Development of a macro-prudential framework. Example of a macro-prudential policy framework for Europe презентация
Содержание
- 2. Overview 27/04/2016 Slide Introduction Macro-prudential policy strategy Macro-prudential policy cycle - Risk identification and assessment -
- 3. Development of a macro-prudential framework Introduction – Rationale for macro-prudential policy 27/04/2016 Slide
- 4. Development of a macro-prudential framework Introduction – Rationale for macro-prudential policy 27/04/2016 Slide
- 5. Overview 27/04/2016 Slide Introduction Macro-prudential policy strategy Macro-prudential policy cycle - Risk identification and assessment -
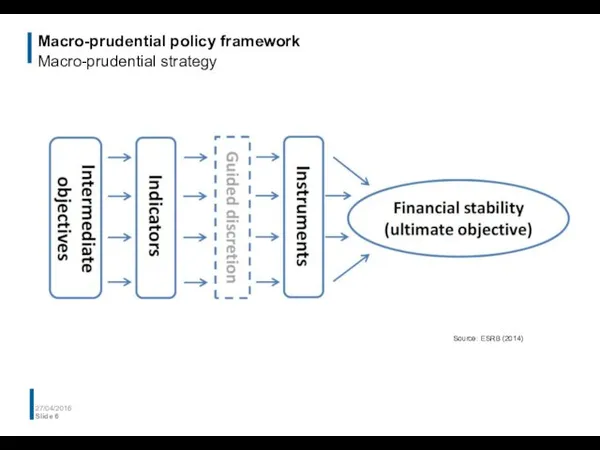
- 6. Macro-prudential policy framework Macro-prudential strategy 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
- 7. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Macro-prudential strategy: intermediate objectives 27/04/2016 Slide
- 8. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Examples on how to link intermediate objectives with indicators 27/04/2016
- 9. Overview 27/04/2016 Slide Introduction Macro-prudential policy strategy Macro-prudential policy cycle - Risk identification and assessment -
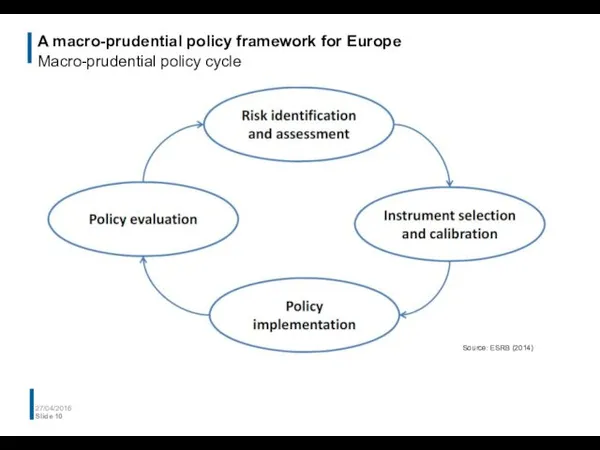
- 10. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Macro-prudential policy cycle 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
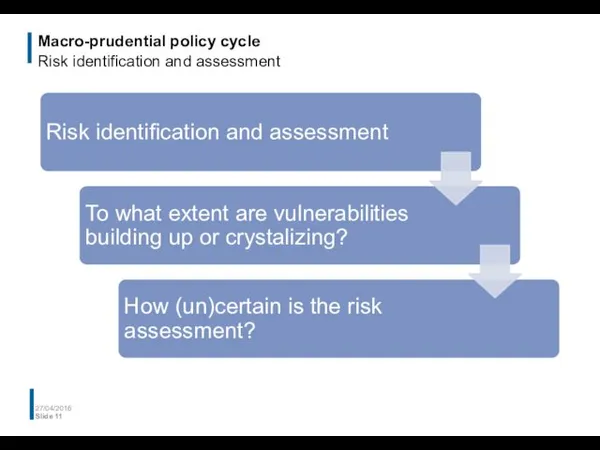
- 11. Macro-prudential policy cycle Risk identification and assessment 27/04/2016 Slide
- 12. Macro-prudential policy cycle Risk identification and assessment Key indicator books help to monitor and assess sources
- 13. Macro-prudential policy cycle Risk identification and assessment: Indicators – key findings 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
