Содержание
- 2. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) + Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) II Small-angle scattering (SAS)
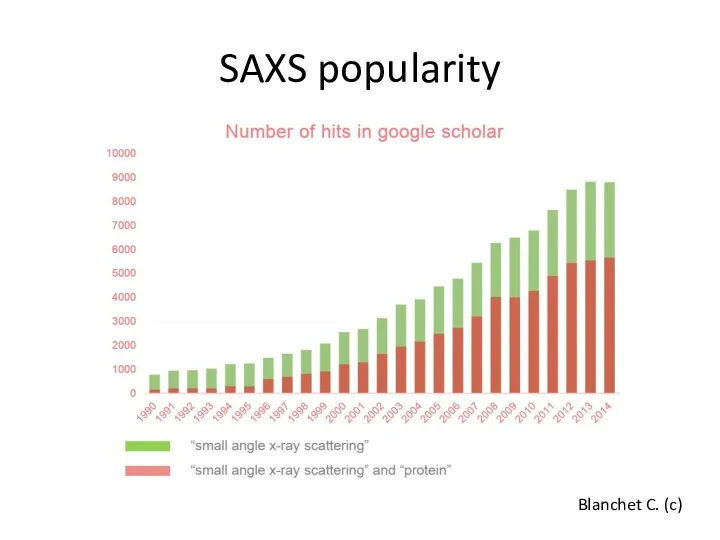
- 3. SAXS popularity Blanchet C. (c)
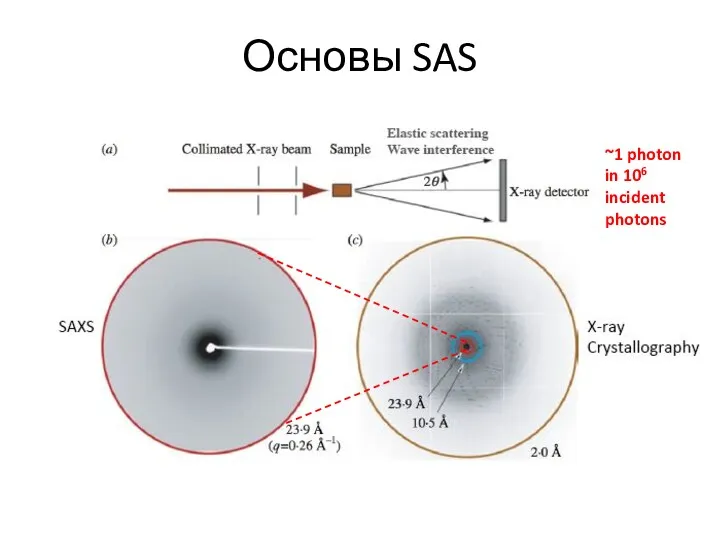
- 4. Основы SAS ~1 photon in 106 incident photons
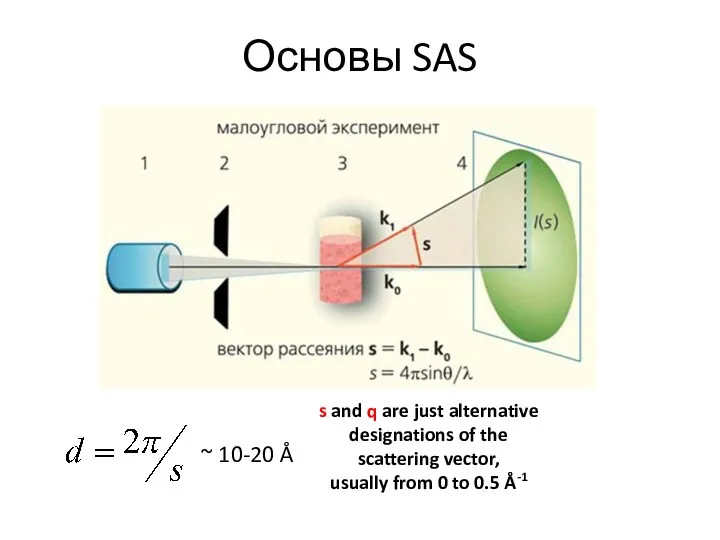
- 5. Основы SAS s and q are just alternative designations of the scattering vector, usually from 0
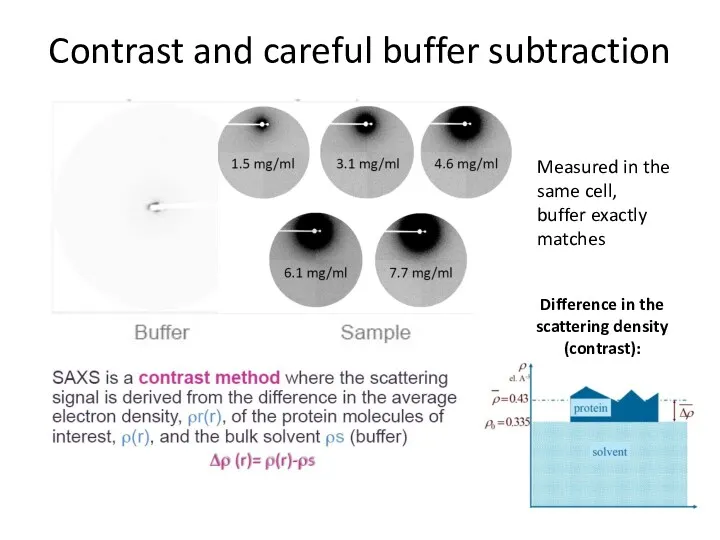
- 6. Contrast and careful buffer subtraction Measured in the same cell, buffer exactly matches Difference in the
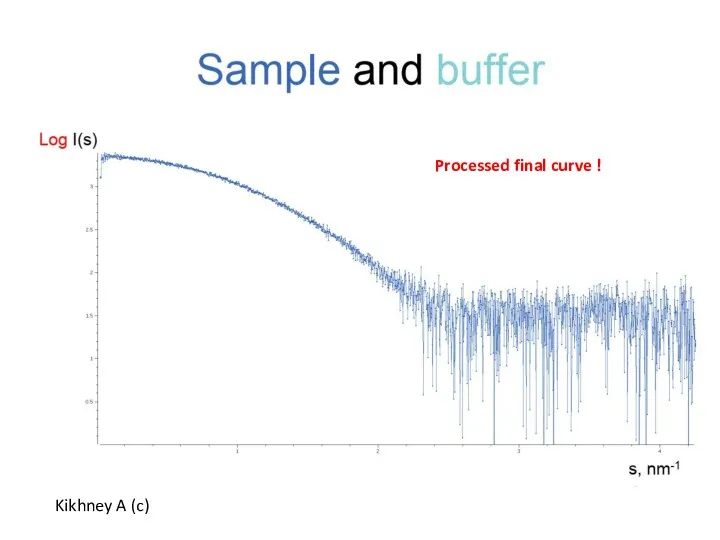
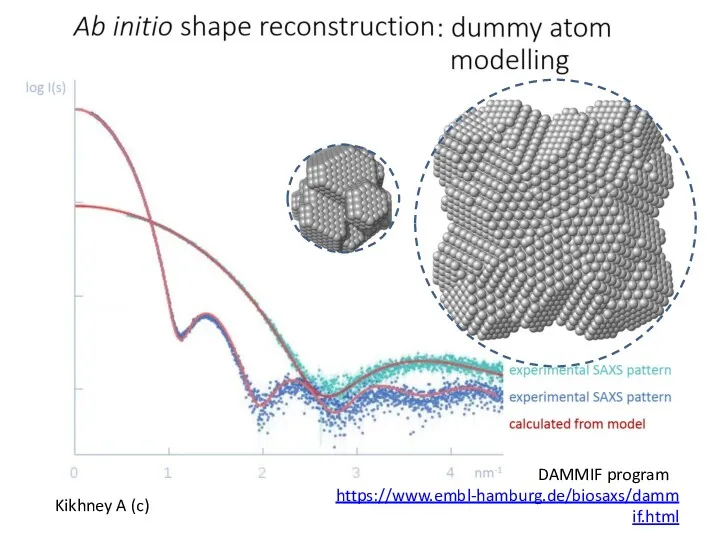
- 7. Kikhney A (c) Processed final curve !
