Содержание
- 2. Advanced chapters of theoretical electroengineering. HSHVPE, IE SPbPU, Prof. A.G. Kalimov 2022
- 3. General information Общая информация Лектор – Калимов Александр Гелиевич, профессор ВШВЭ ИЭ СПбПУ Базовая литература: K.
- 4. Analysis and computation of electromagnetic fields.
- 5. Fundamental concepts of electromagnetics. Electrostatics. Lecture 1 (after: Gunther Lehner. Electromagnetic Field Theory for Engineers and
- 6. Vectors and scalar fields.
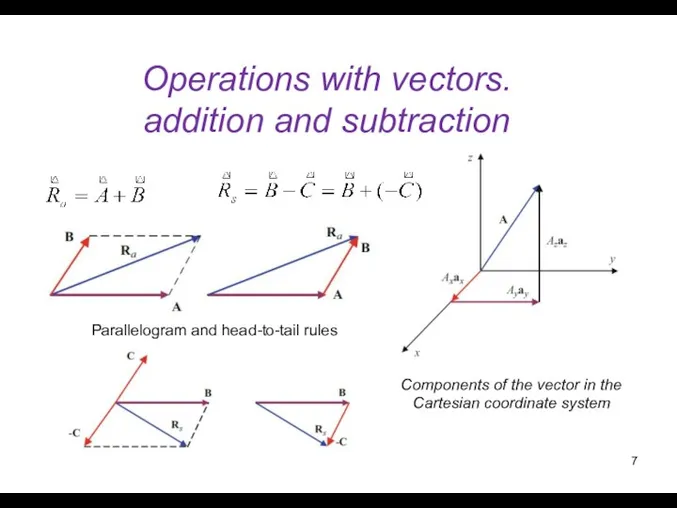
- 7. Operations with vectors. addition and subtraction Components of the vector in the Cartesian coordinate system Parallelogram