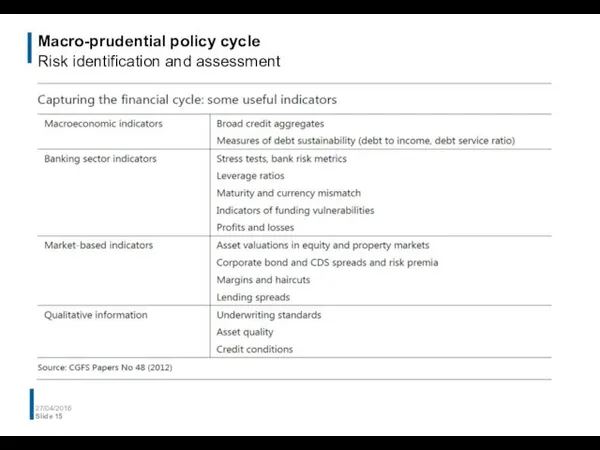
- 14. Macro-prudential policy cycle Risk identification and assessment 27/04/2016 Slide Potential questions to provide qualitative information about
- 15. Macro-prudential policy cycle Risk identification and assessment 27/04/2016 Slide
- 16. Macro-prudential policy cycle Instrument selection and calibration 27/04/2016 Slide Selecting macro-prudential instruments Macro-prudential policy must account
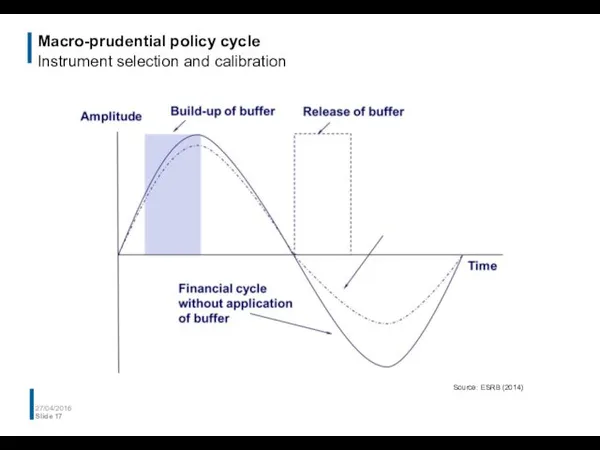
- 17. Macro-prudential policy cycle Instrument selection and calibration 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
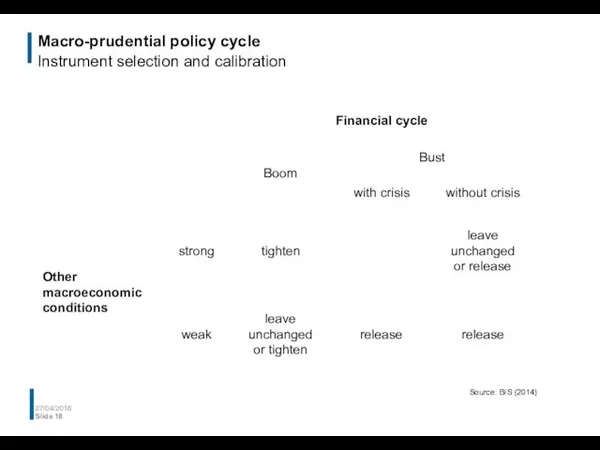
- 18. Macro-prudential policy cycle Instrument selection and calibration 27/04/2016 Slide Source: BIS (2014)
- 19. Macro-prudential policy cycle Instrument selection and calibration 27/04/2016 Slide Is there are robust link between changes
- 20. Macro-prudential policy cycle Instrument selection and calibration Effectiveness Degree to which market failure can be addressed
- 21. Macro-prudential policy cycle Instrument selection and calibration 27/04/2016 Slide Economic considerations Selection and calibration must of
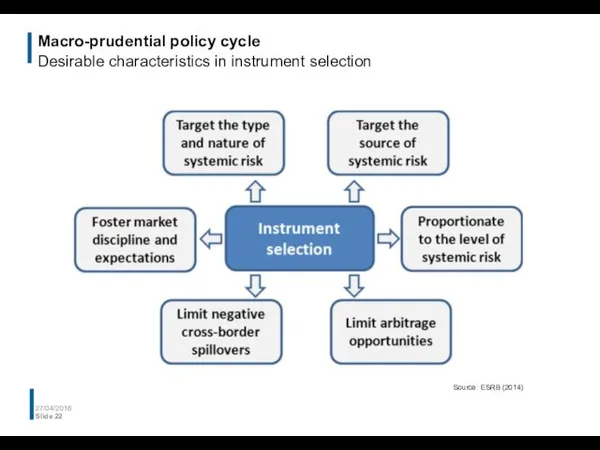
- 22. Macro-prudential policy cycle Desirable characteristics in instrument selection 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
- 23. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Indicative set of macro-prudential instruments 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2013)
- 24. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Instrument selection and calibration Design of the instruments: Broad-based versus
