Содержание
- 3. Типы обёртки
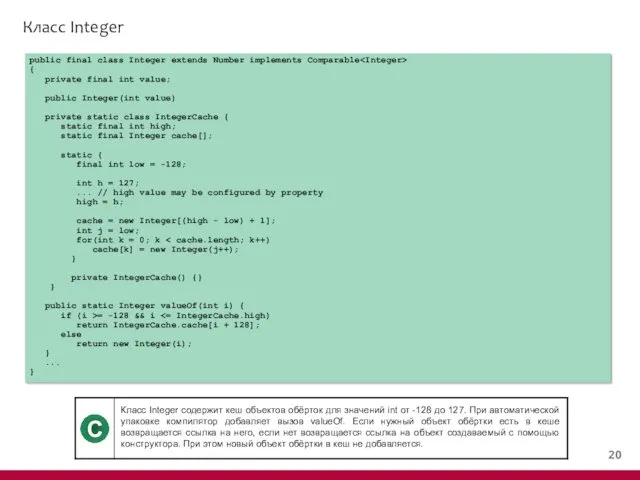
- 4. Класс Integer public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable { private final int value; public
- 5. Упаковка и распаковка
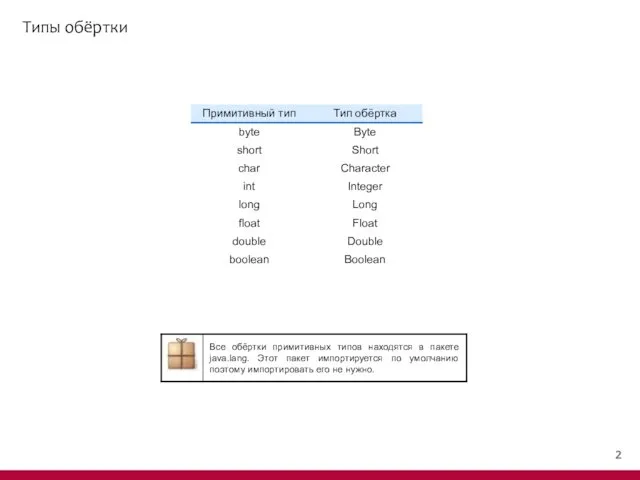
- 7. Упаковка public static void main(String[] args) { boolean boo = false; Boolean wboo = new Boolean(boo);
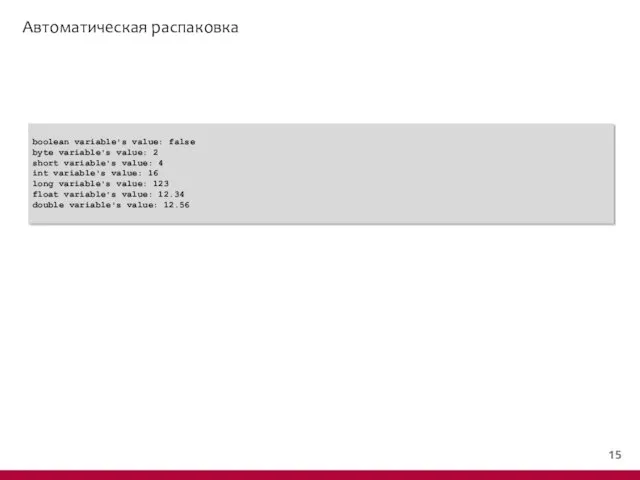
- 8. Упаковка boolean variable's value: false byte variable's value: 2 short variable's value: 4 int variable's value:
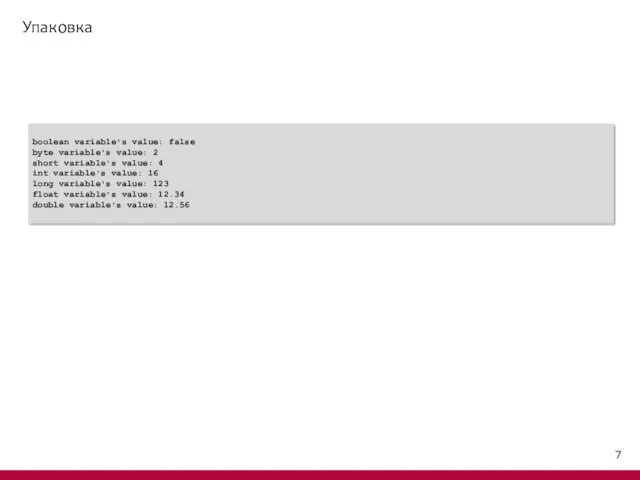
- 9. Распаковка public class UnwrapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Boolean wboo = new Boolean(false);
- 10. Распаковка boolean variable's value: false byte variable's value: 2 short variable's value: 4 int variable's value:
- 11. Автоматическая упаковка и распаковка
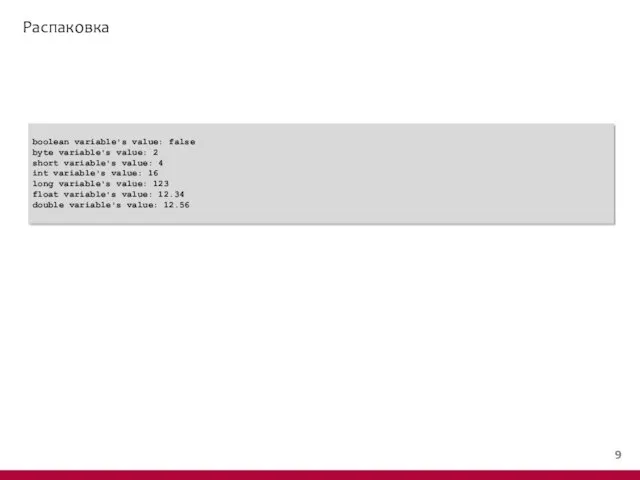
- 13. Автоматическая упаковка public class AutoWrapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean boo = false;
- 14. Автоматическая упаковка boolean variable's value: false byte variable's value: 2 short variable's value: 4 int variable's
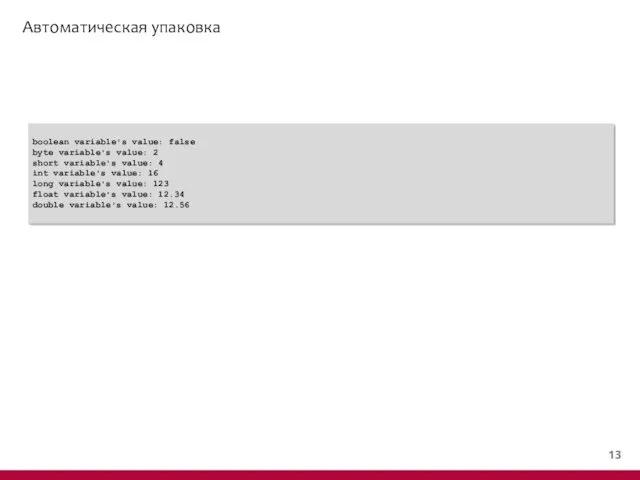