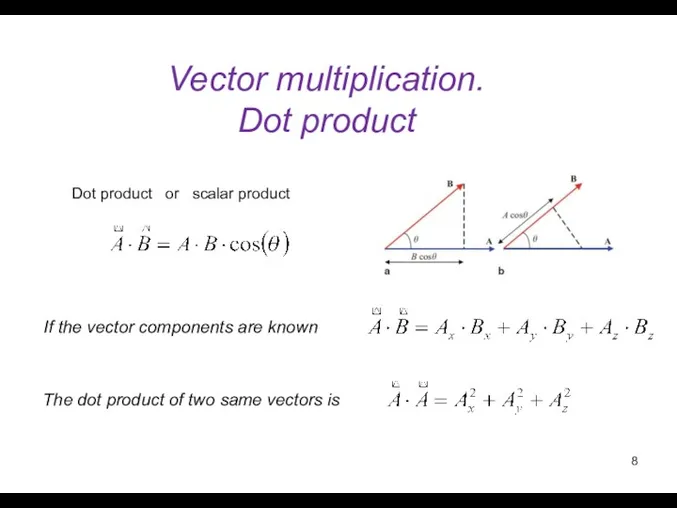
- 8. Vector multiplication. Dot product If the vector components are known Dot product or scalar product The
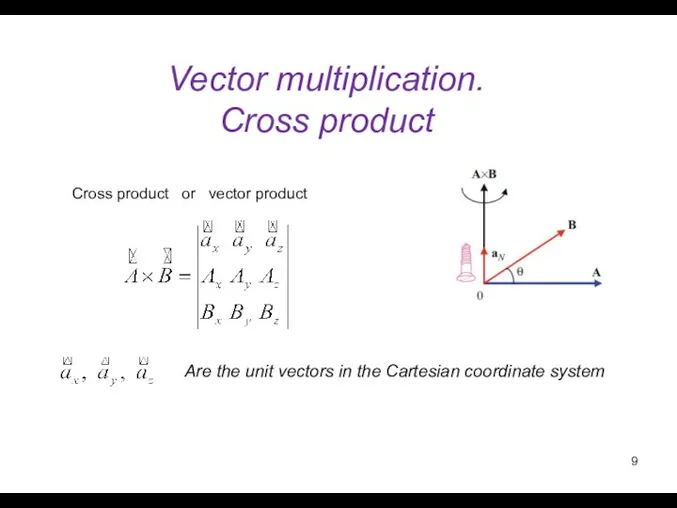
- 9. Vector multiplication. Cross product Are the unit vectors in the Cartesian coordinate system Cross product or
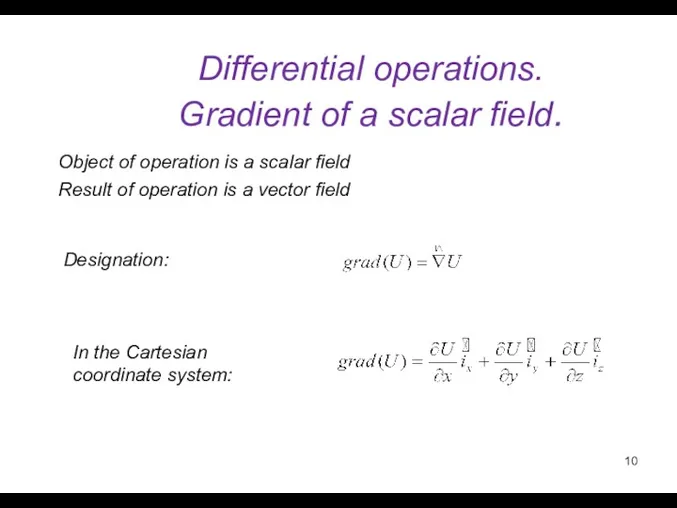
- 10. Differential operations. Gradient of a scalar field. Designation: In the Cartesian coordinate system: Object of operation
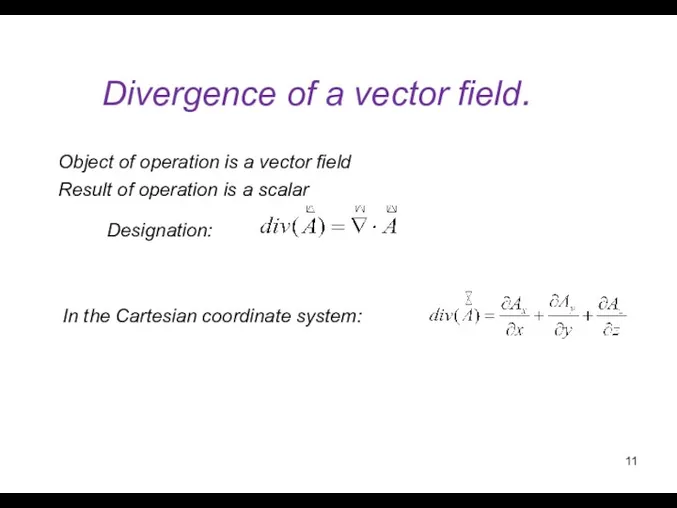