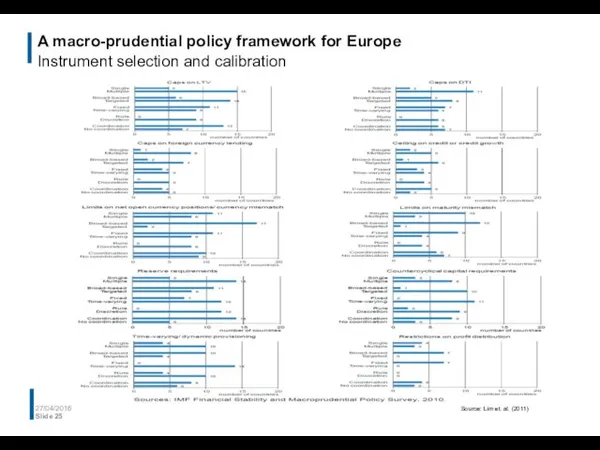
- 25. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Instrument selection and calibration 27/04/2016 Slide Source: Lim et. al.
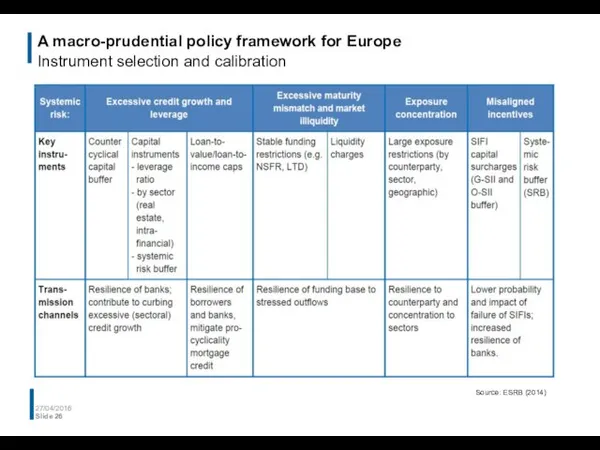
- 26. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Instrument selection and calibration 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
- 27. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation 27/04/2016 Slide Decisions on instrument implementation are based on a wide
- 28. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation 27/04/2016 Slide Policy implementation Guided discretion Communication Interaction with other policy
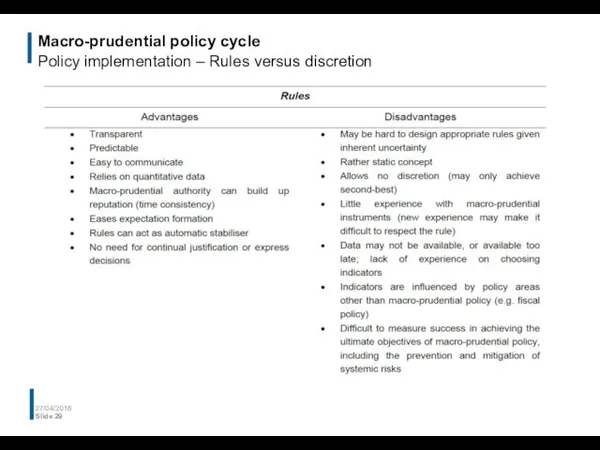
- 29. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation – Rules versus discretion 27/04/2016 Slide
- 30. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation – Rules versus discretion 27/04/2016 Slide
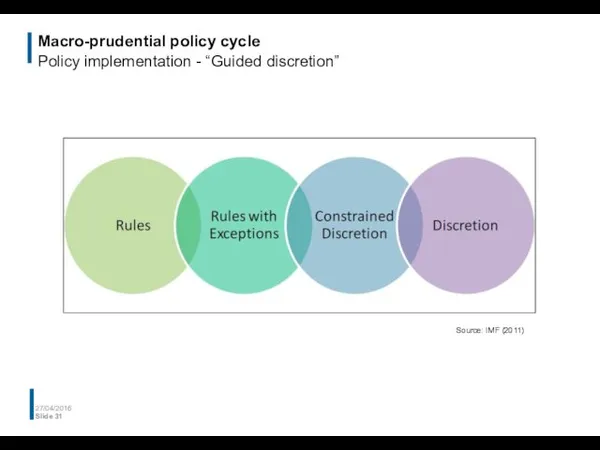
- 31. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation - “Guided discretion” 27/04/2016 Slide Source: IMF (2011)
- 32. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation - Communication Communication is key to macro-prudential policy: Fosters understanding among
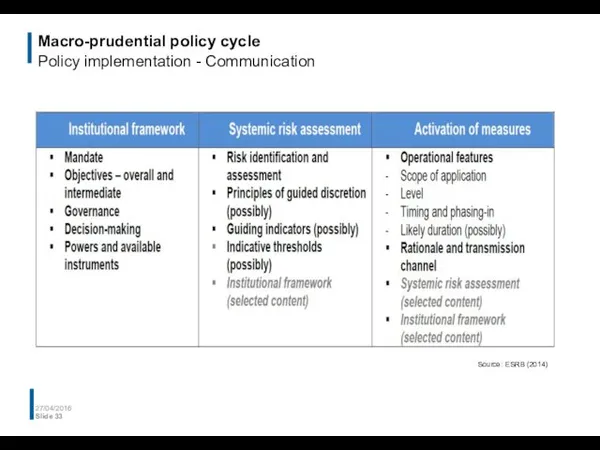
- 33. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation - Communication 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
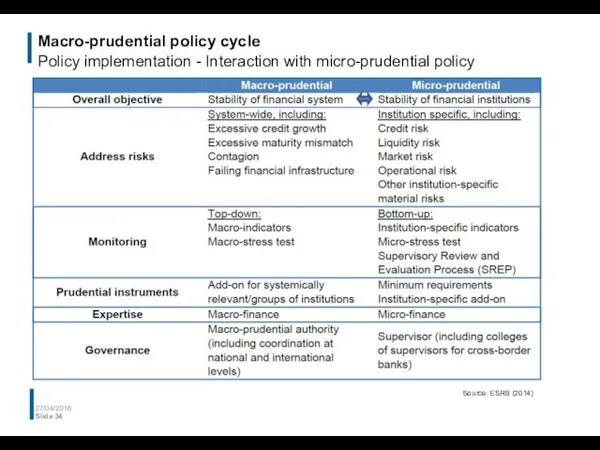
- 34. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation - Interaction with micro-prudential policy 27/04/2016 Slide Source: ESRB (2014)
- 35. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation - Interaction with other policy areas 27/04/2016 Slide Monetary policy Fiscal
