Содержание
- 2. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Breakdown of normal host barriers (cervical mucous, lysozymes, local IgA, cervix) allows ascension
- 3. P.I.D. Classic picture is a sexually active woman with bilateral abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever and
- 4. What is the differential for the same presentation with UNI-lateral adnexal tenderness? Ectopic Tubo-ovarian abscess Adnexal
- 5. Diagnostic Studies: CBC Endocervical specimens B-Hcg Ultrasound Laparoscopy
- 6. Diagnosing PID Definitively diagnosed by: confirmation of fluid filled tubes or TOA histopathologic confirmation of endometritis
- 7. Treatment: All regimens cover GC, chlamydia, anaerobes, G – rods, strep Who warrants inpatient treatment? Outpt:
- 8. Why do we care about PID? It is a risk factor for future ectopic, infertility and
- 9. Cervicitis May be GC, Chlamydia or trich Clinical diagnosis (pelvic exam and wet prep) Think of
- 10. Vaginal Discharge and Vulvovaginosis Differentiating between trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis and PID...
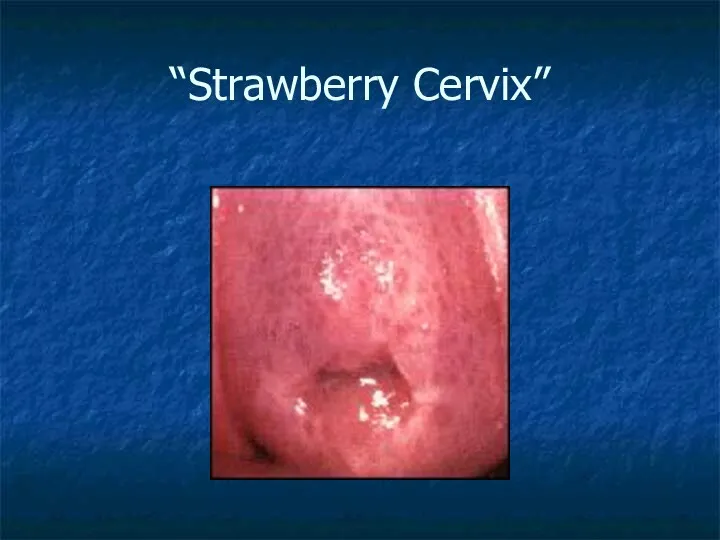
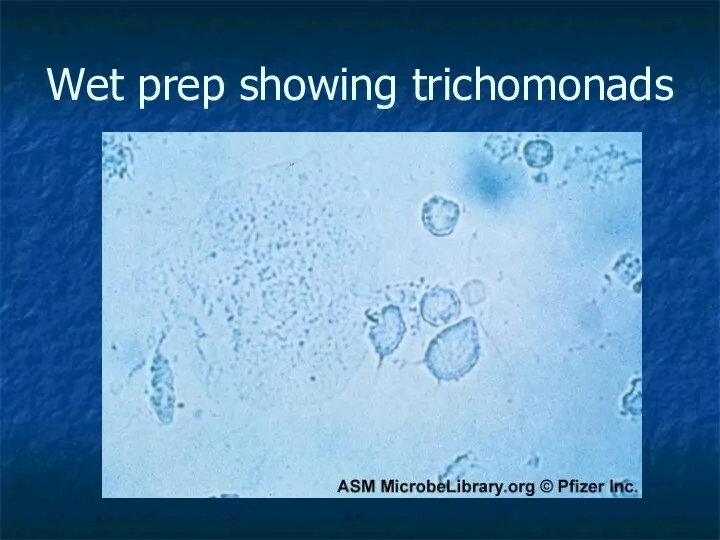
- 11. Trichomonas Vaginitis Foul smelling d/c with vaginal itching, lower abdominal pain and dysuria 4-28d incubation period
- 12. “Strawberry Cervix”
- 13. Wet prep showing trichomonads
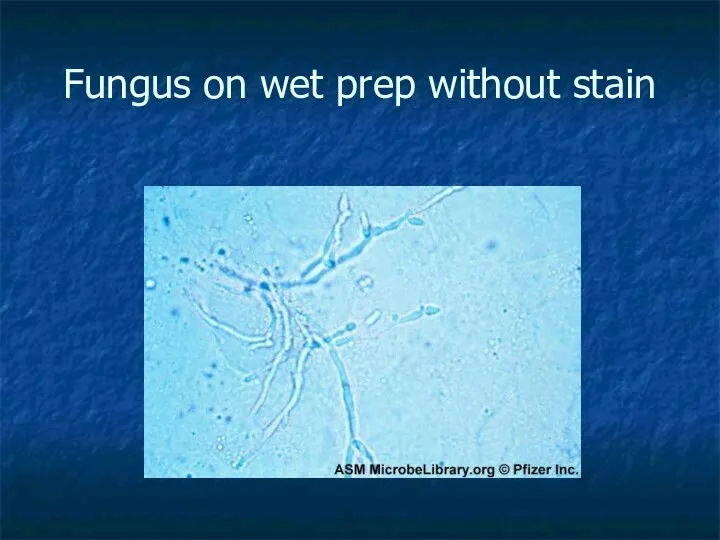
- 14. Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Overgrowth of normal vaginal flora Pt with vaginal itching and thin, watery to thick,
- 15. Fungus on wet prep without stain
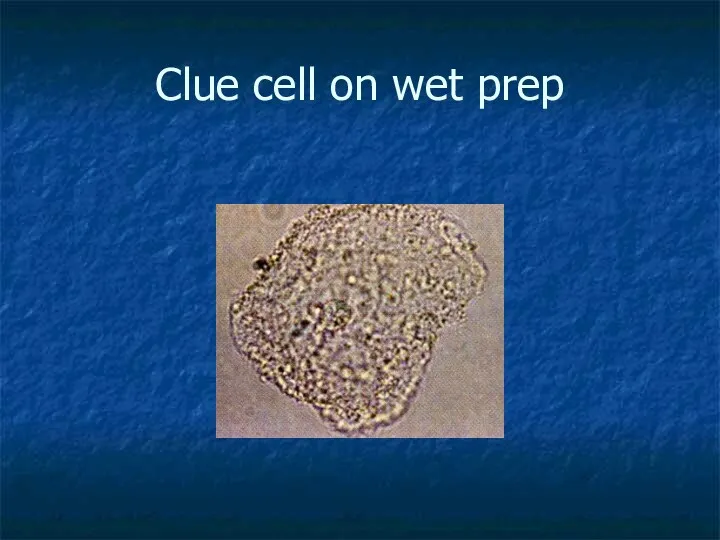