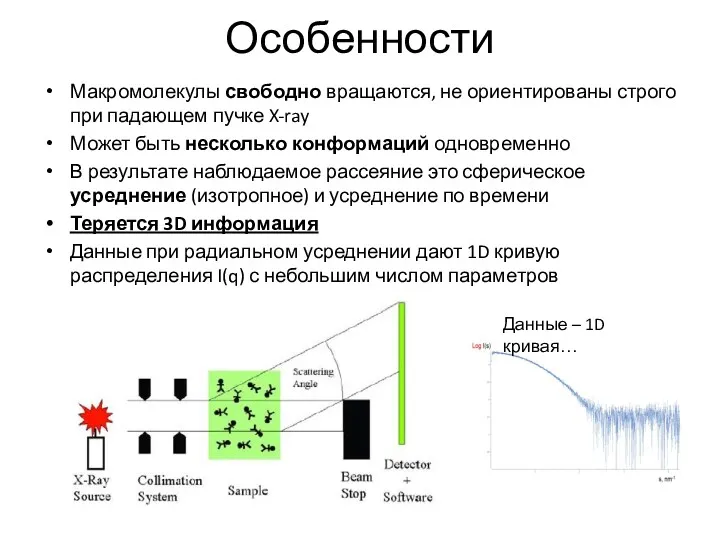
- 8. Особенности Макромолекулы свободно вращаются, не ориентированы строго при падающем пучке X-ray Может быть несколько конформаций одновременно
- 10. https://www.embl-hamburg.de/biosaxs/software.html
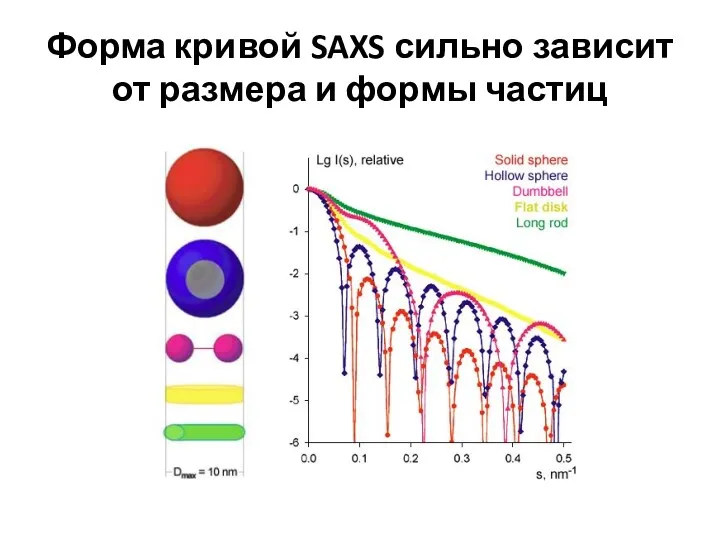
- 11. Форма кривой SAXS сильно зависит от размера и формы частиц
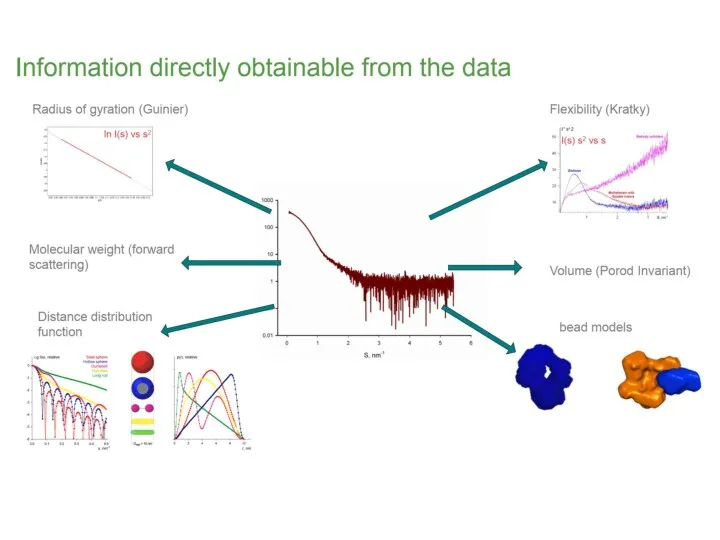
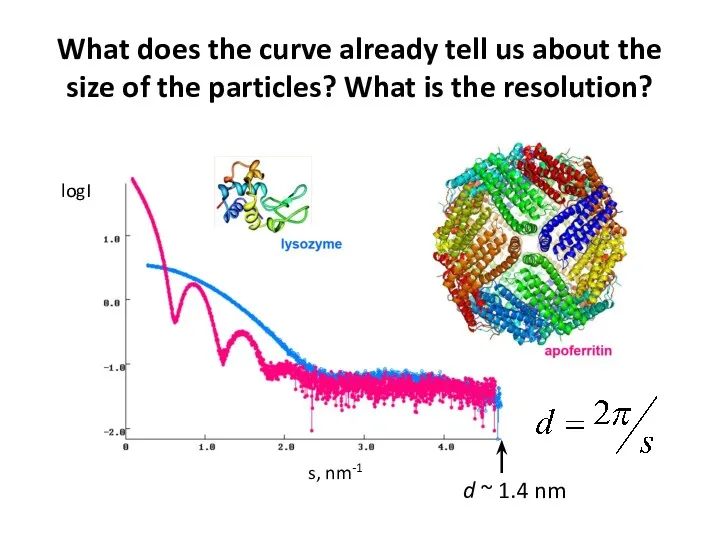
- 12. What does the curve already tell us about the size of the particles? What is the
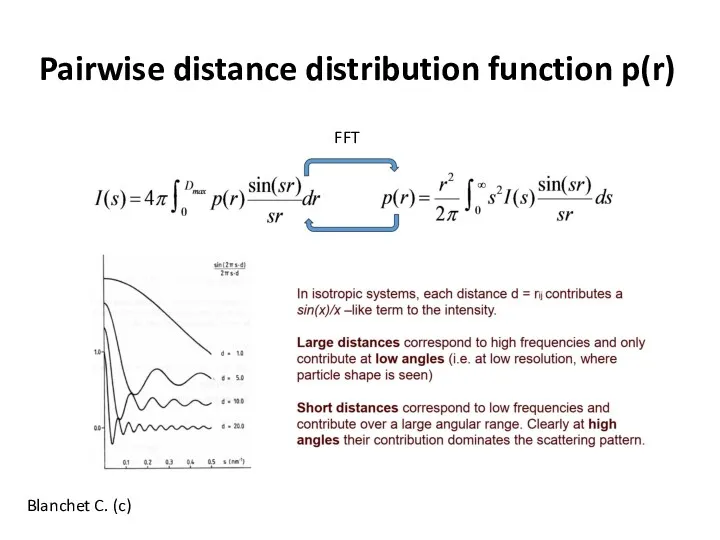
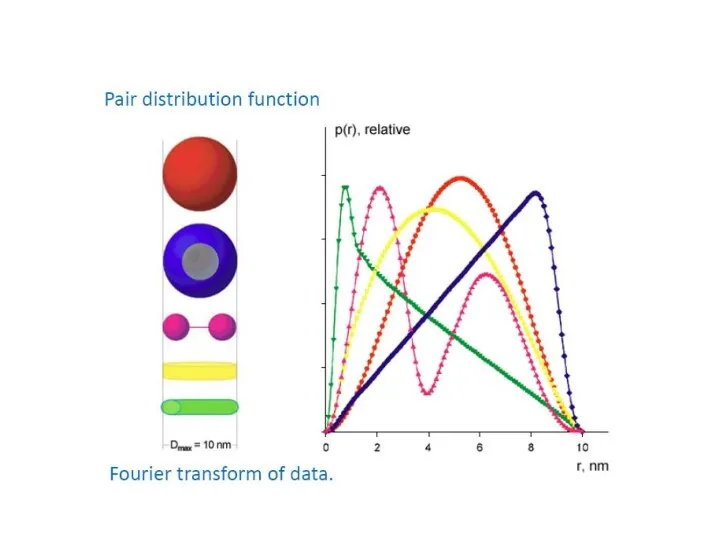
- 13. Pairwise distance distribution function p(r) Blanchet C. (c) FFT
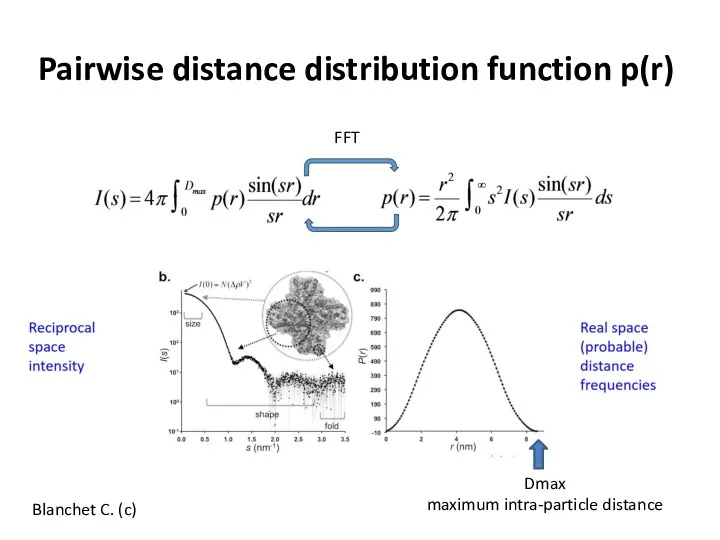
- 14. Pairwise distance distribution function p(r) Blanchet C. (c) FFT Dmax maximum intra-particle distance
- 16. Kikhney A (c) DAMMIF program https://www.embl-hamburg.de/biosaxs/dammif.html
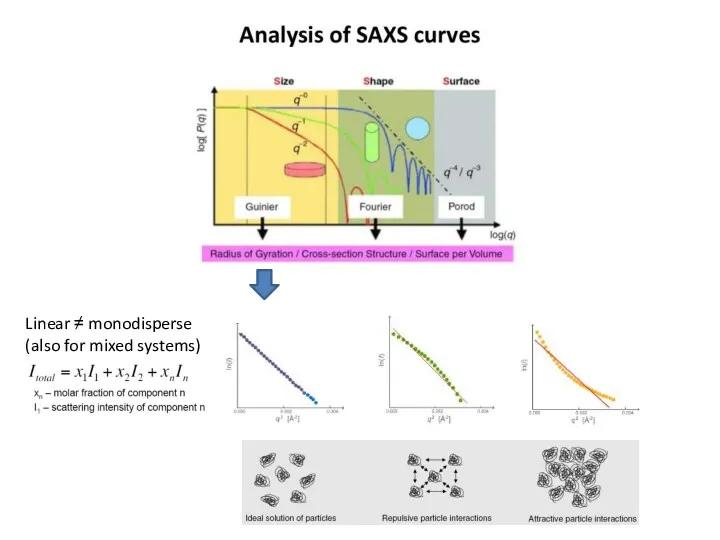
- 20. Linear ≠ monodisperse (also for mixed systems)
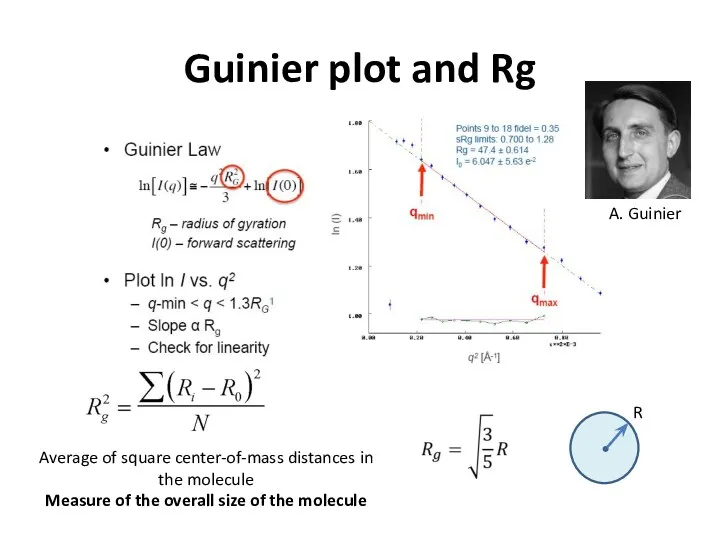
- 21. Guinier plot and Rg Average of square center-of-mass distances in the molecule Measure of the overall
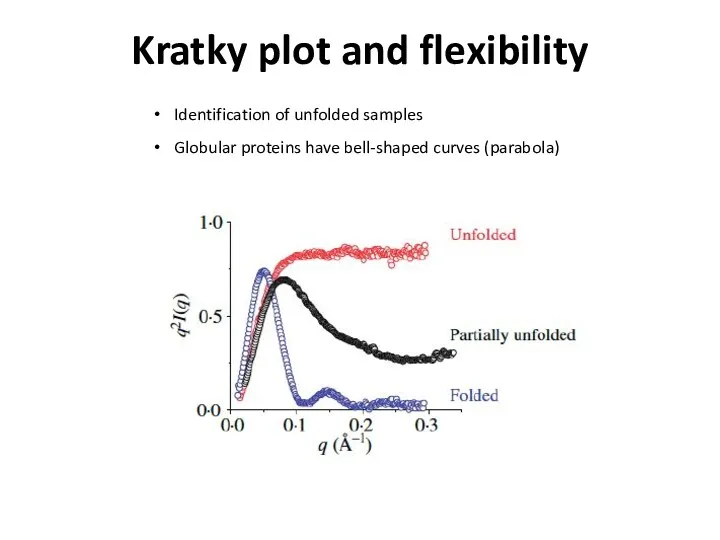
- 22. Kratky plot and flexibility Identification of unfolded samples Globular proteins have bell-shaped curves (parabola)
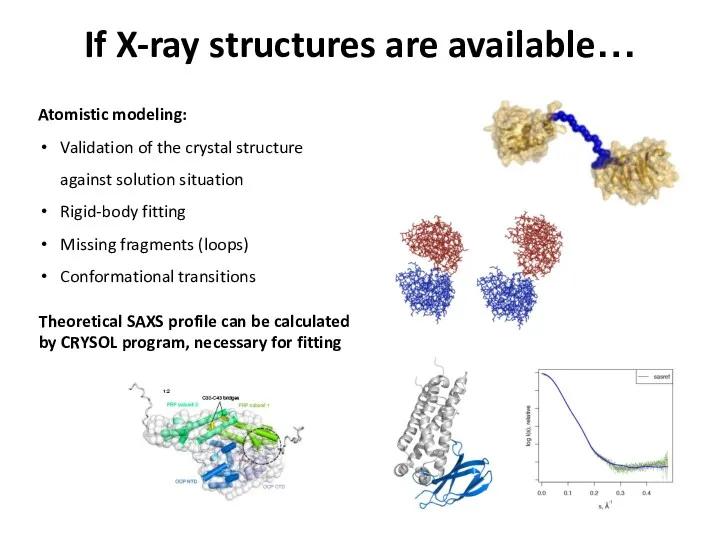
- 23. If X-ray structures are available… Atomistic modeling: Validation of the crystal structure against solution situation Rigid-body
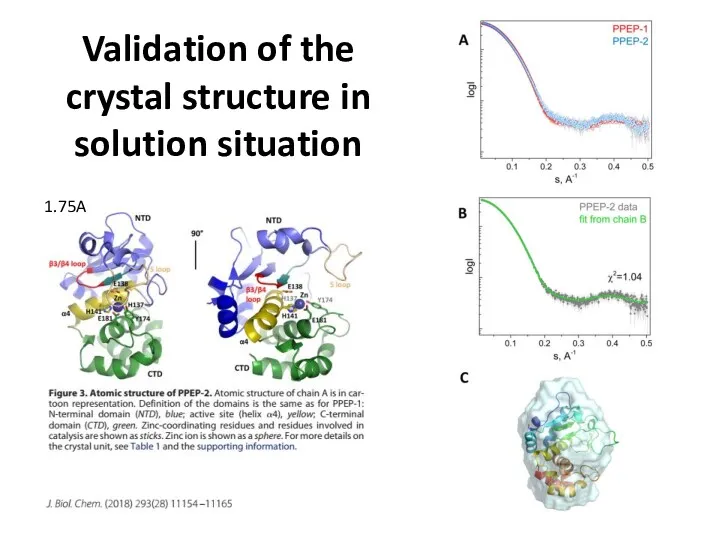
- 24. Validation of the crystal structure in solution situation 1.75A
