Содержание
- 2. ENERGISER Can you name all of these logos?
- 3. AIMS Today’s lesson will move away from computer hardware and we will start to cover the
- 4. OBJECTIVES Define the role & purpose of an operating system Identify & list different Microsoft Operating
- 5. OPERATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE (ROLE) At the very heart of any computer system is the operating system
- 6. INTRO A computer is made up of many parts. You have the hardware e.g. monitor, keyboard
- 7. WHAT IS AN OS There are two main categories of software. There is 'application software' with
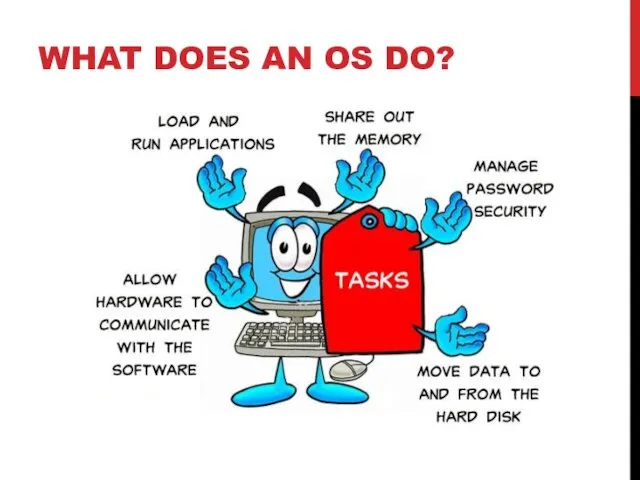
- 8. WHAT DOES AN OS DO?
- 9. SINGLE USER, SINGLE APP OS This type of OS only has to deal with one person
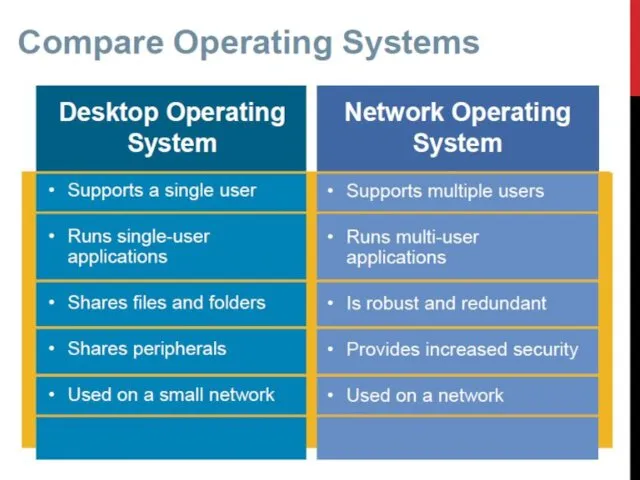
- 10. SINGLE USER OS Whilst you are using your computer it is likely that you don't need
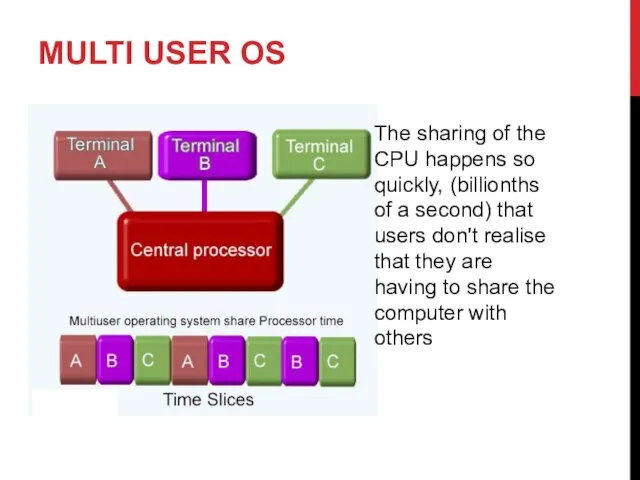
- 11. MULTI USER OS Large companies often use a mainframe computer system These are very expensive, powerful
- 12. MULTI USER OS The sharing of the CPU happens so quickly, (billionths of a second) that
- 13. MULTI TASKING When you have more than one application open on your desktop You are able
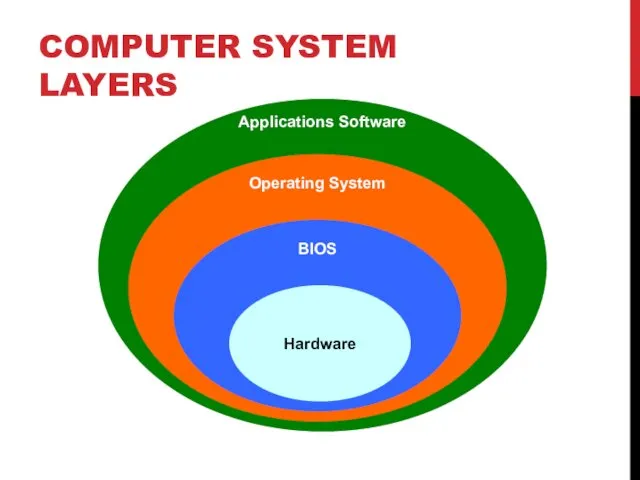
- 15. COMPUTER SYSTEM LAYERS Applications Software Operating System BIOS Hardware
- 16. THE KERNEL The kernel is the central component of most computer operating systems It is a
- 17. CORE INTERLOCKING COMPONENTS Resource Management User Interface Input / Output (peripheral control) Filing system Security Task
- 18. RESOURCE MANAGEMENT What resources are found on a modern computer system? Physical Memory Virtual Memory Disk
- 19. USER INTERFACE What is the interface responsible for? Accepting user commands Parsing user commands (working out
- 20. COMMAND LINE AND GUI OPERATING SYSTEMS Prior to the introduction of the WIMP environment, early computers
- 21. COMMAND LINE AND GUI OPERATING SYSTEMS CONT. Windows: a WIMP environment system developed by Microsoft Corporation
