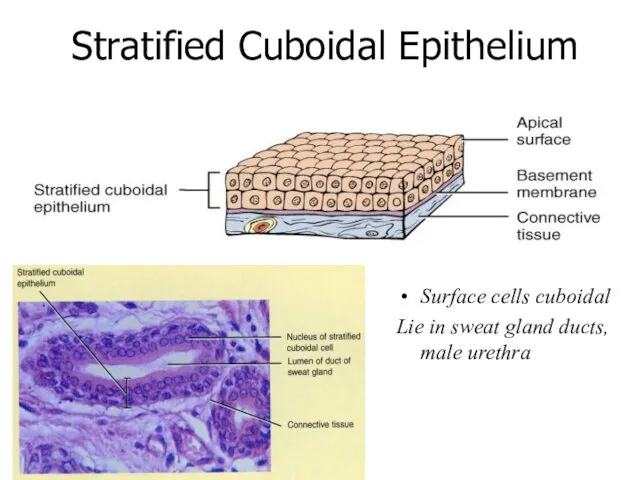
- 20. Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Surface cells cuboidal Lie in sweat gland ducts, male urethra
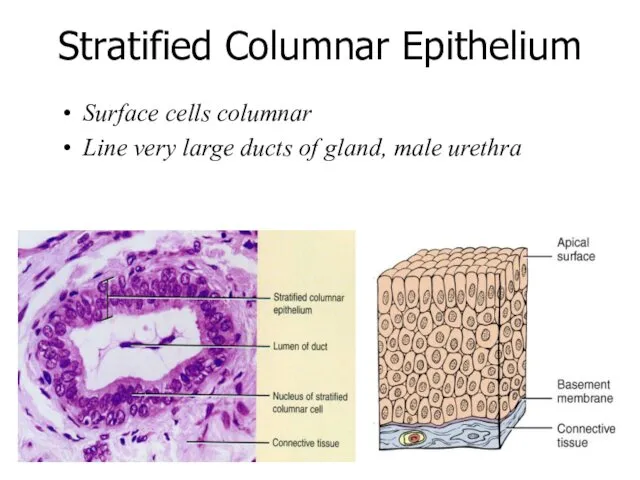
- 21. Stratified Columnar Epithelium Surface cells columnar Line very large ducts of gland, male urethra
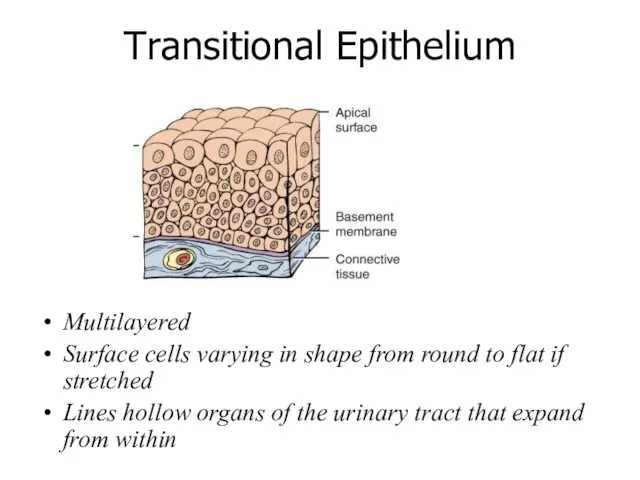
- 22. Multilayered Surface cells varying in shape from round to flat if stretched Lines hollow organs of
- 23. Please, note and write down: !! The morphology of an epithelium often correlates with its function:
- 24. GLANDULAR EPITHELIA - form glands. Function – secretion = synthesis and releasing of substances.