- 36. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy implementation Objectives of monetary policy are distinct, but complement each other Monetary
- 37. Macro-prudential policy cycle Policy evaluation 27/04/2016 Slide Policy evaluation Evaluation is key element of the policy
- 38. Macro-prudential policy framework for Europe Coordination issues In order to arrive a holistic view on how
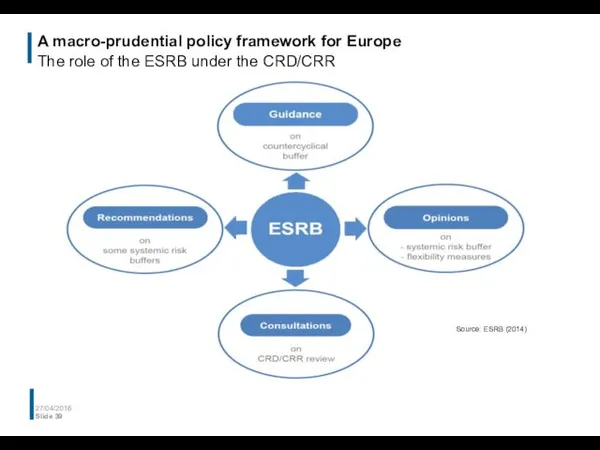
- 39. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe The role of the ESRB under the CRD/CRR 27/04/2016 Slide
- 40. A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe The role of the ESRB under the CRD/CRR 27/04/2016 Slide
- 41. Overview 27/04/2016 Slide Introduction Macro-prudential policy strategy Macro-prudential policy cycle - Risk identification and assessment -
- 42. Looking ahead Discussion 27/04/2016 Slide Key strategic directions for macro-prudential authorities Developing a macro-prudential strategy Such
- 43. References Bank for International Settlements, Committee on the Global Financial system, Operationalising the selection and application
- 45. Скачать презентацию




























 Социальная сфера
Социальная сфера Исследование и разработка системы автоматического управления процессом сушки аммиачной селитры
Исследование и разработка системы автоматического управления процессом сушки аммиачной селитры Психология межличностных и межгрупповых отношений
Психология межличностных и межгрупповых отношений Стили управления временным детским коллективом. Лидерство
Стили управления временным детским коллективом. Лидерство Виды треугольников
Виды треугольников Презентация для классного часа Моя малая родина
Презентация для классного часа Моя малая родина Месячник ЗОЖ в начальной школе
