Содержание
- 2. Learning Objective Monday, 22 January 2024 Understand the products of dehydration of alcohols
- 3. Success Criteria Monday, 22 January 2024 Identify and describe other reactions of alcohols. Explain what is
- 4. Keywords Monday, 22 January 2024 Primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols Carbocation Carbocation stability Dehydration Elimination mechanism Zaitsev’s
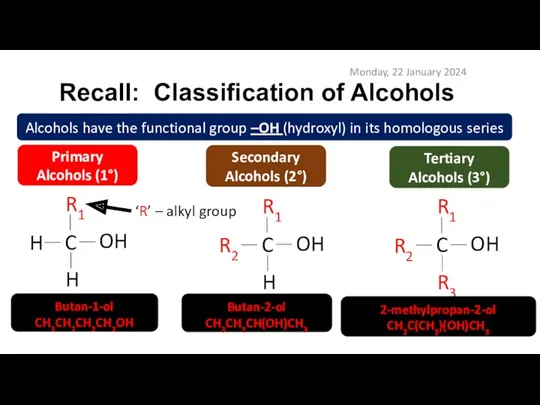
- 5. Recall: Classification of Alcohols Monday, 22 January 2024 Alcohols have the functional group –OH (hydroxyl) in
- 6. Monday, 22 January 2024 C Harris - Allery Chemistry
- 7. Monday, 22 January 2024 C Harris - Allery Chemistry
- 8. Monday, 22 January 2024 C Harris - Allery Chemistry
- 9. 4. Dehydration of alcohols Monday, 22 January 2024 Alkenes can be made sustainably from alcohols –
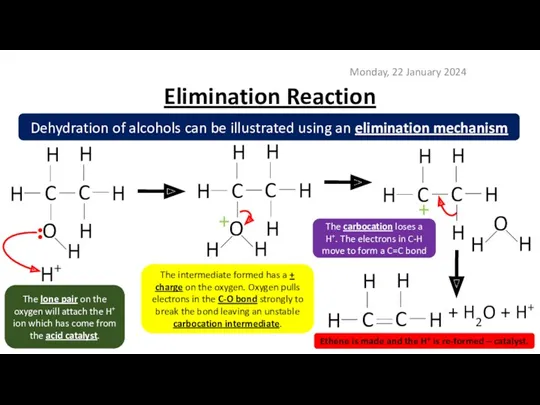
- 10. Elimination Reaction Monday, 22 January 2024 Dehydration of alcohols can be illustrated using an elimination mechanism
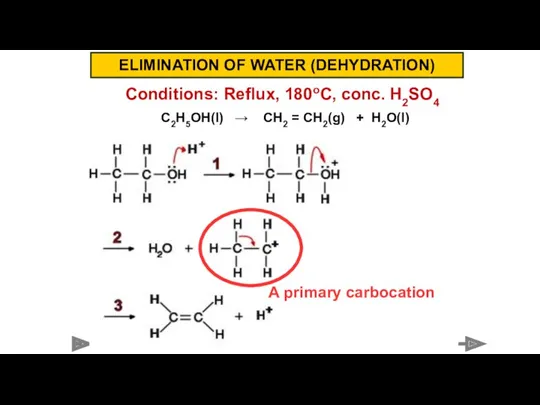
- 11. Conditions: Reflux, 180oC, conc. H2SO4 C2H5OH(l) → CH2 = CH2(g) + H2O(l) ELIMINATION OF WATER (DEHYDRATION)
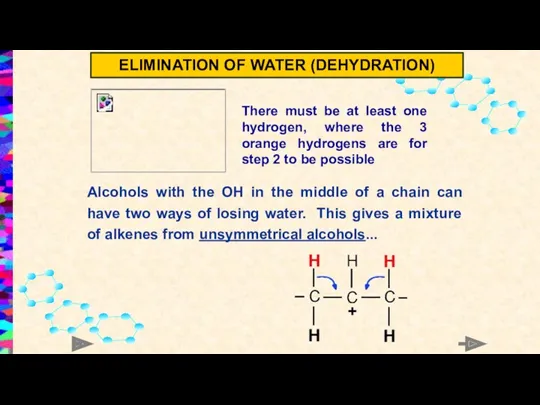
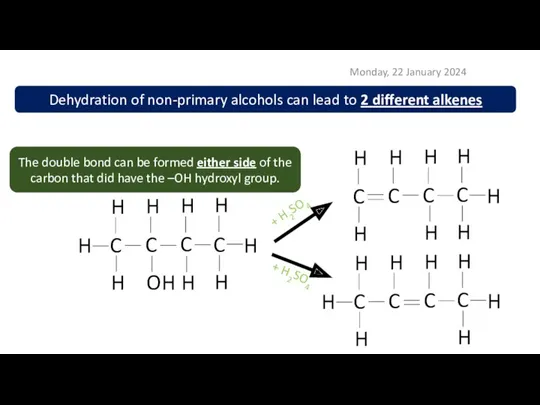
- 12. Alcohols with the OH in the middle of a chain can have two ways of losing
- 14. Monday, 22 January 2024 Dehydration of non-primary alcohols can lead to 2 different alkenes The double
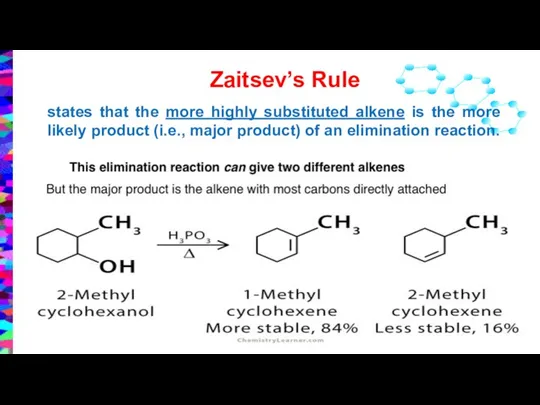
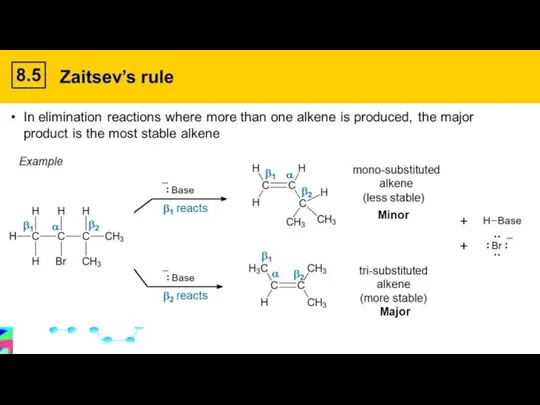
- 15. Zaitsev’s Rule states that the more highly substituted alkene is the more likely product (i.e., major
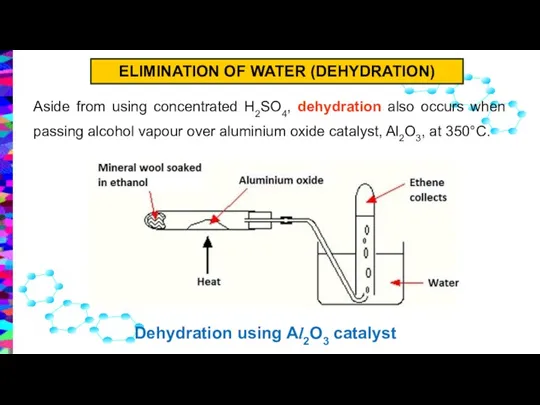
- 17. Aside from using concentrated H2SO4, dehydration also occurs when passing alcohol vapour over aluminium oxide catalyst,
- 18. TASK #1 Draw the structures of the alkene(s) you might get if you dehydrate the following
- 20. Скачать презентацию









 Особенности устройства рельсовой колеи на кривом участке двухпутной линии
Особенности устройства рельсовой колеи на кривом участке двухпутной линии Применение метода фотограмметрии для моделирования архитектурных сооружений
Применение метода фотограмметрии для моделирования архитектурных сооружений Марина Цветаева