- 11. Divergence of a vector field. Designation: Result of operation is a scalar In the Cartesian coordinate
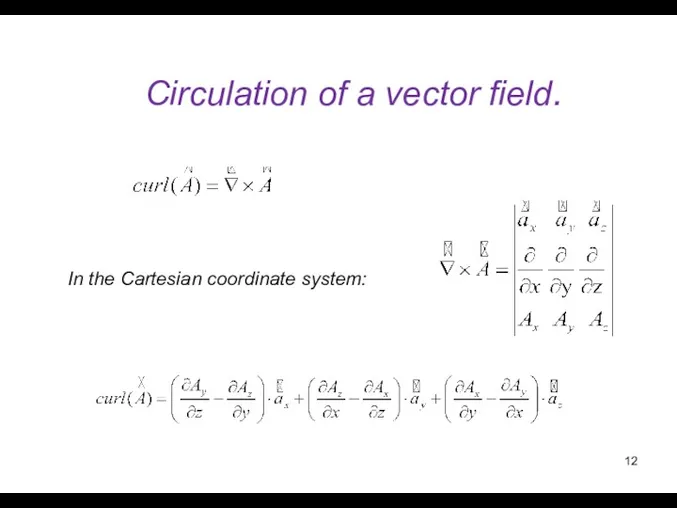
- 12. Circulation of a vector field. In the Cartesian coordinate system:
- 13. Properties of the differential operators. Differential operations are linear: Important Vector Identities:
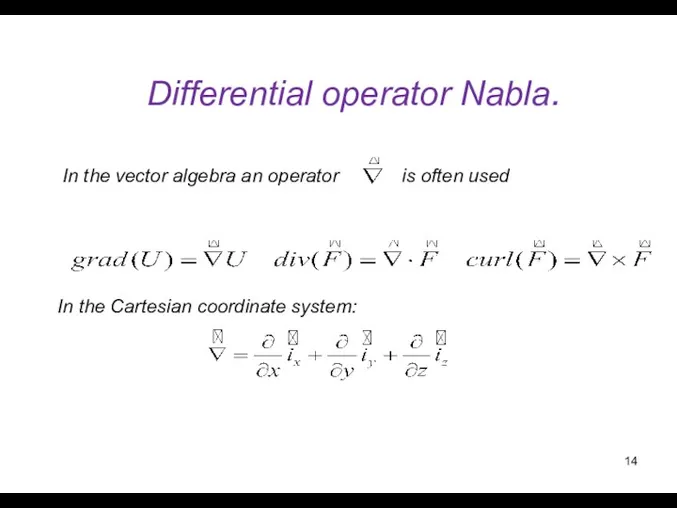
- 14. Differential operator Nabla. In the vector algebra an operator is often used In the Cartesian coordinate
- 15. Integral theorems. Different forms of the Gauss theorem Stoke’s theorem
- 16. Electrostatic field.
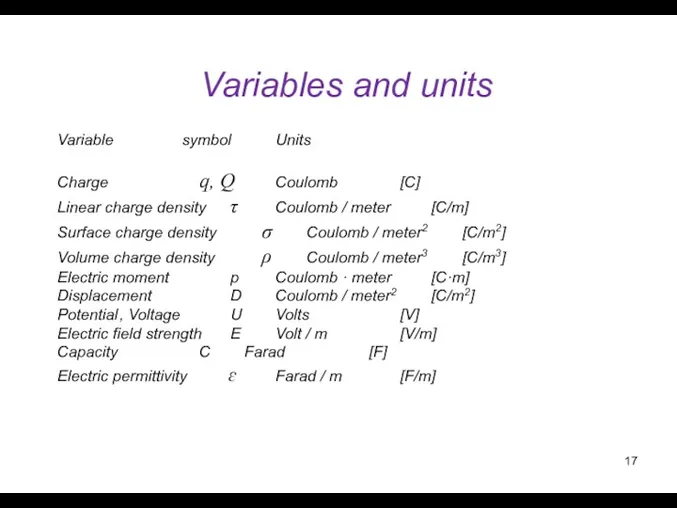