- 22. OPERATING SYSTEM EXAMPLES MS DOS Promo Advert DOS was the name of an operating system developed
- 23. INPUT / OUTPUT (PERIPHERAL CONTROL) It is the computers job to control the amount of CPU
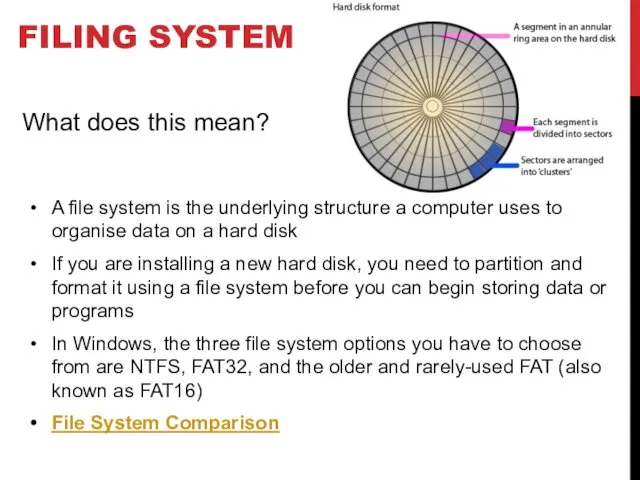
- 24. FILING SYSTEM A file system is the underlying structure a computer uses to organise data on
- 25. SECURITY Where does Security fit into an OS? Your task is to find out!
- 26. TASK MANAGEMENT Where does Task Management come into this? The Process Manager handles the scheduling of
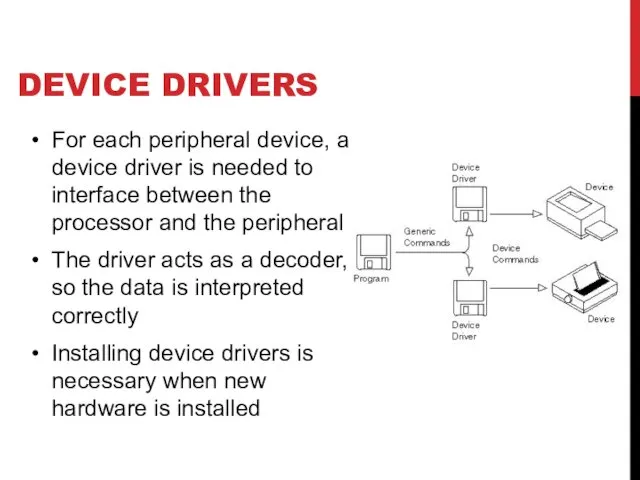
- 27. DEVICE DRIVERS For each peripheral device, a device driver is needed to interface between the processor
- 28. UPDATING & DEVICE DRIVERS Automatic Updates Driver Installs Driver Updates System Restore Last known good configuration
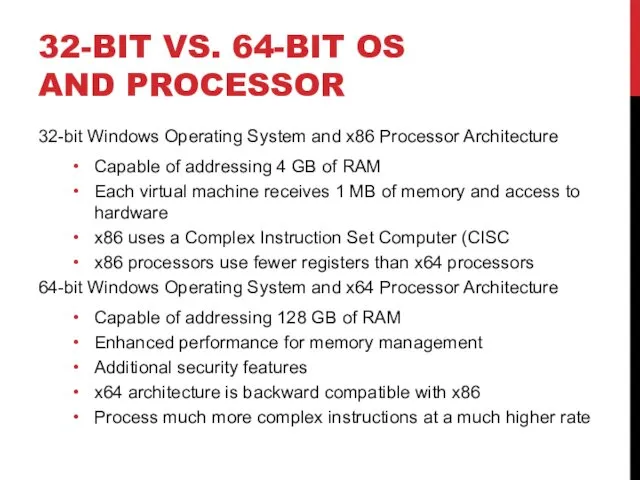
- 29. 32-BIT VS. 64-BIT OS AND PROCESSOR 32-bit Windows Operating System and x86 Processor Architecture Capable of
- 30. IDENTIFY MICROSOFT OPERATING SYSTEMS Whiteboard Exercise
- 32. MINIMUM/RECOMMENDED REQUIREMENTS Microsoft Windows Seven Requirements
- 35. THE START MENU The Start menu is one of the primary connections between the user and
- 36. THE TASK BAR The Task Bar is another of the primary connections between the user and
- 37. THE CONTROL PANEL The Control Panel is a part of the Microsoft Windows graphical user interface
- 39. RESOURCE PAGE OS resource 1 OS resource 2 OS resource 3 OS resource 4
- 40. A BREAKDOWN OF P2 Describe the features and functions of an operating system Describe what an
- 41. P2 CRITERIA Operating System Types Command line Graphic User Interface Functions The Kernel - This is
- 42. P2 CRITERIA CONT. Services including... Machine and peripheral management Security: data security including encryption, usernames and
- 43. MERIT TASK (VIA ASSIGNMENT) You must produce a report that explains the purpose of Operating Systems
- 45. Скачать презентацию





























 Внутренняя политика Николая I