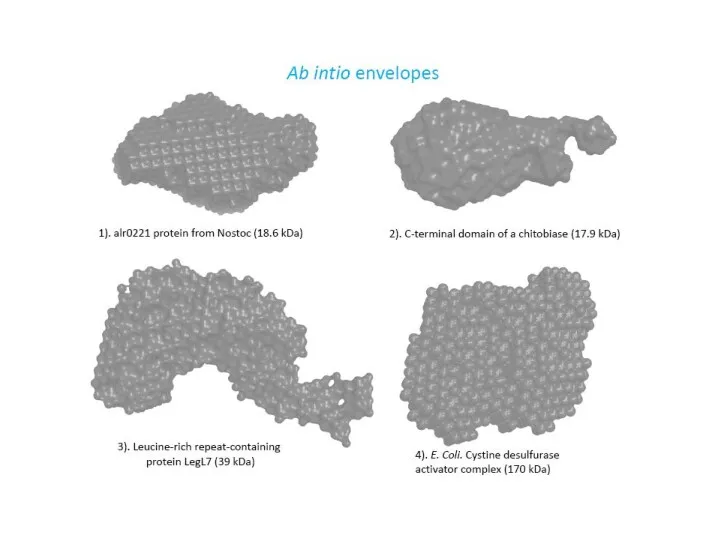
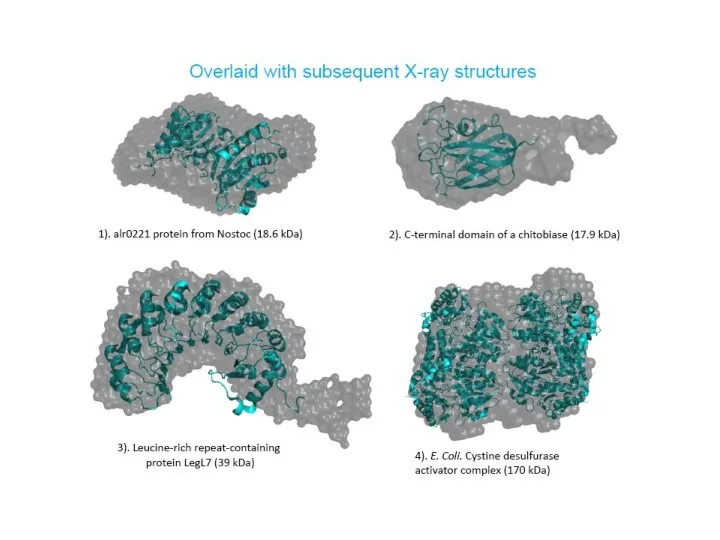
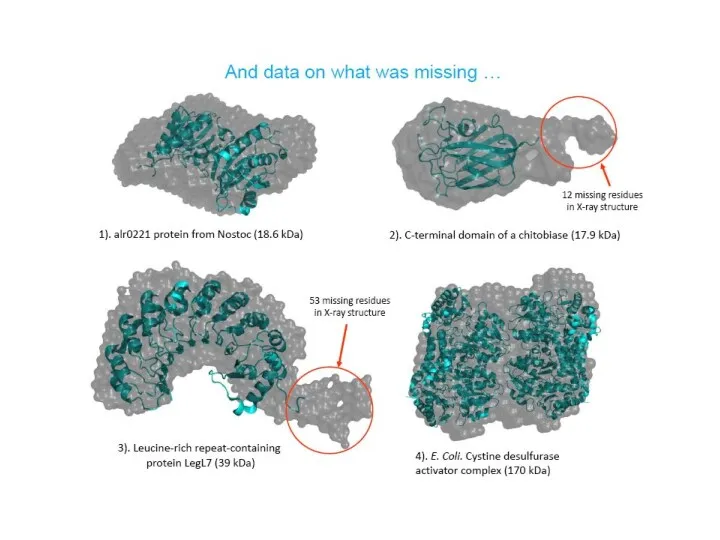
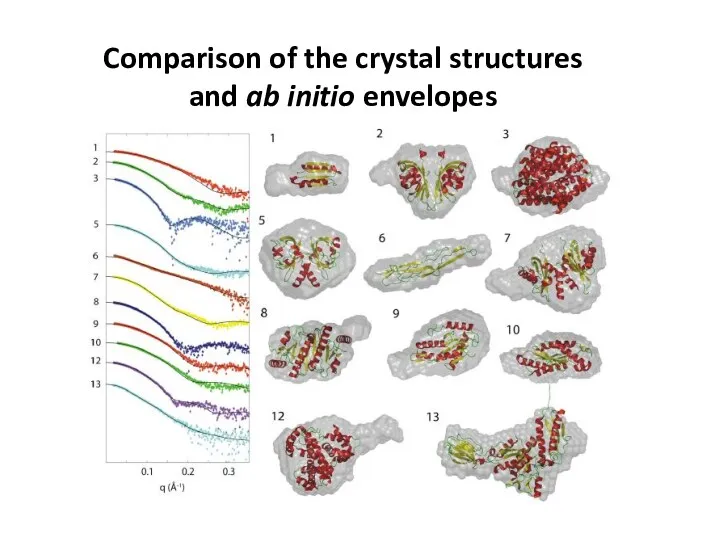
- 25. Comparison of the crystal structures and ab initio envelopes
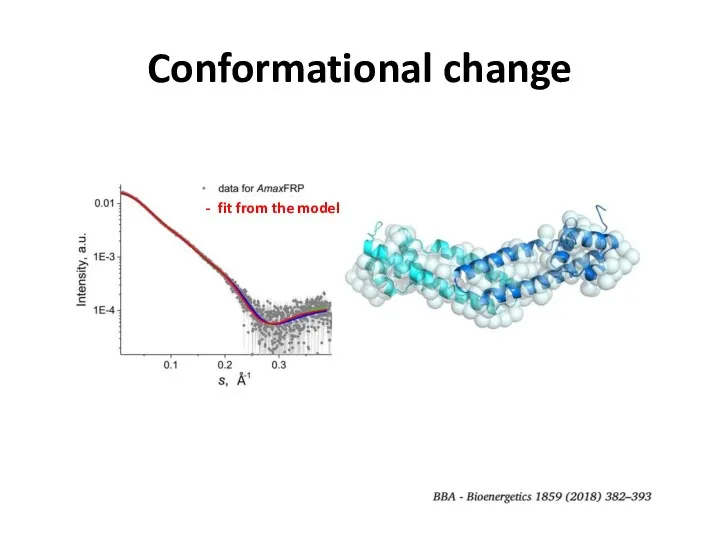
- 26. Conformational change
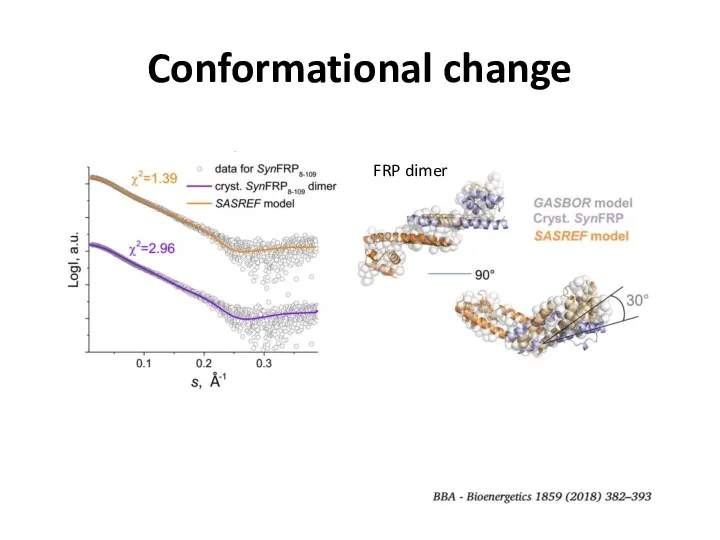
- 27. Conformational change FRP dimer
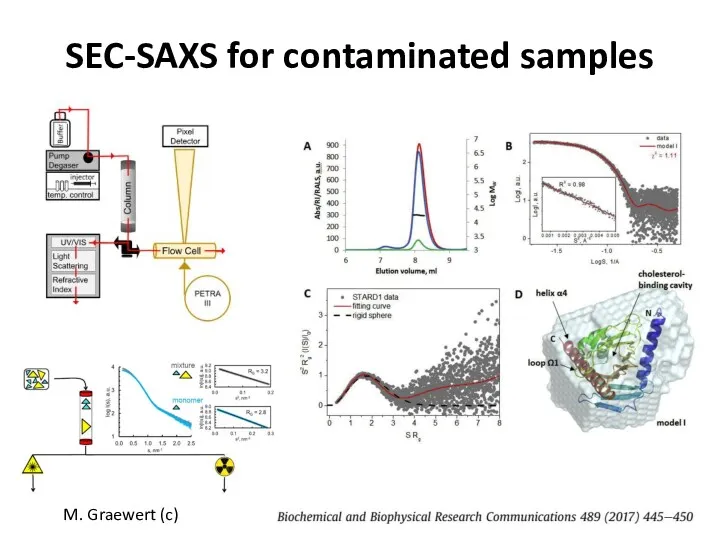
- 28. SEC-SAXS for contaminated samples M. Graewert (c)
- 29. SASBDB https://www.sasbdb.org/aboutSASBDB/
- 30. Трезвый взгляд на SAXS Дает хорошую информацию о гидродинамических свойствах частиц (структурных свойствах) в растворе Хорош
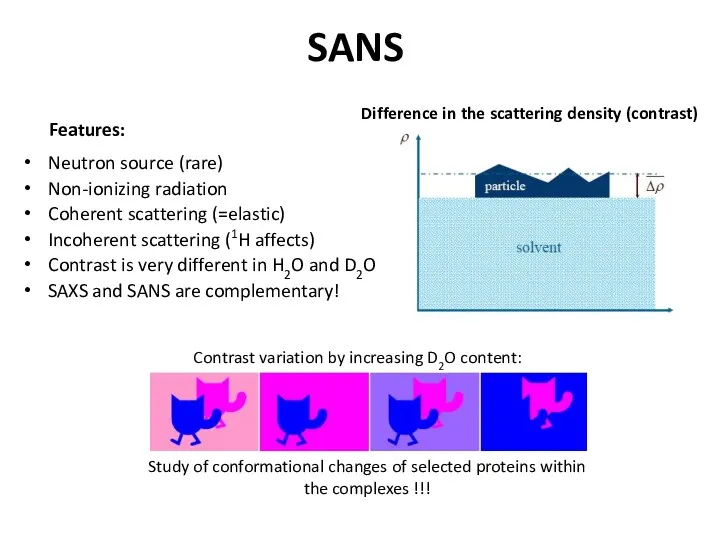
- 31. SANS Neutron source (rare) Non-ionizing radiation Coherent scattering (=elastic) Incoherent scattering (1H affects) Contrast is very
- 32. Samples for SAXS and SANS
- 33. CryoEM https://www.nature.com/news/the-revolution-will-not-be-crystallized-a-new-method-sweeps-through-structural-biology-1.18335 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aHhmnxD6RCI
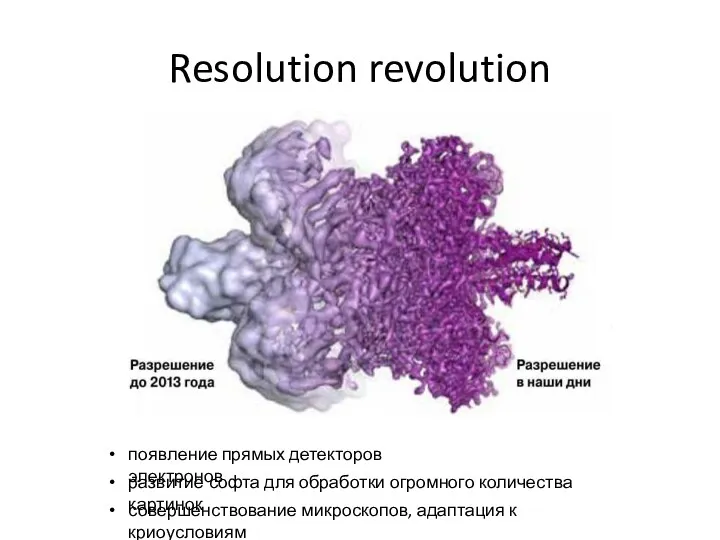
- 34. Resolution revolution появление прямых детекторов электронов развитие софта для обработки огромного количества картинок совершенствование микроскопов, адаптация
- 35. The recipe includes https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJKkC0W-6Qk
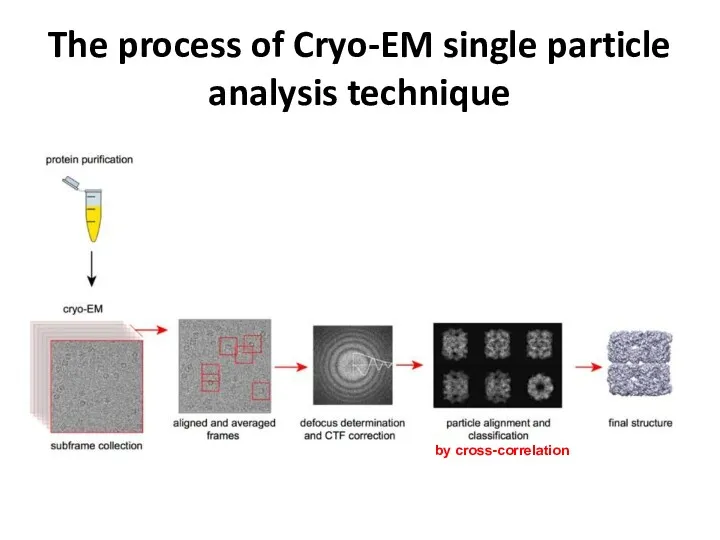
- 36. The process of Cryo-EM single particle analysis technique by cross-correlation
- 37. Features, 2D->3D Biological samples – low doses and dehydration (high vacuum) Freezing allows to avoid these,