- 17. Variables and units Variable symbol Units Charge q, Q Coulomb [C] Linear charge density τ Coulomb
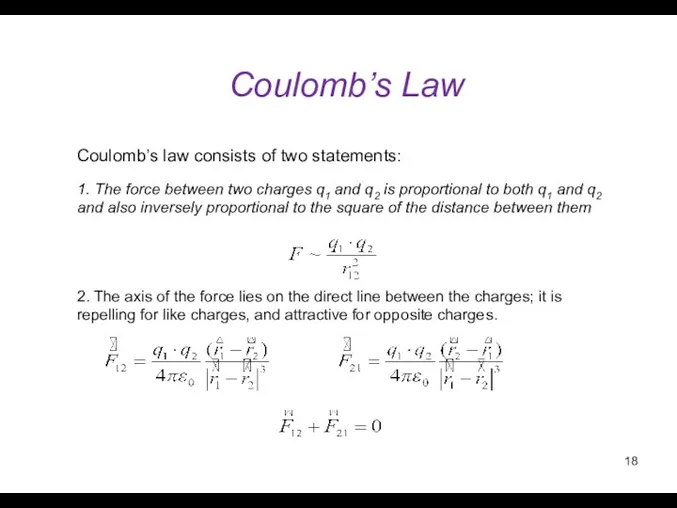
- 18. Coulomb’s Law 1. The force between two charges q1 and q2 is proportional to both q1
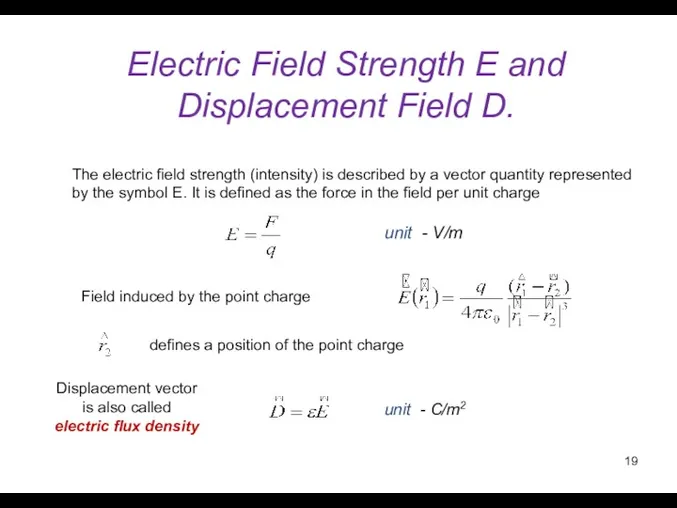
- 19. Electric Field Strength E and Displacement Field D. unit - V/m The electric field strength (intensity)
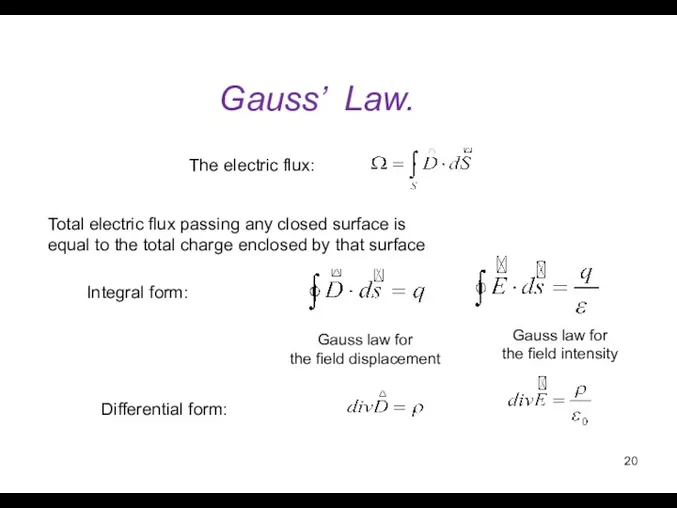
- 20. Gauss’ Law. Gauss law for the field displacement Total electric flux passing any closed surface is
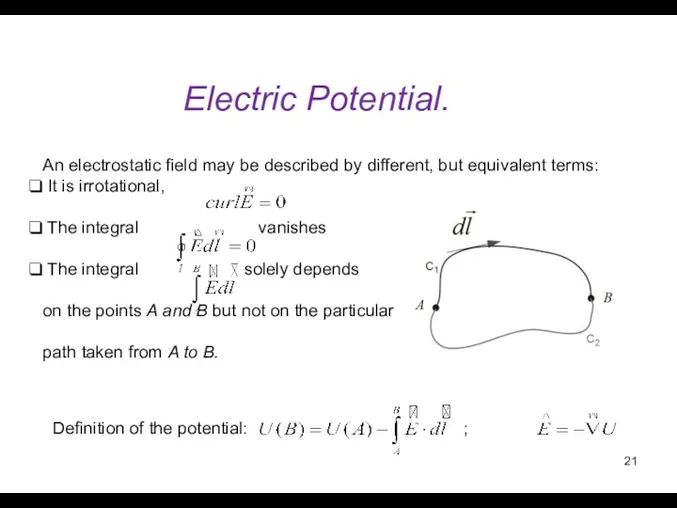