- 16. Bacterial Vaginosis The most common cause Believed to be polymicrobial Pt. complains of itching and fishy
- 17. Clue cell on wet prep
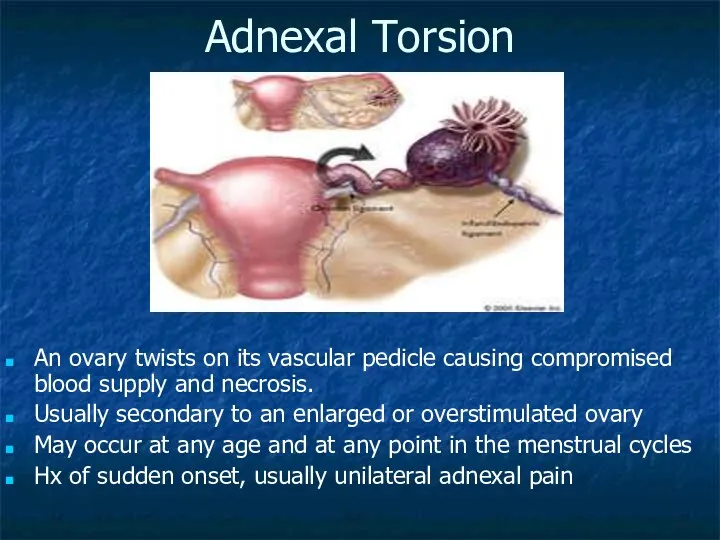
- 18. Adnexal Torsion An ovary twists on its vascular pedicle causing compromised blood supply and necrosis. Usually
- 19. Evaluation and Management: CMT may be present, may be bilateral though typically unilateral May palpate an
- 20. Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding (Non-pregnancy related) There are multiple etiologies: Endocrine alterations (menopause) Drugs (ABX, anticonvulsants, anticoagulants)
- 21. Our responsibilities are the same... Assuring hemodynamic stability Stabilizing the life-threatening bleeds Identifying correctable causes
- 23. Скачать презентацию















 Зороастризм
Зороастризм Аттестация педагогических работников
Аттестация педагогических работников Агропромышленный комплекс России (АПК)
Агропромышленный комплекс России (АПК) Су, оның гигиеналық және халықшаруашылықтың маңызы Жер үсті және жер асты суларының ластану көздері
Су, оның гигиеналық және халықшаруашылықтың маңызы Жер үсті және жер асты суларының ластану көздері Состав числа 14
Состав числа 14 Разработка урока Черная металлургия России.
Разработка урока Черная металлургия России. Генераторы несинусоидальных напряжений
Генераторы несинусоидальных напряжений Разработка конструкции системы управления
Разработка конструкции системы управления Общественное движение в годы правления Николая I. 8 класс
Общественное движение в годы правления Николая I. 8 класс Академия новых лиц
Академия новых лиц Открытое мероприятие в МБОУ НОШ 39 Семейные посиделки
Открытое мероприятие в МБОУ НОШ 39 Семейные посиделки Презентация Зеркала
