Содержание
- 2. LECTURE No. 2 CARBON BASED MATERIALS
- 3. OBJECTIVES To describe the structure and the most important characteristics of fullerenes, their formation and properties.
- 4. OUTLINE Fullerenes. The structure and its characteristics. Types of fullerenes. Mechanism of formation. Chemical properties. Applications.
- 5. Importance of the carbon atoms The most studied chemical element Forms organic compounds with: H, O
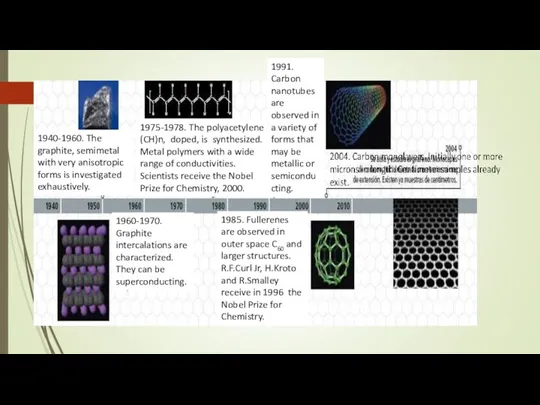
- 6. 1940-1960. The graphite, semimetal with very anisotropic forms is investigated exhaustively. 1975-1978. The polyacetylene (CH)n, doped,
- 7. Carbon based materials
- 8. Fullerenes They were discovered in 1985 by Harold Kroto, James R. Heath, Sean O'Brien, Robert Curl,
- 9. Characteristics of Fullerenes Structural beauty and versatility to form new compounds. Forms like spheres, ellipsoids or
- 10. Characteristics of Fullerenes Geodesic dome (Buckminster Fuller)
- 11. Characteristics of Fullerenes Geodesic dome (Buckminster Fuller) (Buckminsterfullerenes)
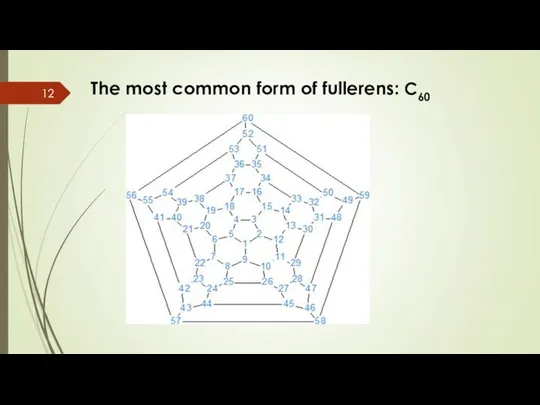
- 12. The most common form of fullerens: C60
- 13. Characteristics of C60 There are 60 carbon atoms bonding together like hexagons and pentagons in a