- 21. Electric Potential. An electrostatic field may be described by different, but equivalent terms: It is irrotational,
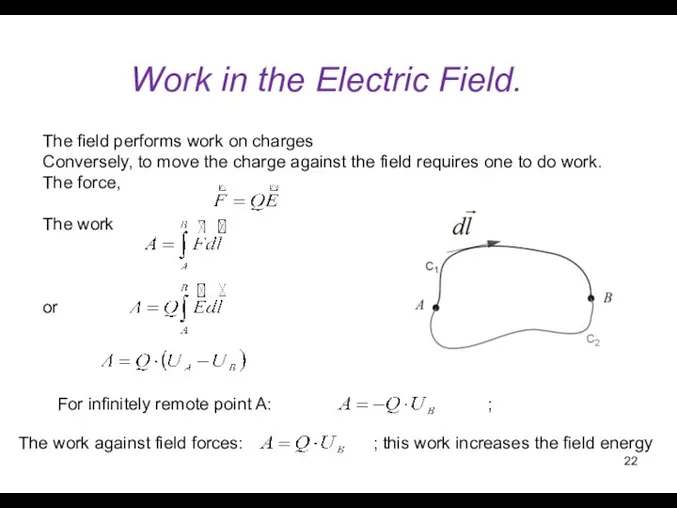
- 22. Work in the Electric Field. The field performs work on charges Conversely, to move the charge
- 23. Dielectric polarization. Dielectric materials are polarized when an electric field is applied to them. As a
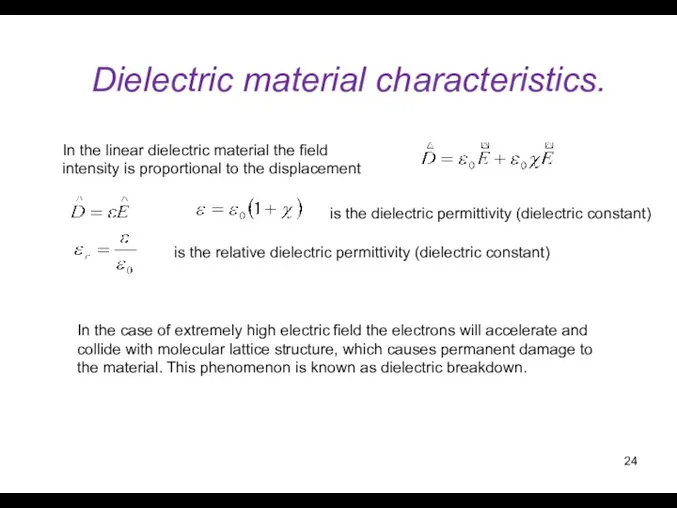
- 24. Dielectric material characteristics. In the linear dielectric material the field intensity is proportional to the displacement
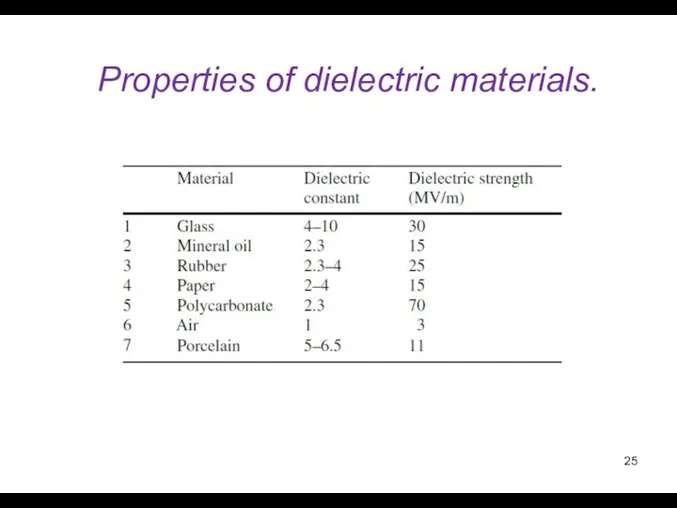
- 25. Properties of dielectric materials.