Презентация Зеркала Классный час Мы разные– и в этом наше богатство, мы вместе – и в этом наша сила
Классный час Мы разные– и в этом наше богатство, мы вместе – и в этом наша сила Презентация.Мой класс и моя школа
Презентация.Мой класс и моя школа Dzhakanovaar_English
Dzhakanovaar_English Методы расчета количества сплава для литья
Методы расчета количества сплава для литья Классификация и типы залежей углеводородного сырья. Свойства пород-коллекторов. (Лекция 1)
Классификация и типы залежей углеводородного сырья. Свойства пород-коллекторов. (Лекция 1) Экологические проблемы, связанные с нефтью
Экологические проблемы, связанные с нефтью ВКР: Действия локомотивной бригады при отправлении поезда
ВКР: Действия локомотивной бригады при отправлении поезда Шаблон СВОЕЙ ИГРЫ с примерами демонстрирующими игровой процесс
Шаблон СВОЕЙ ИГРЫ с примерами демонстрирующими игровой процесс Декоративный пейзаж
Декоративный пейзаж Праздник Осени
Праздник Осени Догмат о Церкви Христова (часть 2)
Догмат о Церкви Христова (часть 2) Человек и человечность
Человек и человечность ФОТО МАТЕРИАЛ О ПРОФИЛАКТИЧЕСКОЙ РАБОТЕ ПРАВОНАРУШЕНИЙ, ИНЫХ СОЦИАЛЬНО-НЕГАТИВНЫХ ТЕНДЕНЦИЙ (терроризма и экстремизма) СРЕДИ ОБУЧАЮЩИХСЯ
ФОТО МАТЕРИАЛ О ПРОФИЛАКТИЧЕСКОЙ РАБОТЕ ПРАВОНАРУШЕНИЙ, ИНЫХ СОЦИАЛЬНО-НЕГАТИВНЫХ ТЕНДЕНЦИЙ (терроризма и экстремизма) СРЕДИ ОБУЧАЮЩИХСЯ Государственная служба, как особый вид профессиональной деятельности
Государственная служба, как особый вид профессиональной деятельности Проект Моя Семья
Проект Моя Семья Воспитание успехом. Концепция педагогической философии.
Воспитание успехом. Концепция педагогической философии.