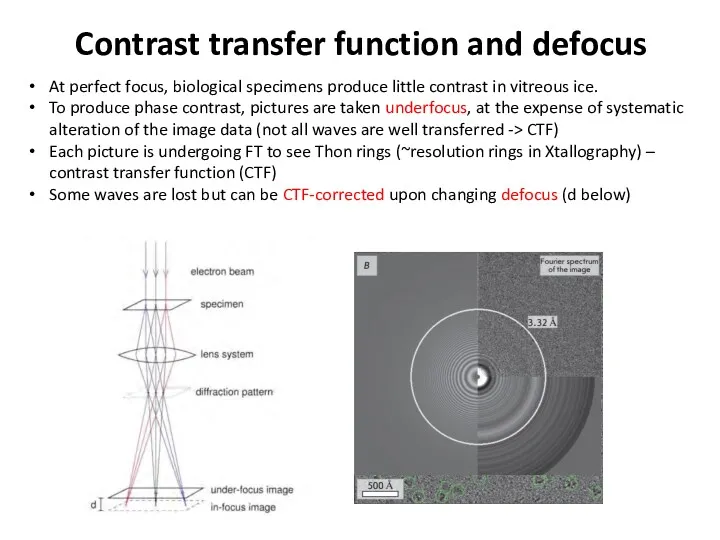
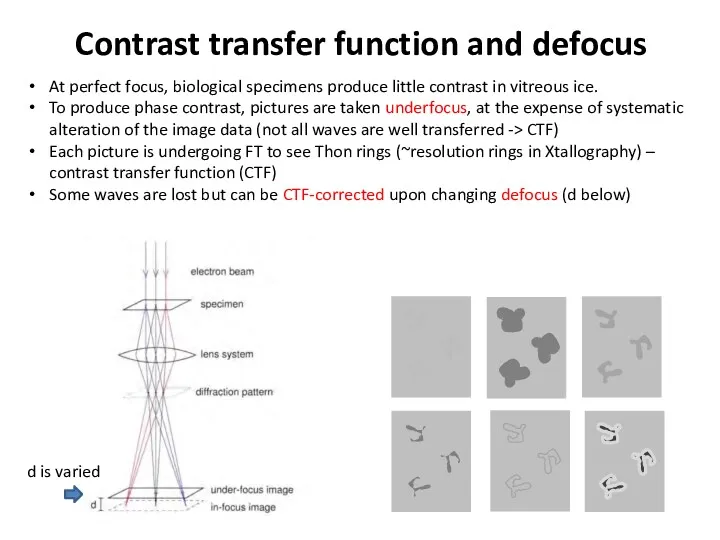
- 38. Contrast transfer function and defocus At perfect focus, biological specimens produce little contrast in vitreous ice.
- 39. Contrast transfer function and defocus At perfect focus, biological specimens produce little contrast in vitreous ice.
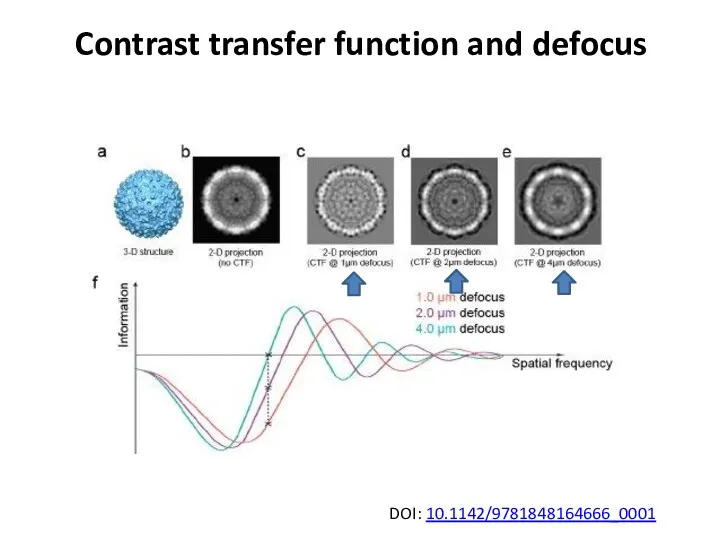
- 40. Contrast transfer function and defocus DOI: 10.1142/9781848164666_0001
- 41. Single particle cryoEM requires tons of images Particle orientations are classified by cross-correlation Each class should
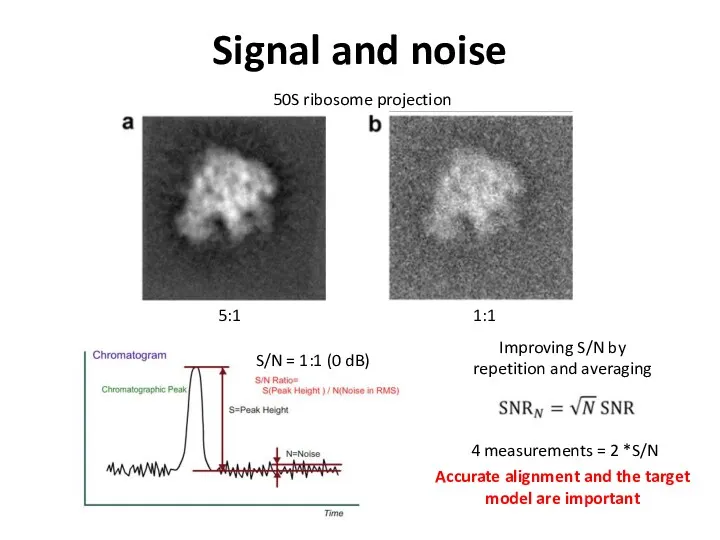
- 42. Signal and noise 5:1 1:1 S/N = 1:1 (0 dB) Improving S/N by repetition and averaging
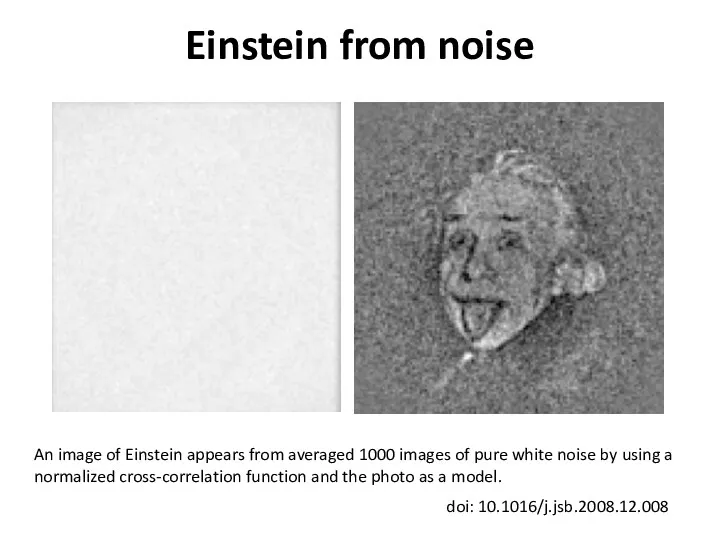
- 43. Einstein from noise An image of Einstein appears from averaged 1000 images of pure white noise
- 44. Обучение криоЭМ https://ru.coursera.org/learn/cryo-em https://em-learning.com https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bk5lBvwSe-s Prof. Yifan Cheng
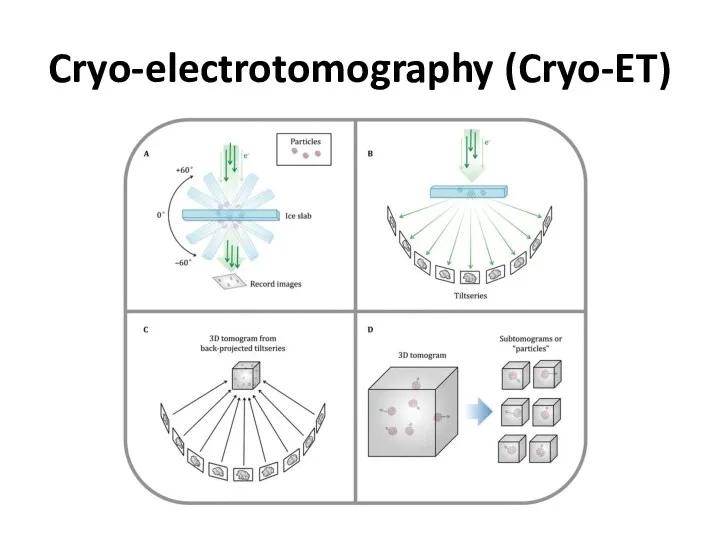
- 46. Cryo-electrotomography (Cryo-ET)
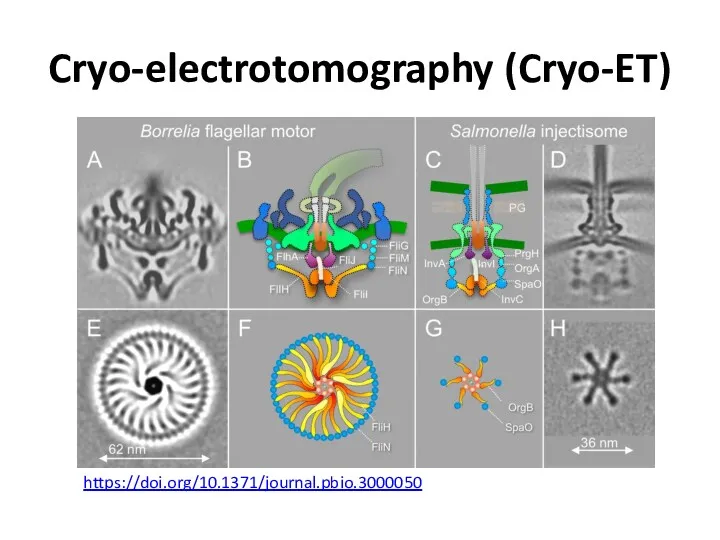
- 47. Cryo-electrotomography (Cryo-ET) https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000050
- 48. NMR – nuclear magnetic resonance https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0s7Cbl8bZLM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eY0NyE0SQjE ☺ NMR made super easy:
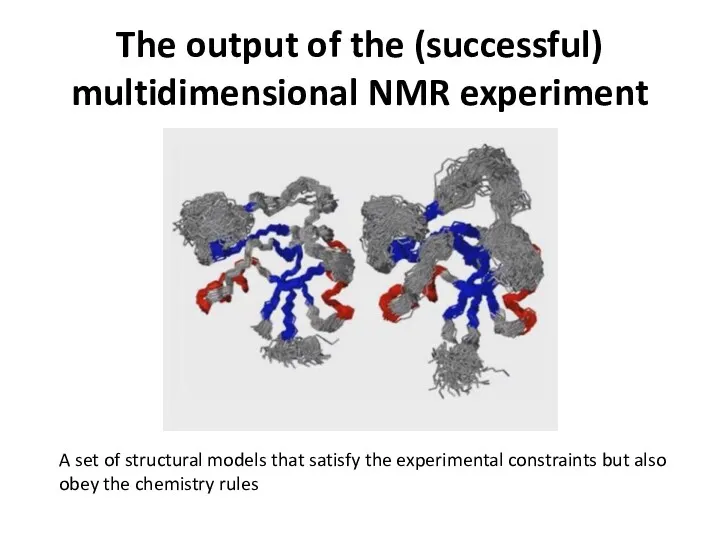
- 49. The output of the (successful) multidimensional NMR experiment A set of structural models that satisfy the