- 27. Скачать презентацию








 20 марта - Международный День счастья
20 марта - Международный День счастья МУРАЛЫ И ГРАФФИТИ КАК ЭЛЕМЕНТ НАСКАЛЬНОЙ ЖИВОПИСИ
МУРАЛЫ И ГРАФФИТИ КАК ЭЛЕМЕНТ НАСКАЛЬНОЙ ЖИВОПИСИ Бизнес идея создания продовольственного магазина Продукты
Бизнес идея создания продовольственного магазина Продукты Острые отравления окисью углерода, амидо- и нитросоединениями
Острые отравления окисью углерода, амидо- и нитросоединениями Проектирование электрических сетей
Проектирование электрических сетей Отдел МВД России по Усть-Катавскому городскому округу. Дети России 2018
Отдел МВД России по Усть-Катавскому городскому округу. Дети России 2018 Мой папа
Мой папа Дважды Герой Советского Союза Муса Гайсинович Гареев - мой прадедушка
Дважды Герой Советского Союза Муса Гайсинович Гареев - мой прадедушка Опыт использования ГУП Мосгортранс подвижного состава, использующего в качестве топлива компримированный природный газ
Опыт использования ГУП Мосгортранс подвижного состава, использующего в качестве топлива компримированный природный газ Сравнительная оценка сортов озимой тритикале по урожайности зерна
Сравнительная оценка сортов озимой тритикале по урожайности зерна Тайна имени Юлия, толкование имени
Тайна имени Юлия, толкование имени Неотложные состояния при стоматологических вмешательствах у детей
Неотложные состояния при стоматологических вмешательствах у детей Компьютерные сети
Компьютерные сети Технологии ремонта элементов систем водоснабжения и канализации. Общие сведения о системах водоснабжения и канализации
Технологии ремонта элементов систем водоснабжения и канализации. Общие сведения о системах водоснабжения и канализации Рентгенодиагностика и дифференциальная диагностика частных форм туберкулеза. Великий Р. Кох и его палочки
Рентгенодиагностика и дифференциальная диагностика частных форм туберкулеза. Великий Р. Кох и его палочки ТЭС және АЭС
ТЭС және АЭС Эссе по обществознанию
Эссе по обществознанию Правила уборки на кухне на каждый день
Правила уборки на кухне на каждый день Наш космодром
Наш космодром История создания романа Война и мир. Особенности жанра
История создания романа Война и мир. Особенности жанра Организация, виды и условия потребительского кредитования в коммерческих банках
Организация, виды и условия потребительского кредитования в коммерческих банках Сергей Сергеевич Прокофьев (1891-1953)
Сергей Сергеевич Прокофьев (1891-1953)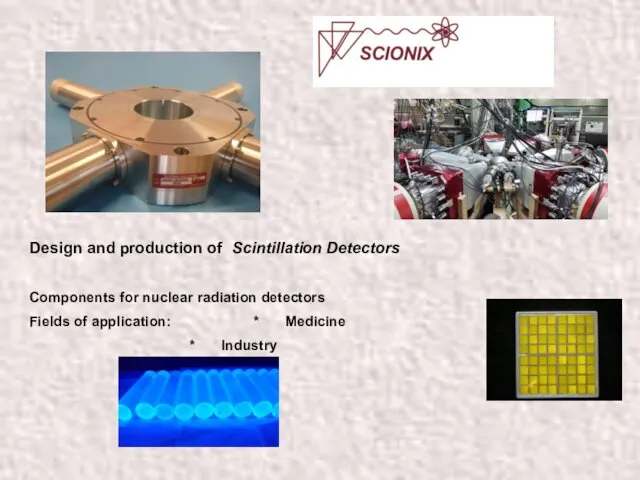 Design and production of Scintillation Detectors. SCIONIX general 2016
Design and production of Scintillation Detectors. SCIONIX general 2016 М.Е. Салтыков-Щедрин. Сатирическое изображение градоначальников в романе История одного города
М.Е. Салтыков-Щедрин. Сатирическое изображение градоначальников в романе История одного города Воинские звания РФ
Воинские звания РФ Преподобный Сергий. Душа России
Преподобный Сергий. Душа России Движение воздуха. Ветер
Движение воздуха. Ветер Роль биологии в формировании современной научной картины мира, практическое значение биологических знаний
Роль биологии в формировании современной научной картины мира, практическое значение биологических знаний