- 15. Автоматическая распаковка public class AutoUnwrapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Boolean wboo = new
- 16. Автоматическая распаковка boolean variable's value: false byte variable's value: 2 short variable's value: 4 int variable's
- 17. Кеширование обёрток
- 19. Интересный пример public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = 127; Integer j = 127;
- 20. Неожиданный результат i==j >> true a==b >> false k==l >> false
- 21. Класс Integer public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable { private final int value; public
- 22. Ошибки с автоматической упаковкой / распаковкой
- 23. Медленный цикл public class SlowCycleDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
- 24. Медленный цикл It took 1375 milliseconds to execute this cycle It took 156 milliseconds to execute
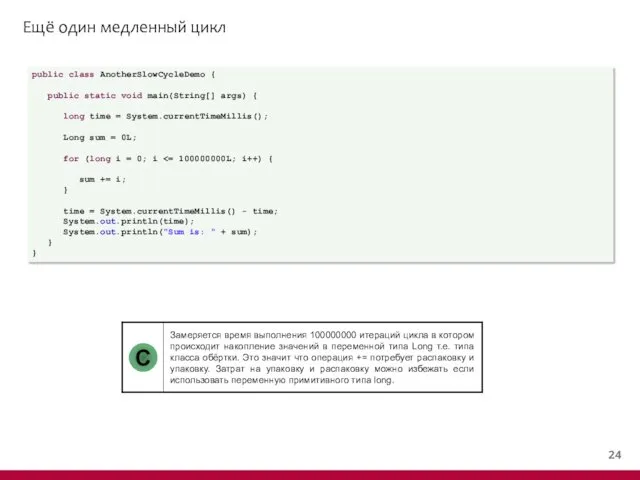
- 25. Ещё один медленный цикл public class AnotherSlowCycleDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { long time
- 26. Ещё один медленный цикл It took 1110 milliseconds to execute this cycle Sum is: 5000000050000000 It
- 27. Ошибка с оператором == public class WrapErrorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Compare 50
- 29. Скачать презентацию