Внутренняя политика Николая I Патология световосприятия
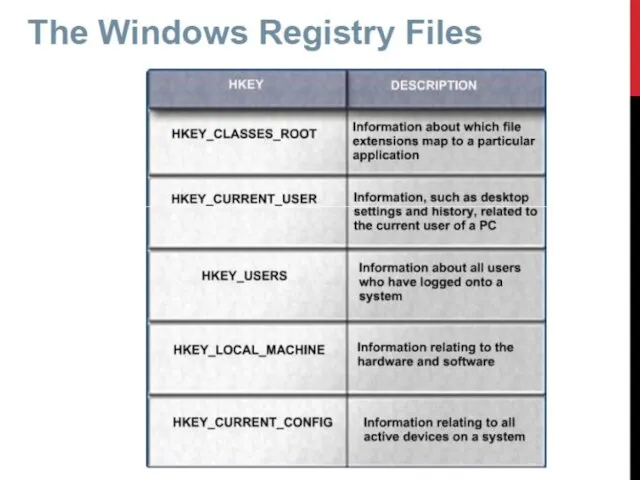
Патология световосприятия Информатика
Информатика Профессия электрик
Профессия электрик Крестовые походы. Повод к началу крестовых походов
Крестовые походы. Повод к началу крестовых походов Южная Европа
Южная Европа Деревенское подворье: Стиль кантри в ландшафтном дизайне.
Деревенское подворье: Стиль кантри в ландшафтном дизайне. Знаменитые жители СПб
Знаменитые жители СПб День Матери Диск
День Матери Диск Приглашение на свадьбу
Приглашение на свадьбу Возобновляемые углеводородные ресурсы и их использование в системах распределенной энергетики
Возобновляемые углеводородные ресурсы и их использование в системах распределенной энергетики Организация деятельности приёмной Апатитского городского суда
Организация деятельности приёмной Апатитского городского суда Анализ напряженно-деформированного состояния инженерных конструкций. Освоение подземного пространства
Анализ напряженно-деформированного состояния инженерных конструкций. Освоение подземного пространства Методы выделения и очистки ДНК
Методы выделения и очистки ДНК فناوری نانو در روسازی
فناوری نانو در روسازی Презентация для детей Домашние животные
Презентация для детей Домашние животные 20 лет вместе с вами. Condor
20 лет вместе с вами. Condor Буквия. Гласные
Буквия. Гласные Осенние фантазии
Осенние фантазии Социальный проект в 6 классе
Социальный проект в 6 классе Неопределённая форма глагола
Неопределённая форма глагола население Африки
население Африки Мотивация успеха и боязнь неудачи (опросник А.А.Реана)
Мотивация успеха и боязнь неудачи (опросник А.А.Реана) Матрёшка
Матрёшка ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Почва. Состав, образование. 5 класс
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Почва. Состав, образование. 5 класс Правовое регулирование занятости и трудоустройства
Правовое регулирование занятости и трудоустройства Своя игра 5-6 классы
Своя игра 5-6 классы История успеха компании Sony
История успеха компании Sony