- 25. GLANDULAR EPITHELIA - Secretion – cyclic process. 4 phases: 1. diffusion of metabolites into the cell
- 26. There are two types of gland in the body: exocrine and endocrine. Exocrine glands secrete through
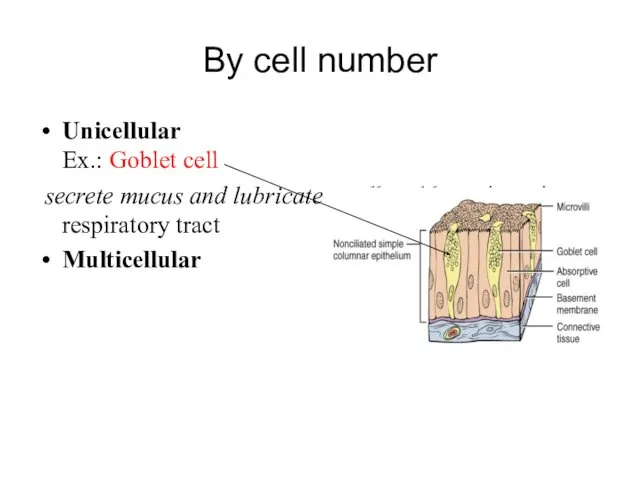
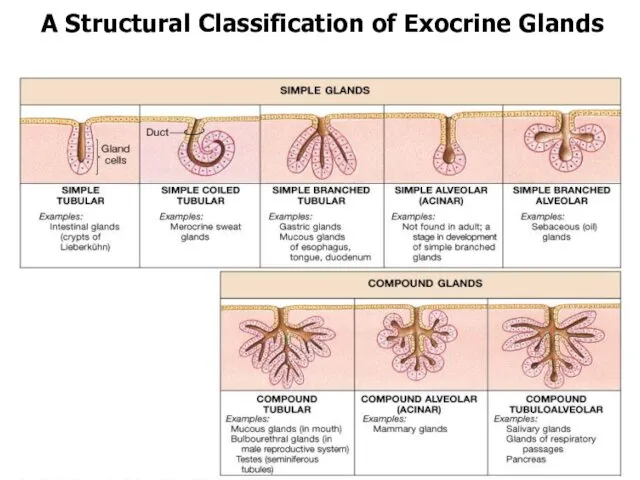
- 27. By cell number Unicellular Ex.: Goblet cell secrete mucus and lubricate small and large intestine, respiratory
- 28. 2 portions of gland: Parenchyma and Stroma Parenchyma - the epithelial, secreting cells of the gland
- 29. Two type of secretion of Exocrine Glands Mucous - viscous, slimy (mucus lines and lubricates cavities
- 31. Classification of Exocrine Glands by type of secretion 3. Mixed (Seromucous) Ex.: Submandibular and sublingual salivary
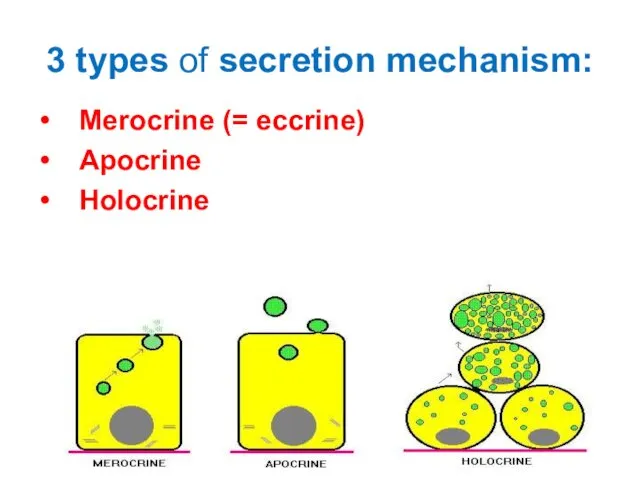
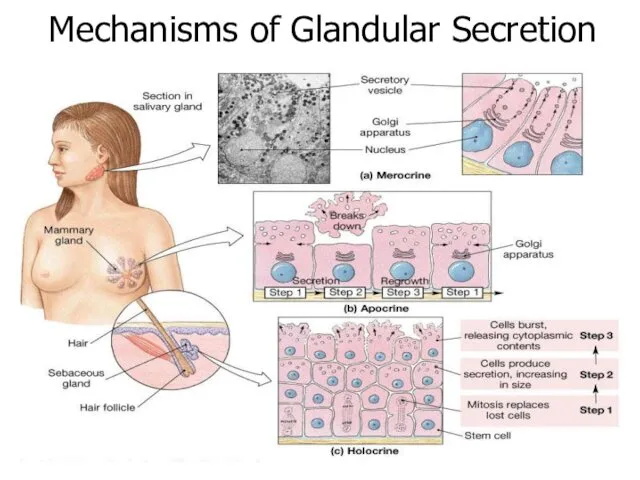
- 32. 3 types of secretion mechanism: Merocrine (= eccrine) Apocrine Holocrine
- 33. Merocrine (most common): Secretory granules fuse with the apical plasma membrane and are secreted into the
- 34. Apocrine (ex.: lactating mammary gland (fat droplet)) small portion of apical cytoplasm with secretory granules is
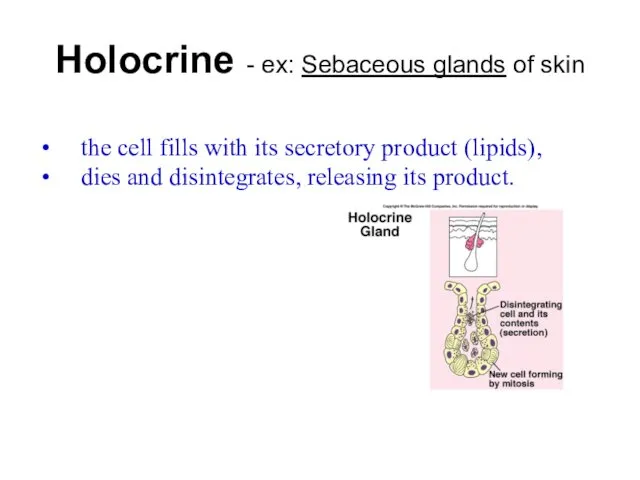
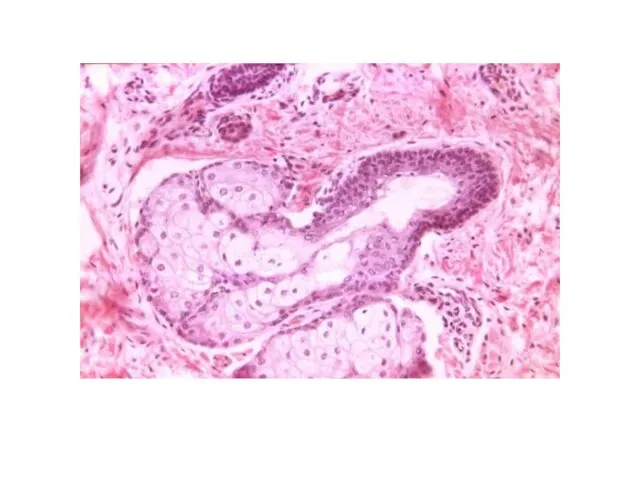
- 35. Holocrine - ex: Sebaceous glands of skin the cell fills with its secretory product (lipids), dies
- 37. Mechanisms of Glandular Secretion
- 38. A Structural Classification of Exocrine Glands
- 40. Скачать презентацию





















 Бездари. Евгений Кириллов, Игорь Вербицкий, Олег Кириллов, Игорь Пономарёв
Бездари. Евгений Кириллов, Игорь Вербицкий, Олег Кириллов, Игорь Пономарёв Конспект непосредственно образовательной деятельности по духовно-нравственному воспитанию для детей старшего дошкольного возраста Праздник Покрова Пресвятой Богородицы
Конспект непосредственно образовательной деятельности по духовно-нравственному воспитанию для детей старшего дошкольного возраста Праздник Покрова Пресвятой Богородицы Интегральная микросхема