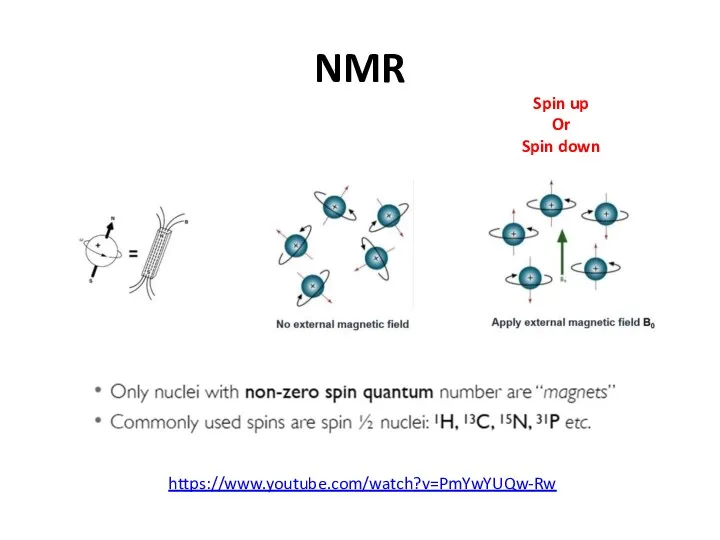
- 50. NMR Spin up Or Spin down https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PmYwYUQw-Rw
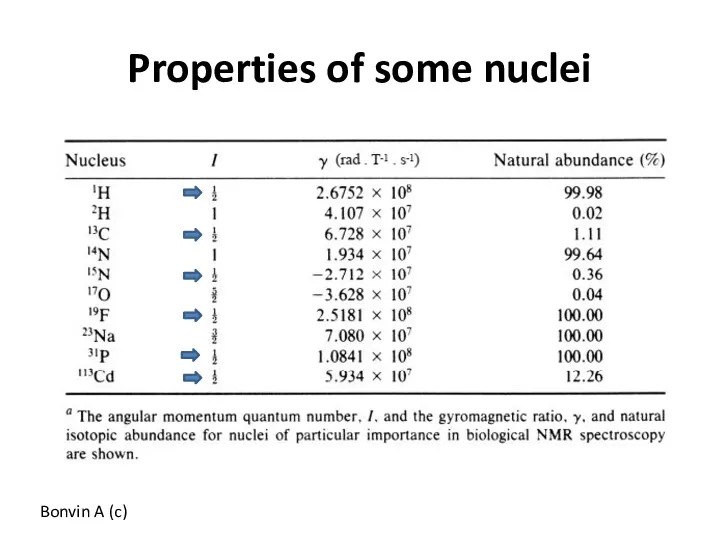
- 51. Properties of some nuclei Bonvin A (c)
- 52. NMR sample Bonvin A (c)
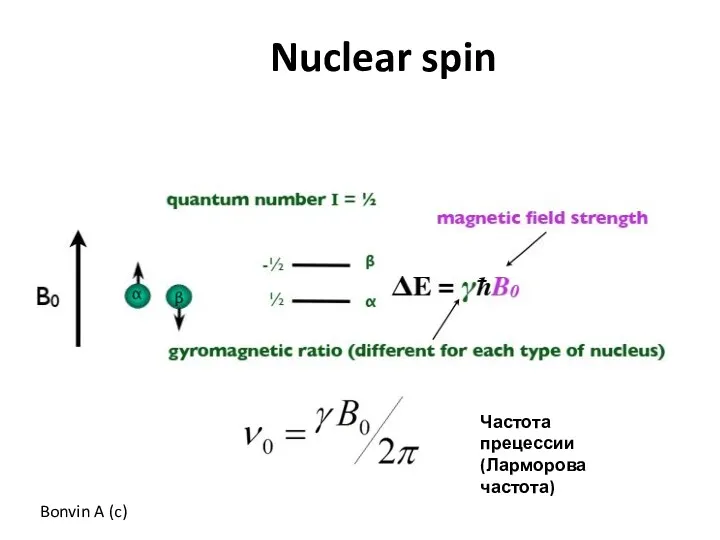
- 53. Bonvin A (c) Nuclear spin Частота прецессии (Ларморова частота)
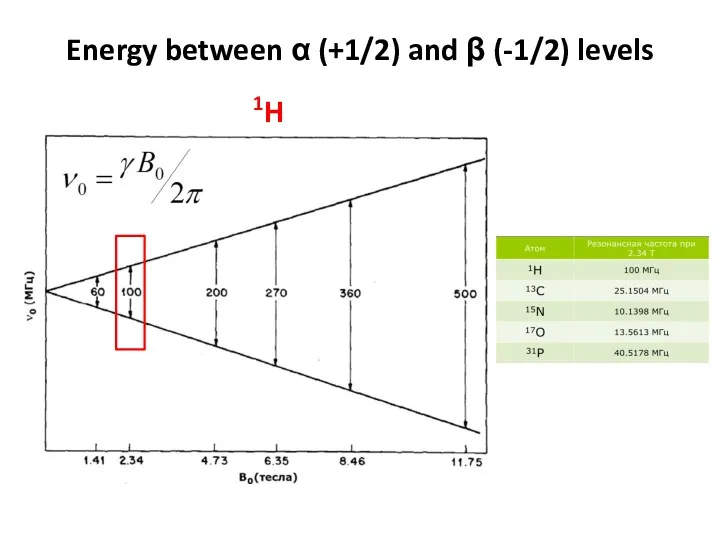
- 54. Energy between α (+1/2) and β (-1/2) levels 1H
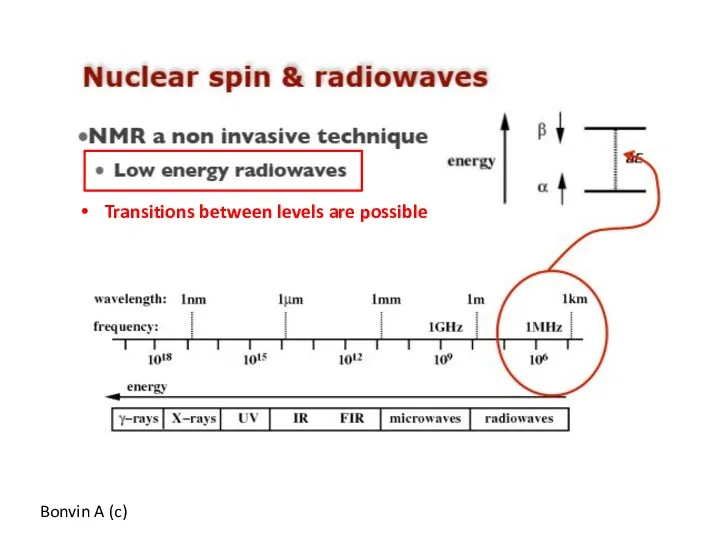
- 55. Transitions between levels are possible
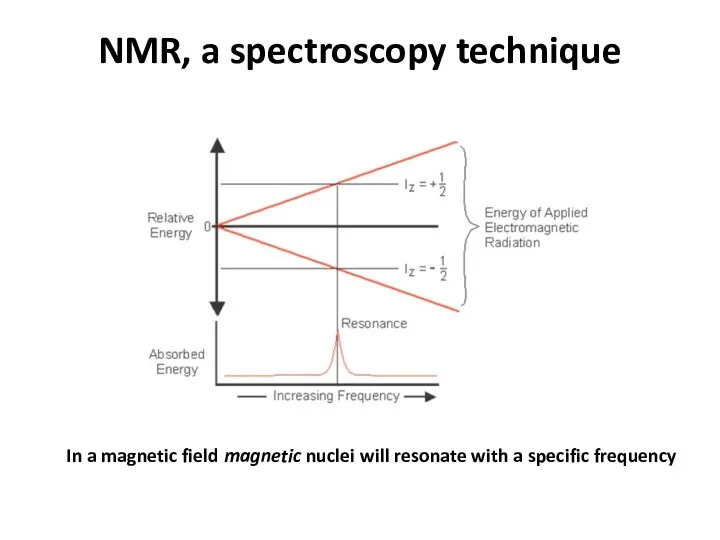
- 56. NMR, a spectroscopy technique In a magnetic field magnetic nuclei will resonate with a specific frequency
- 57. Bonvin A (c)
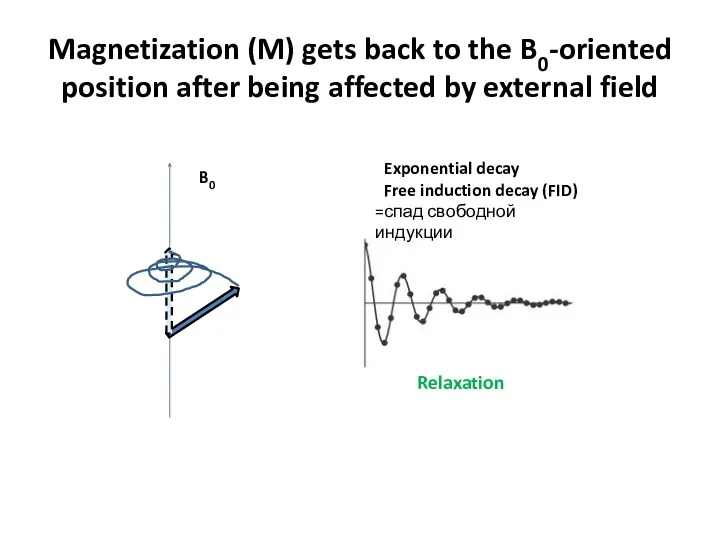
- 58. Magnetization (M) gets back to the B0-oriented position after being affected by external field B0 Exponential
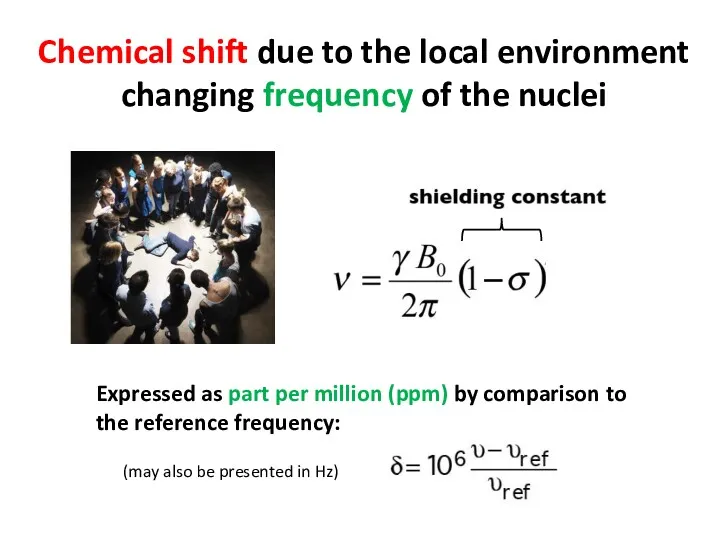
- 59. Chemical shift due to the local environment changing frequency of the nuclei Expressed as part per
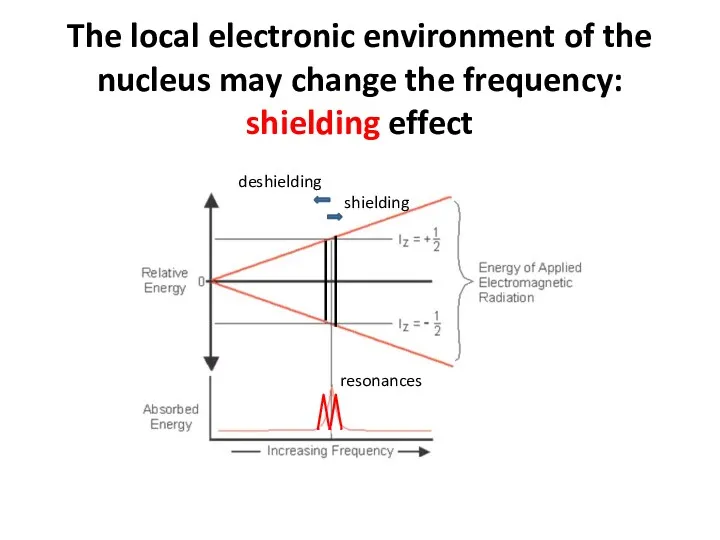
- 60. The local electronic environment of the nucleus may change the frequency: shielding effect resonances deshielding shielding
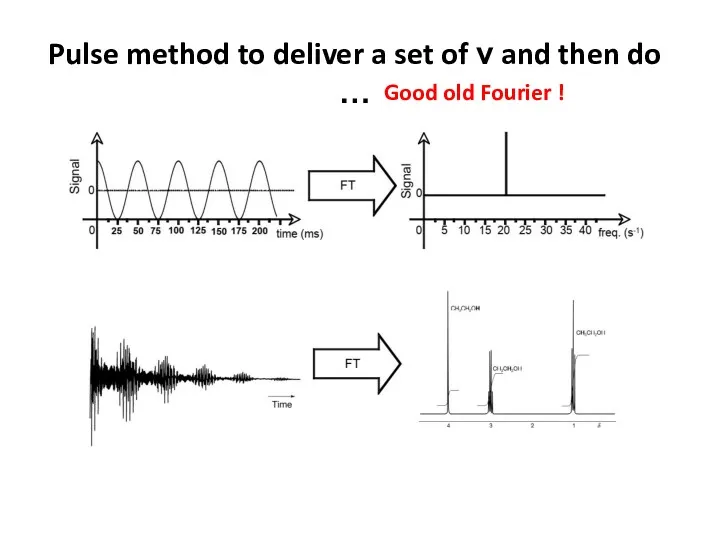
- 61. Pulse method to deliver a set of ν and then do … Good old Fourier !
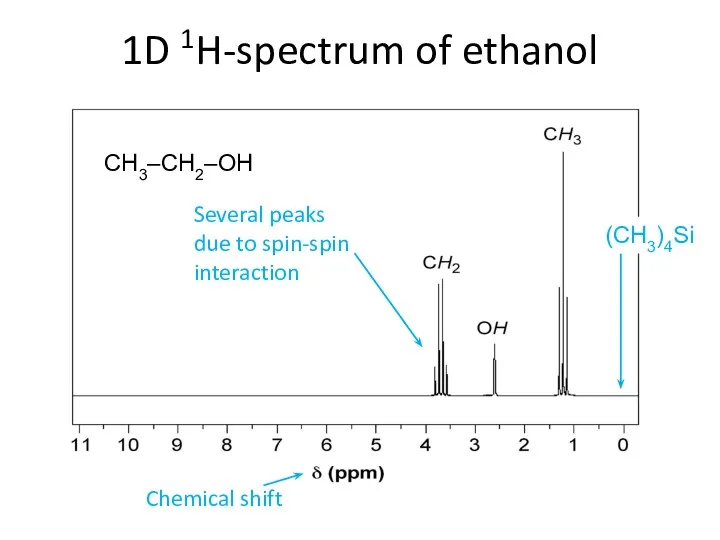
- 62. 1D 1H-spectrum of ethanol CH3–CH2–OH (CH3)4Si Chemical shift Several peaks due to spin-spin interaction
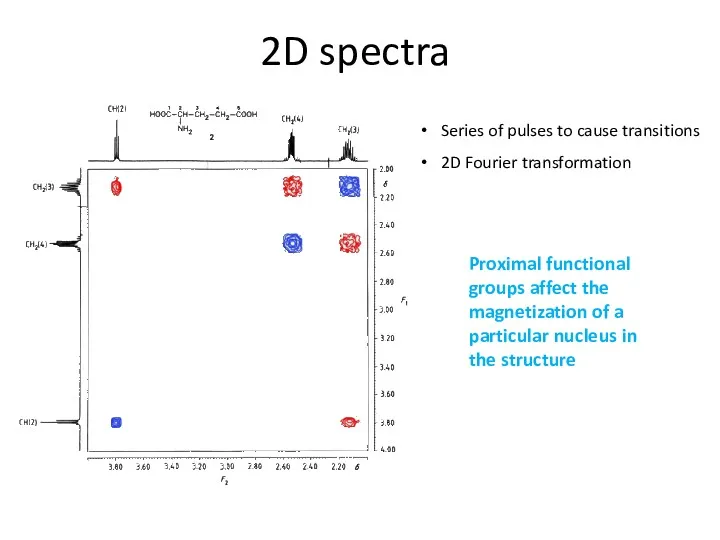
- 63. 2D spectra Series of pulses to cause transitions 2D Fourier transformation Proximal functional groups affect the
