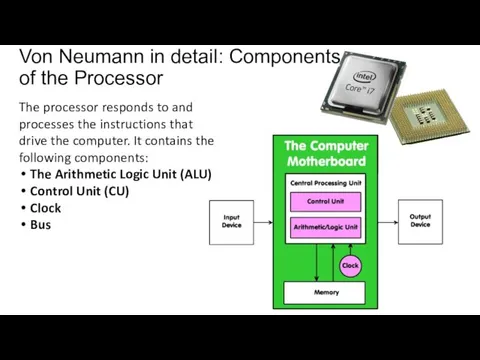
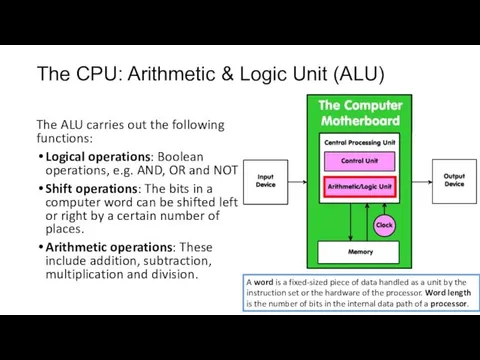
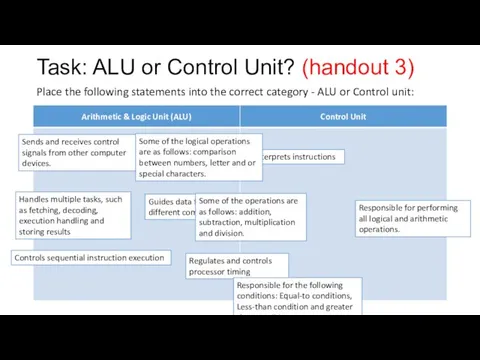
Task: ALU or Control Unit? (handout 3)
Place the following statements into
the correct category - ALU or Control unit:
Controls sequential instruction execution
Handles multiple tasks, such as fetching, decoding, execution handling and storing results
Sends and receives control signals from other computer devices.
Regulates and controls processor timing
Guides data flow through different computer areas
Interprets instructions
Responsible for performing all logical and arithmetic operations.
Some of the operations are as follows: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Some of the logical operations are as follows: comparison between numbers, letter and or special characters.
Responsible for the following conditions: Equal-to conditions, Less-than condition and greater than condition.







 Как хороша ты, родная весна!
Как хороша ты, родная весна! Водный транспорт. Морской и речной транспорт
Водный транспорт. Морской и речной транспорт Этапы вязания крючком
Этапы вязания крючком Компанія ЗМ
Компанія ЗМ Принципы имитационного моделирования. Математические методы моделирования
Принципы имитационного моделирования. Математические методы моделирования Словарные слова (1-2 класс)
Словарные слова (1-2 класс) Визволення України від нацистських загарбників
Визволення України від нацистських загарбників Компанія Federal. Розподільче обладнання
Компанія Federal. Розподільче обладнання Halloween. On the 31st of October British people celebrate Halloween
Halloween. On the 31st of October British people celebrate Halloween Единые сроки каникул в московских школах
Единые сроки каникул в московских школах Глобальные сети и перспективные сетевые технологии. Глобальные сети (Wide Area Networks, WAN)
Глобальные сети и перспективные сетевые технологии. Глобальные сети (Wide Area Networks, WAN) презентация 6 класс Горные породы и минералы
презентация 6 класс Горные породы и минералы Федеральные СМИ
Федеральные СМИ Leongardt_mikrofinansovye_organizatsii
Leongardt_mikrofinansovye_organizatsii Брюгге. Достопримечательности
Брюгге. Достопримечательности Бронхиальная астма
Бронхиальная астма Формирование у детей старшего дошкольного возраста положительной учебной мотивации
Формирование у детей старшего дошкольного возраста положительной учебной мотивации Проверочная работа по теме Мировой океан Диск
Проверочная работа по теме Мировой океан Диск История и методология науки
История и методология науки Презентация Металлические деньги в истории России
Презентация Металлические деньги в истории России Программная обработка данных на компьютере
Программная обработка данных на компьютере Праздник Троицы. Церковное песнопение,
Праздник Троицы. Церковное песнопение, Счетчики. Четырехразрядный суммирующий асинхронный двоичный счетчик
Счетчики. Четырехразрядный суммирующий асинхронный двоичный счетчик Электронный конструктор Знаток
Электронный конструктор Знаток Интегрированный урок по английскому языку и физической культуре. 3 класс
Интегрированный урок по английскому языку и физической культуре. 3 класс Энергетические характеристики агрегатов и ГЭС
Энергетические характеристики агрегатов и ГЭС Защита прав человека в Японии
Защита прав человека в Японии Лепка фигуры человека с каркасом
Лепка фигуры человека с каркасом