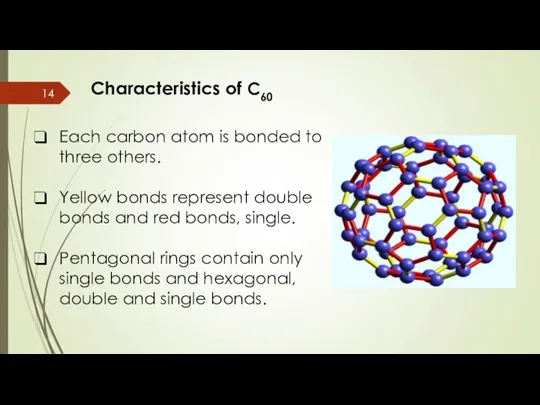
- 14. Characteristics of C60 Each carbon atom is bonded to three others. Yellow bonds represent double bonds
- 15. Characteristics of C60 Double bonds have shorter bond lenght: Instability in the pentagonal rings Poor delocalization
- 16. Physical properties Density: 1,72 g/cm3 Poorly soluble in most solvents (toluene and carbon disulfide. Solutions of
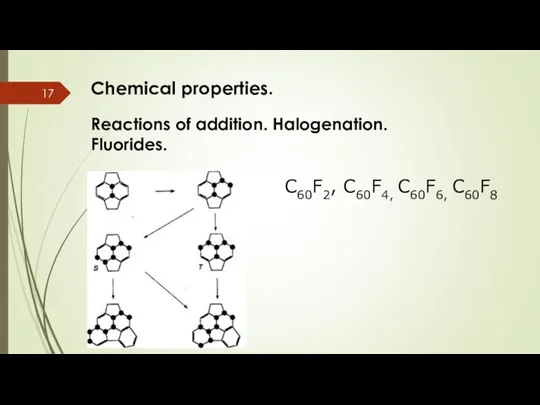
- 17. Chemical properties. Reactions of addition. Halogenation. Fluorides. C60F2, C60F4, C60F6, C60F8
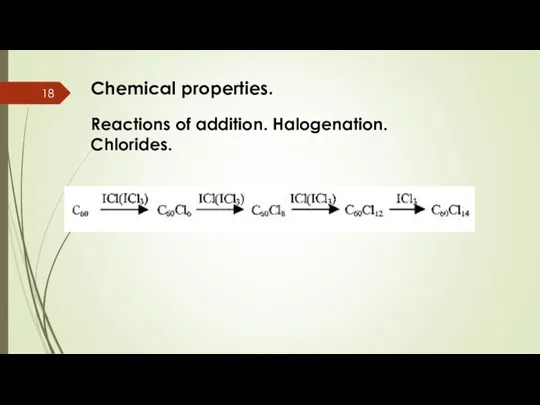
- 18. Chemical properties. Reactions of addition. Halogenation. Chlorides.
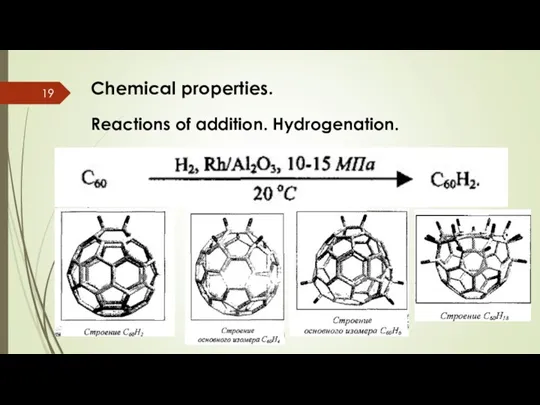
- 19. Chemical properties. Reactions of addition. Hydrogenation.
- 20. Chemical properties. Endohedral fullerenes They are fullerenes that have additional atoms, ions, or clusters enclosed within
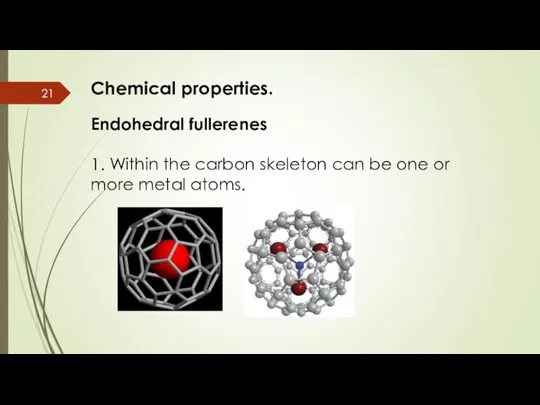
- 21. Chemical properties. Endohedral fullerenes 1. Within the carbon skeleton can be one or more metal atoms.
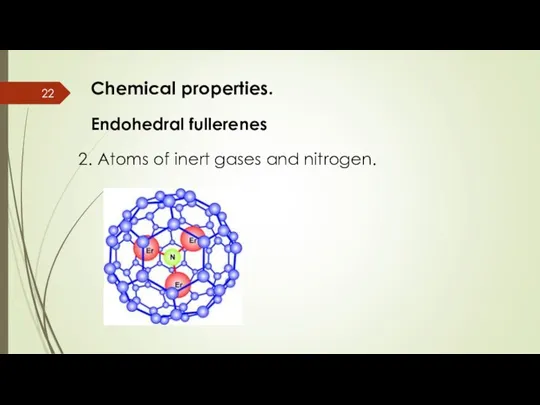
- 22. Chemical properties. Endohedral fullerenes 2. Atoms of inert gases and nitrogen.