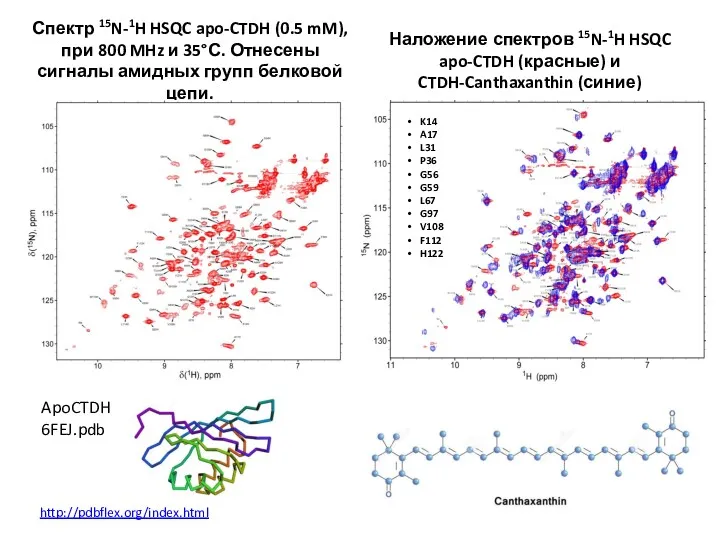
- 64. Спектр 15N-1H HSQC apo-CTDH (0.5 mM), при 800 MHz и 35°С. Отнесены сигналы амидных групп белковой
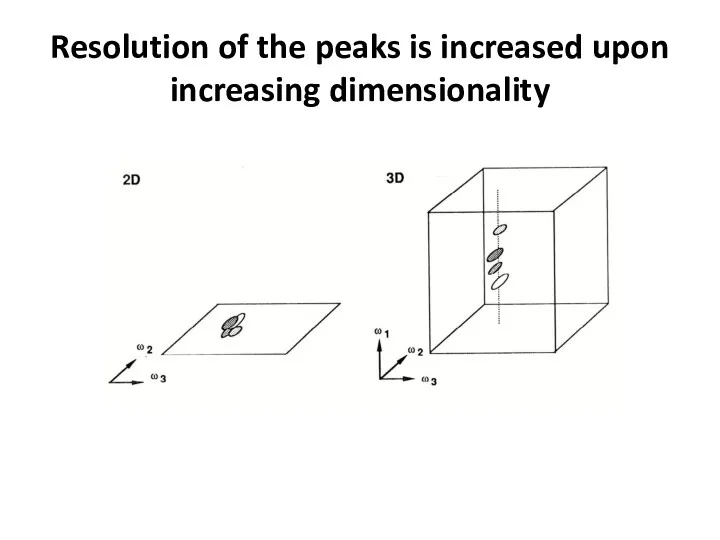
- 65. Resolution of the peaks is increased upon increasing dimensionality
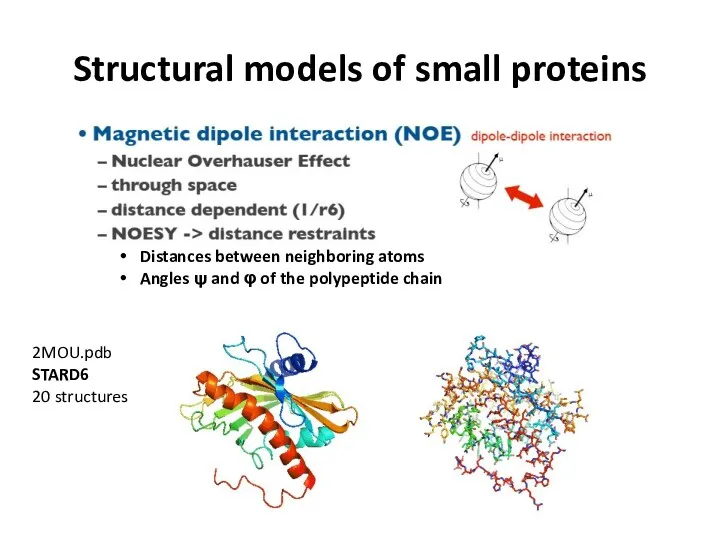
- 66. Structural models of small proteins Distances between neighboring atoms Angles ψ and φ of the polypeptide
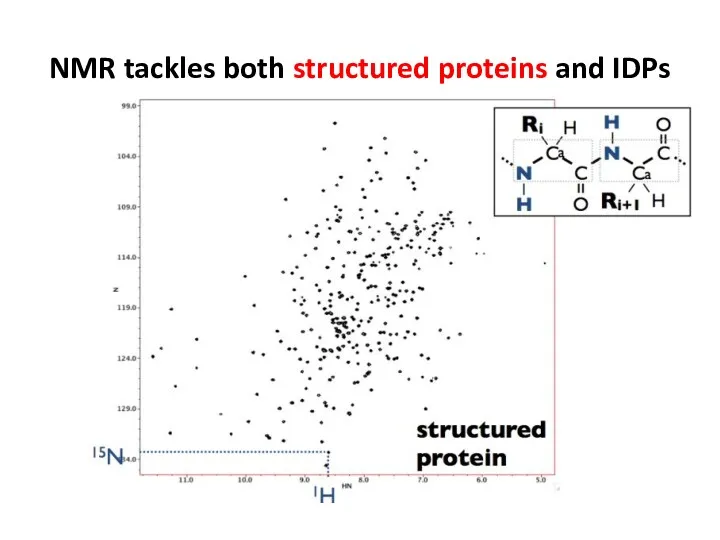
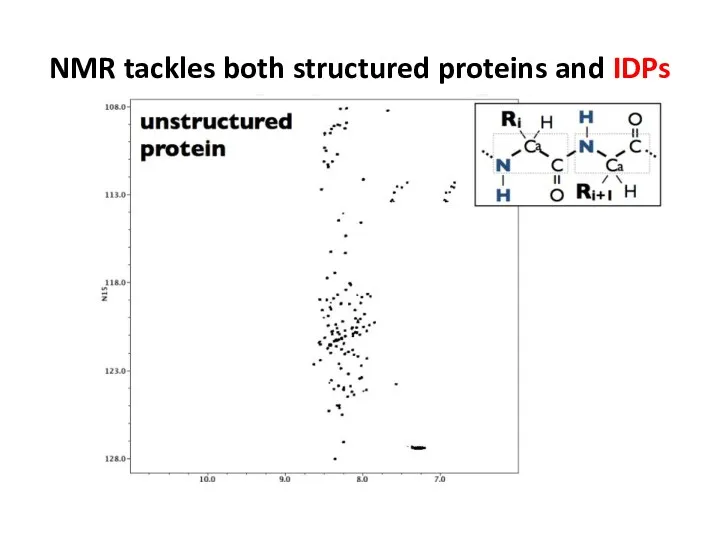
- 67. NMR tackles both structured proteins and IDPs
- 68. NMR tackles both structured proteins and IDPs
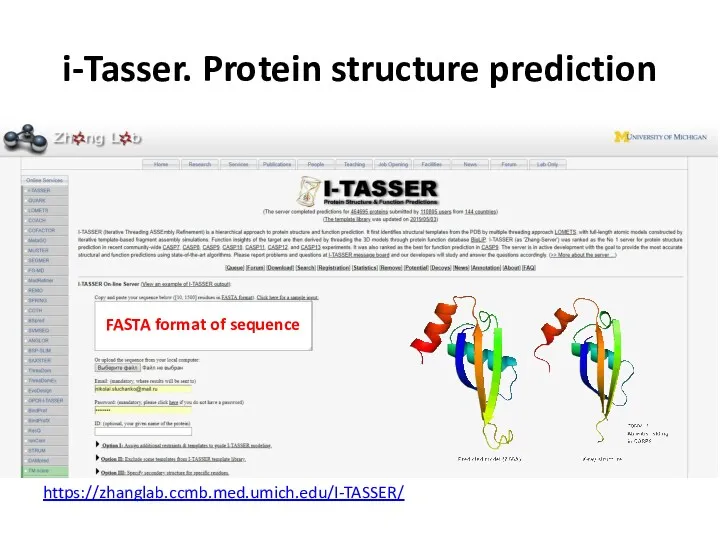
- 69. i-Tasser. Protein structure prediction FASTA format of sequence https://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/I-TASSER/
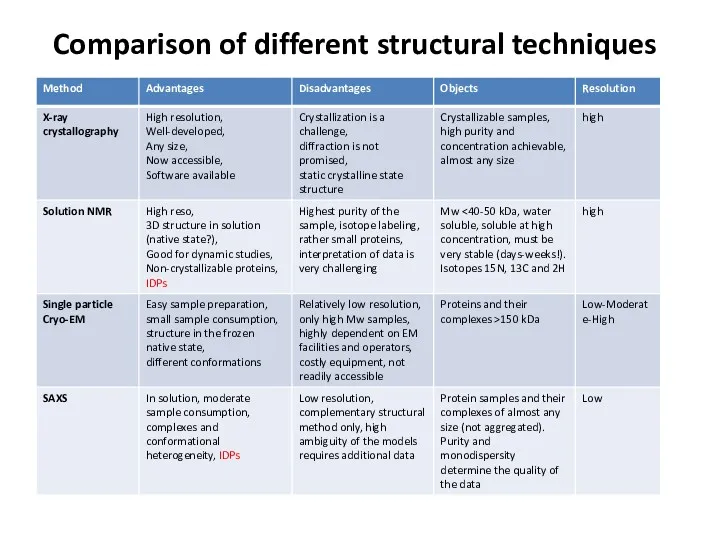
- 70. Comparison of different structural techniques
- 71. Integrated approaches in structural biology X-ray crystallography SAXS NMR CryoEM Auxillary techniques: fluorescence resonanse energy transfer
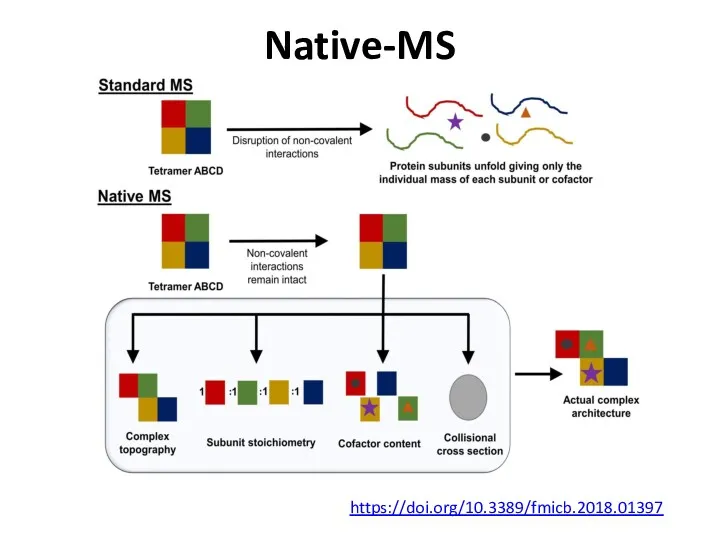
- 72. Native-MS https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01397
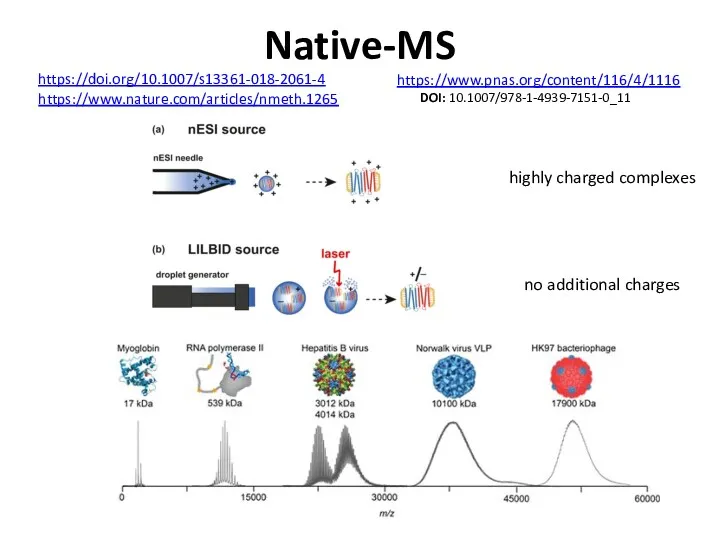
- 73. Native-MS https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-018-2061-4 highly charged complexes no additional charges https://www.nature.com/articles/nmeth.1265 https://www.pnas.org/content/116/4/1116 DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7151-0_11
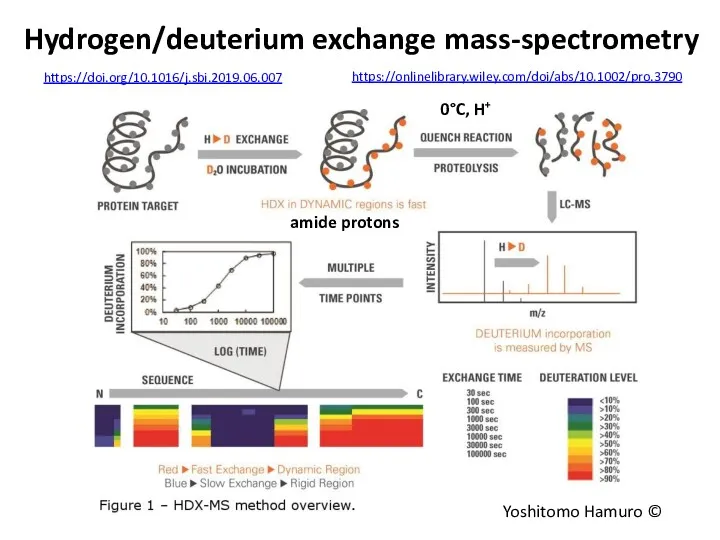