Марина Цветаева Технология выполнения оклеивания стен виниловыми обоями с полной подготовкой основания. Настилка пола керамической плиткой
Технология выполнения оклеивания стен виниловыми обоями с полной подготовкой основания. Настилка пола керамической плиткой Практическое занятие № 5. Защита населения в ЧС
Практическое занятие № 5. Защита населения в ЧС Война 1812 года и Бородинское сражение
Война 1812 года и Бородинское сражение Презентация по сказке В. Сутеева Петух и краски
Презентация по сказке В. Сутеева Петух и краски Каша-матушка наша!
Каша-матушка наша! Суверенитет народа и формы его осуществления в Российской Федерации
Суверенитет народа и формы его осуществления в Российской Федерации Презентация Угадай страну.
Презентация Угадай страну. Rail and intermodal transport
Rail and intermodal transport Ажарлайтын станоктардың типтері және қолдану салалары
Ажарлайтын станоктардың типтері және қолдану салалары Методология исследовательской деятельности в ландшафтной архитектуре
Методология исследовательской деятельности в ландшафтной архитектуре Понятие, сущность и основные функции менеджмента
Понятие, сущность и основные функции менеджмента Синтетическая теория эволюции
Синтетическая теория эволюции Методологические основы научной деятельности. Исследовательский инструментарий
Методологические основы научной деятельности. Исследовательский инструментарий угадай сказку
угадай сказку Історія виникнення етикету
Історія виникнення етикету Основные этапы накопления знаний о Земле
Основные этапы накопления знаний о Земле Перинатальные поражения нервной системы и их последствия
Перинатальные поражения нервной системы и их последствия Логопедический проект Вместе весело шагать
Логопедический проект Вместе весело шагать Методический семинар Создание персонального сайта учителя
Методический семинар Создание персонального сайта учителя Заповедник Столбы
Заповедник Столбы метод проектов в начальной школе
метод проектов в начальной школе Расчет смешивающих литейных бегунов с вертикально-вращающимися катками
Расчет смешивающих литейных бегунов с вертикально-вращающимися катками Развитие международного туризма
Развитие международного туризма Строение ногтя
Строение ногтя Природа процесса принятия управленческого решения
Природа процесса принятия управленческого решения