- 23. Chemical properties. Endohedral fullerenes The first C60 complex was synthesized in 1985 and called lanthanum C60
- 24. Applications Electronics, chemistry, medicine, optics As the basis to produce batteries Optical gates As additives for
- 25. Control questions 1. Describe in briefly what is fullerenes? 2. Mention the main characteristics of fullerenes.
- 27. Скачать презентацию















 Сердечно-сосудистая система. Возрастные особенности и развитие
Сердечно-сосудистая система. Возрастные особенности и развитие Методы и стили семейного воспитания
Методы и стили семейного воспитания Конспект урока по математике Решение примеров на нахождение неизвестного слагаемого
Конспект урока по математике Решение примеров на нахождение неизвестного слагаемого Конкурс Социальная Звезда- 2018. Мальчишник -2018
Конкурс Социальная Звезда- 2018. Мальчишник -2018 Презентация к Уроку Знаний и Мира Сад летних впечатлений
Презентация к Уроку Знаний и Мира Сад летних впечатлений Embracing_Your_Diversity
Embracing_Your_Diversity Турнир по быстрым шахматам 2015-16-01
Турнир по быстрым шахматам 2015-16-01 ЕДИНЫЕ ТРЕБОВАНИЯ К СОСТАВЛЕНИЮ РАБОЧИХ ПРОГРАММ
ЕДИНЫЕ ТРЕБОВАНИЯ К СОСТАВЛЕНИЮ РАБОЧИХ ПРОГРАММ Лечебное питание
Лечебное питание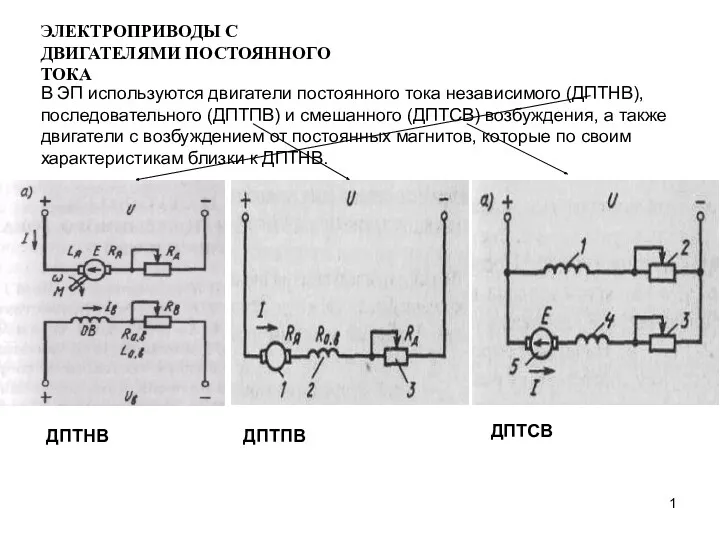 Электроприводы с двигателями постоянного тока
Электроприводы с двигателями постоянного тока Туристический слет
Туристический слет Язык Turbo Pascal и его практическое применение
Язык Turbo Pascal и его практическое применение lence skills
lence skills Проект: Торгівельний центр
Проект: Торгівельний центр Урок речевого творчества
Урок речевого творчества Диоды
Диоды Отёки. Повышенное гидростатическoе давление
Отёки. Повышенное гидростатическoе давление Автоматизація процесу переміщення сипучих матеріалів стрічковим конвеєром
Автоматизація процесу переміщення сипучих матеріалів стрічковим конвеєром Алкалоидтар. Алкалоидтар туралы түсінік
Алкалоидтар. Алкалоидтар туралы түсінік Сокращенное опробование тормозов поезда
Сокращенное опробование тормозов поезда Смартфон арқылы видео түсіру
Смартфон арқылы видео түсіру Презентация к тематической линейке Никто не забыт, ничто не забыто
Презентация к тематической линейке Никто не забыт, ничто не забыто Спутниковая аппаратура пользователей
Спутниковая аппаратура пользователей Мой электронный Portfolio
Мой электронный Portfolio Профессия стропальщик
Профессия стропальщик Бизнес идея: бюро добрых услуг Радуга
Бизнес идея: бюро добрых услуг Радуга Проектная работа
Проектная работа Кухня Индонезии
Кухня Индонезии