- 74. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass-spectrometry Yoshitomo Hamuro © 0°C, H+ https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.06.007 https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pro.3790 amide protons
- 75. Pseudoatomic models built by a combination of: Single particle Cryo-EM Crosslinking MS HDX MS Modelling
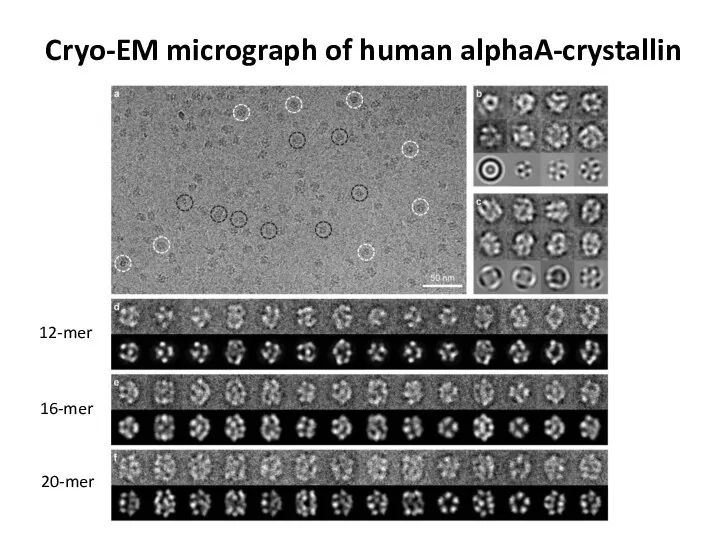
- 76. Cryo-EM micrograph of human alphaA-crystallin 12-mer 16-mer 20-mer
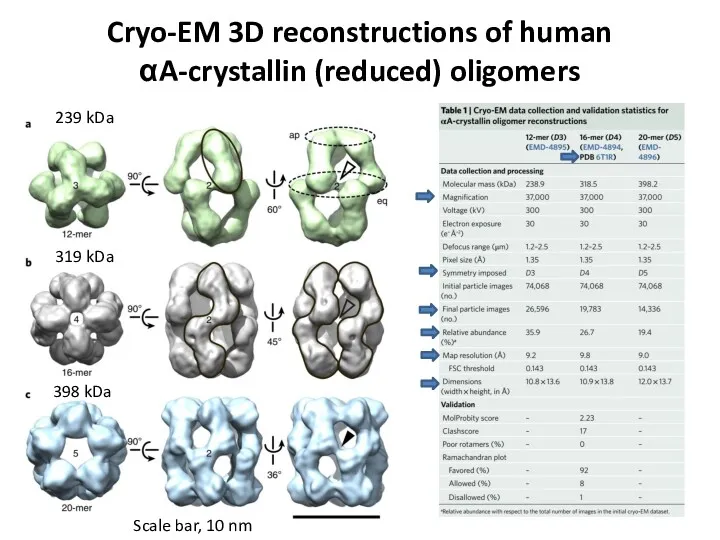
- 77. Cryo-EM 3D reconstructions of human αA-crystallin (reduced) oligomers Scale bar, 10 nm 239 kDa 319 kDa
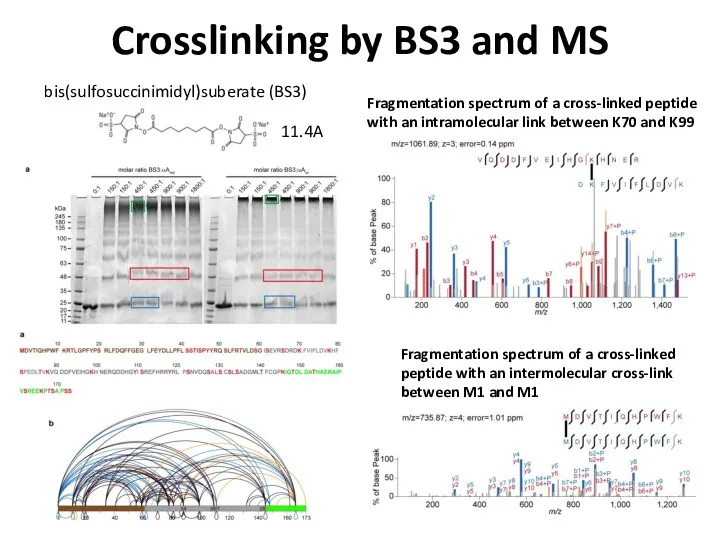
- 78. Crosslinking by BS3 and MS Fragmentation spectrum of a cross-linked peptide with an intramolecular link between
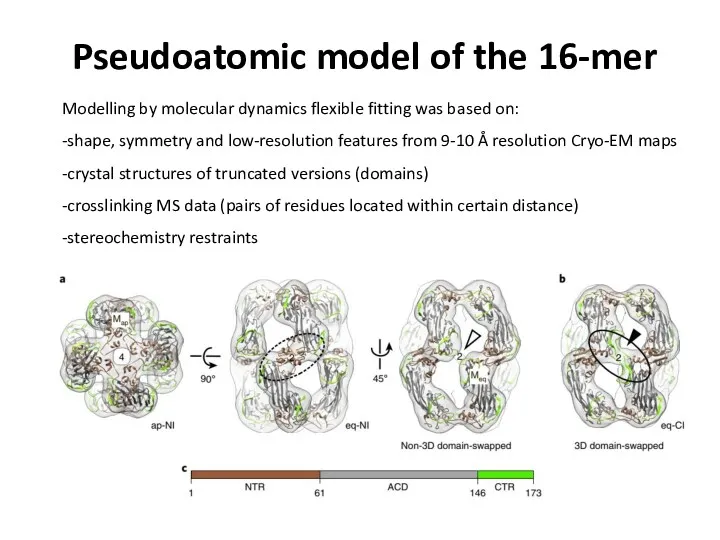
- 79. Pseudoatomic model of the 16-mer Modelling by molecular dynamics flexible fitting was based on: -shape, symmetry
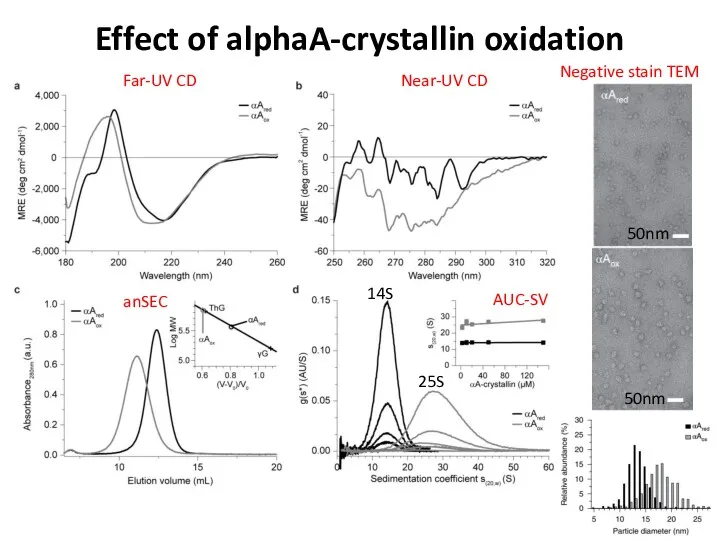
- 80. Effect of alphaA-crystallin oxidation Far-UV CD Near-UV CD anSEC AUC-SV 14S 25S 50nm 50nm Negative stain
- 82. Скачать презентацию











 Спутниковая связь
Спутниковая связь Конструктор. Что мы знаем о нем? Виды детских конструкторов
Конструктор. Что мы знаем о нем? Виды детских конструкторов Lista de precios Rusia
Lista de precios Rusia Дискалькулия специфическое нарушение обучения счету, проявляющееся в разных возрастах дошкольной и школьной популяции
Дискалькулия специфическое нарушение обучения счету, проявляющееся в разных возрастах дошкольной и школьной популяции Наука первой половины XIX века
Наука первой половины XIX века Психологический подход к проблеме заикания