![Упаковка public static void main(String[] args) { boolean boo =](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/60654/slide-6.jpg)
![Распаковка public class UnwrapDemo { public static void main(String[] args)](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/60654/slide-8.jpg)


![Автоматическая упаковка public class AutoWrapDemo { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/60654/slide-12.jpg)
![Автоматическая распаковка public class AutoUnwrapDemo { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/60654/slide-14.jpg)


![Интересный пример public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/60654/slide-18.jpg)


![Медленный цикл public class SlowCycleDemo { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/60654/slide-22.jpg)



 Методология научного познания
Методология научного познания Технология формирования интонационной стороны речи
Технология формирования интонационной стороны речи Презентация к уроку математики 5 класс (Никольский С.М. идр.)
Презентация к уроку математики 5 класс (Никольский С.М. идр.) Курская Битва. Лето 1943 года
Курская Битва. Лето 1943 года Учебно-методическое пособие. Игры на развитие фонематического анализа и синтеза.
Учебно-методическое пособие. Игры на развитие фонематического анализа и синтеза. Ферменты. Структура и функция. Классификация и номенклатура
Ферменты. Структура и функция. Классификация и номенклатура Терминальные состояния. Основы современной реанимации
Терминальные состояния. Основы современной реанимации Инфинитив и -ing форма
Инфинитив и -ing форма портфолио Диск Диск Диск Диск Диск Диск Диск
портфолио Диск Диск Диск Диск Диск Диск Диск Устройства ввода-вывода
Устройства ввода-вывода Вибраторы. Машины для уплотнения бетонной смеси
Вибраторы. Машины для уплотнения бетонной смеси Сергей Александрович Есенин (1895-1925)
Сергей Александрович Есенин (1895-1925) Презентация по теме Северный Кавказ (9 класс)
Презентация по теме Северный Кавказ (9 класс) Вся жизнь - страна детства
Вся жизнь - страна детства Тауартану – тауарлардың тұтынушылық қасиеттерін зерттейтін ғылыми пәнтауартану ғылым ретінде xvі ғ. Ортасында қалыптасты
Тауартану – тауарлардың тұтынушылық қасиеттерін зерттейтін ғылыми пәнтауартану ғылым ретінде xvі ғ. Ортасында қалыптасты Types of Bulbs
Types of Bulbs презентация Игра как педагогическая технология
презентация Игра как педагогическая технология Дезинфекция
Дезинфекция Адаптация студентов к обучению в медицинском вузе
Адаптация студентов к обучению в медицинском вузе Вместе победим туберкулез
Вместе победим туберкулез Простой компас
Простой компас Школа критики Полярного дня. Есенин vs Слава КПСС
Школа критики Полярного дня. Есенин vs Слава КПСС 20230923_biologiya_nauka_5_kl
20230923_biologiya_nauka_5_kl Зенкерование. Развертывание
Зенкерование. Развертывание Чесотка. Педикулез
Чесотка. Педикулез Алгебра предикатов
Алгебра предикатов Сборник заданий по математике для начальной школы
Сборник заданий по математике для начальной школы Сжатое изложение. Приёмы компрессии текста
Сжатое изложение. Приёмы компрессии текста