Интегральная микросхема Виды орнаментов
Виды орнаментов Культурно-гигиенические навыки, их значение в развитии ребёнка.
Культурно-гигиенические навыки, их значение в развитии ребёнка. Презентация Рефлексия
Презентация Рефлексия Игровое занятие для 2 класса Давайте поиграем!
Игровое занятие для 2 класса Давайте поиграем! Творческий проект Ловец Снов
Творческий проект Ловец Снов Л_1_СТ_Фізико_технічні_основи_променевої_діагностики_
Л_1_СТ_Фізико_технічні_основи_променевої_діагностики_ Если вы никак не можете себя заставить работать
Если вы никак не можете себя заставить работать Знатоки безопасности(задания для старших дошкольников)
Знатоки безопасности(задания для старших дошкольников) Сретение Господне
Сретение Господне Техническое обслуживание тормозных систем современных автомобилей
Техническое обслуживание тормозных систем современных автомобилей Священная Библейская история Нового Завета
Священная Библейская история Нового Завета Мы помним, мы гордимся!
Мы помним, мы гордимся! Права ребёнка и их защита.
Права ребёнка и их защита. Страны Зарубежной Европы
Страны Зарубежной Европы Дидактика высшей школы. Формирование системы знаний о дидактике, как отрасли педагогики
Дидактика высшей школы. Формирование системы знаний о дидактике, как отрасли педагогики Фотография
Фотография 1С:Зарплата и управление персоналом
1С:Зарплата и управление персоналом le passé composé прошедшее время
le passé composé прошедшее время Энергетический расчет РЛС
Энергетический расчет РЛС Disklavier MarkIV Seminar in Europe
Disklavier MarkIV Seminar in Europe математика 14апреля
математика 14апреля Преобразование сумм тригонометрических функций в произведение
Преобразование сумм тригонометрических функций в произведение Особистості Великої Вітчизняної війни
Особистості Великої Вітчизняної війни Мой любимый вид спорта
Мой любимый вид спорта Обращение с отходами
Обращение с отходами