Содержание
- 2. Project Plan Introduction. Definition Of Sharia. General characteristic of Islamic legal system. History of its development.
- 3. 1. Introduction ‘Islamic law’ refers to the diverse legal systems that have been and continue to
- 4. There are significant historical and substantive distinctions between ‘Islamic law’ and ‘Muslim legalities’ . ‘Islamic law’
- 5. The term sharia refers to a body of Islamic religious law that governs Muslims' daily lives
- 6. 3. General characteristic of Islamic legal system After a lot of researches concerning Islamic law, the
- 7. Third : it is rational and realistic because it deals with tangible facts, not illusions and
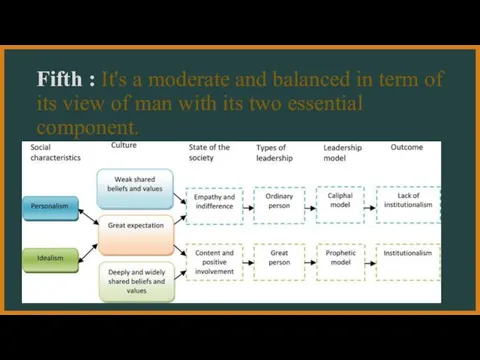
- 8. Fifth : It's a moderate and balanced in term of its view of man with its
- 9. 4. History of its development Before Islam, the nomadic tribes inhabiting the Arabian peninsula worshiped idols.Each
- 10. Only a few verses deal with legal matter. Durring his lifetime muhammed helped clarify the laws
- 11. The major precepts of Sharia were passed down directly from the Islamic prophet Muhammad without "historical
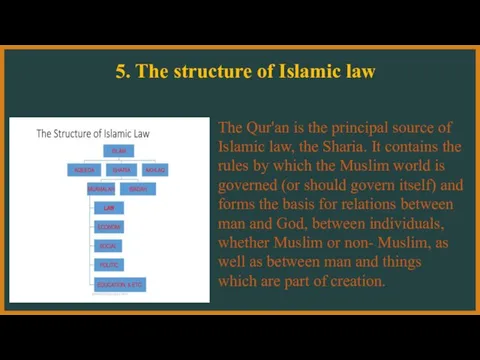
- 12. 5. The structure of Islamic law The Qur'an is the principal source of Islamic law, the
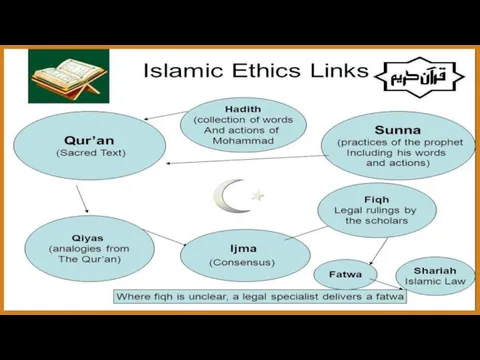
- 13. 6. The Sources of Islamic law Sources of Muslim law is classify into two categories that
- 14. 1) Quran In Islam, the Quran is considered to be the most sacred source of law.
- 16. In Islam, Sunnah are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad, that constitute a
- 17. 3) Ijma It is the consensus that could in principle elevate a ruling based on probable
- 18. 4) Qiyas It is the Analogical reasoning that is used to derive a ruling for a
- 19. 7. The Egyptian Legal System The Egyptian legal system is built on the combination of Islamic
- 20. The Egyptian legal system, being considered as a civil law system, is based upon a well-established
- 22. The main source of legal rules applicable to contracts. Much of the ECC is based upon
- 24. Скачать презентацию


















 Основные понятия и показатели надежности
Основные понятия и показатели надежности Конспект открытого интегрированного занятия в подготовительной группе Путешествие в школу. Диск
Конспект открытого интегрированного занятия в подготовительной группе Путешествие в школу. Диск Литература 07.02.24
Литература 07.02.24 Презентация к уроку географии 11 класс Зарубежная Азия.Зачет
Презентация к уроку географии 11 класс Зарубежная Азия.Зачет Татар теле дәресе 4 сыйныф
Татар теле дәресе 4 сыйныф Русская литература XVIII века
Русская литература XVIII века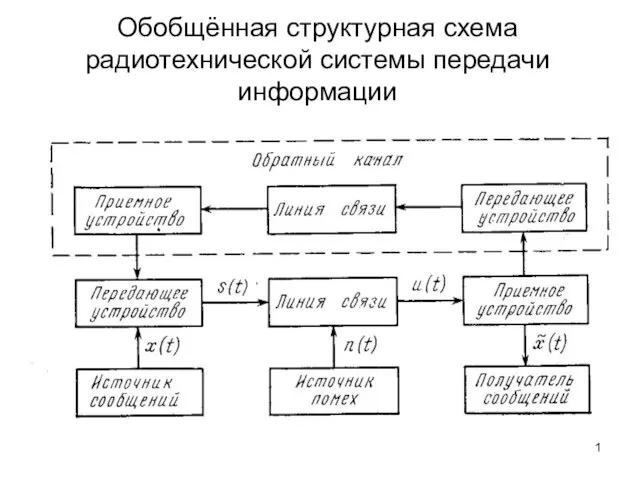 Обобщённая структурная схема радиотехнической системы передачи информации
Обобщённая структурная схема радиотехнической системы передачи информации Семья
Семья План и поисковые маркетинговые исследования: вторичная информация
План и поисковые маркетинговые исследования: вторичная информация Урок географии в 8-9 классах Формирование территории России
Урок географии в 8-9 классах Формирование территории России Изменение политической карты мира. Географические открытия. Конец XV – середина XX вв
Изменение политической карты мира. Географические открытия. Конец XV – середина XX вв Системы оповещения и управления эвакуацией при пожаре (далее СОУЭ)
Системы оповещения и управления эвакуацией при пожаре (далее СОУЭ) Магнітний запис інформації
Магнітний запис інформації Режим дня школьника
Режим дня школьника Шаблоны презентаций по химии
Шаблоны презентаций по химии презентация Найди отличия
презентация Найди отличия Исследовательский проект - лекарственные растения
Исследовательский проект - лекарственные растения Становление и развитие дошкольной педагогики
Становление и развитие дошкольной педагогики Уборочные машины и технологии
Уборочные машины и технологии Мейоз. Гаметогенез
Мейоз. Гаметогенез Иерусалим царя Давида и Соломона. Лекция 2
Иерусалим царя Давида и Соломона. Лекция 2 Гидродинамические исследования скважин
Гидродинамические исследования скважин Славное море - священный Байкал
Славное море - священный Байкал презентация Углерод
презентация Углерод Классный час,посвящённый Дню Победы. Диск Диск Диск
Классный час,посвящённый Дню Победы. Диск Диск Диск История, политическая программа, статистика
История, политическая программа, статистика Презентация Кто есть кто
Презентация Кто есть кто Требования, предъявляемые к строительным конструкциям
Требования, предъявляемые к строительным конструкциям