Месячник ЗОЖ в начальной школе Иммунопрофилактика и иммунотерапия
Иммунопрофилактика и иммунотерапия Выпускники техникума – Герои ВОВ
Выпускники техникума – Герои ВОВ Таблицы истинности. Логические схемы. 10 класс
Таблицы истинности. Логические схемы. 10 класс Презентация История моего города
Презентация История моего города Анатомия и физиология обонятельного анализатора
Анатомия и физиология обонятельного анализатора Падежи имен прилагательных
Падежи имен прилагательных Гендерное воспитание
Гендерное воспитание торговое оборудование
торговое оборудование Додавання раціональних чисел
Додавання раціональних чисел Категории реальное и виртуальное в философии
Категории реальное и виртуальное в философии Irregular Verbs
Irregular Verbs Дизартрия и основные приемы ее коррекции в ДОУ
Дизартрия и основные приемы ее коррекции в ДОУ Компоненты средств ИВТ
Компоненты средств ИВТ Фильтр оценки состояния для непрерывных систем (наблюдатель вектора состояния)
Фильтр оценки состояния для непрерывных систем (наблюдатель вектора состояния) Источники водоснабжения и водозаборные сооружения. (Тема 3)
Источники водоснабжения и водозаборные сооружения. (Тема 3) ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЕ ШКОЛЫ И СЕМЬИ В ДУХОВНО-НРАВСТВЕННОМ ВОСПИТАНИИ МЛАДШЕГО ШКОЛЬНИКА
ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЕ ШКОЛЫ И СЕМЬИ В ДУХОВНО-НРАВСТВЕННОМ ВОСПИТАНИИ МЛАДШЕГО ШКОЛЬНИКА Техногенные чрезвычайные ситуации
Техногенные чрезвычайные ситуации Творчество Салтыкова-Щедрина
Творчество Салтыкова-Щедрина Пыль и её влияние на жизнь человека
Пыль и её влияние на жизнь человека Family
Family Первая помощь при повреждении грудной клетки
Первая помощь при повреждении грудной клетки