Психологический подход к проблеме заикания Мақта матасы
Мақта матасы Пневмонии. Бронхиальная астма. Хроническая обструктивная болезнь легких. Основные клинические проявления. Диагностика
Пневмонии. Бронхиальная астма. Хроническая обструктивная болезнь легких. Основные клинические проявления. Диагностика Презентация портфолио учителя начальных классов
Презентация портфолио учителя начальных классов Презентация День Конституции России
Презентация День Конституции России Татар халык табышмаклары
Татар халык табышмаклары Геморрой. Факторы, способствующие развитию заболевания
Геморрой. Факторы, способствующие развитию заболевания Dydd Gwyl Dewi
Dydd Gwyl Dewi Перелетные птицы. Ознакомление детей с окружающим миром
Перелетные птицы. Ознакомление детей с окружающим миром Електронна біржа праці
Електронна біржа праці Эргономика спальной комнаты.Автоподъемник кровати
Эргономика спальной комнаты.Автоподъемник кровати Военные топографы
Военные топографы Маркетинг территорий: маркетинговая среда
Маркетинг территорий: маркетинговая среда Языки программирования
Языки программирования Памятники Ижевска
Памятники Ижевска Квадратный корень из произведения
Квадратный корень из произведения Комментарии к предложенным высказываниям
Комментарии к предложенным высказываниям Презентация История школьной формы в России. Подготовительная группа.
Презентация История школьной формы в России. Подготовительная группа. Хронический бронхит
Хронический бронхит Экологические правила.
Экологические правила. Миф о Йиркапе
Миф о Йиркапе Арнайы өндеу
Арнайы өндеу Артикуляционная гимнастика для звука Ш
Артикуляционная гимнастика для звука Ш