Содержание
- 2. CONTENTS The right of legation; Diplomatic missions: The functions of diplomatic missions; The structure and staff
- 3. 1. Right of legation Art. 2 of the VCDR “The establishment of diplomatic relations between States,
- 4. Right of legation The dipl. relations between Lithuania and Croatia were established on 18 March 1992.
- 5. Subjects of legation under the VCDR Art. 2 of the VCDR: “The establishment of diplomatic relations
- 6. It is interesting to read http://edition.cnn.com/2015/07/19/politics/cuba-u-s-embassies-opening/index.html the United States and Cuba re-established diplomatic relations. Ties were
- 7. 2. The modern titles of permanent diplomatic missions Remarks: Despite the title, all diplomatic missions are
- 8. Seat of a diplomatic mission On 6 December 2017 President Donald Trump recognised Jerusalem as Israel’s
- 9. Seat of a diplomatic mission Therefore, the President Trump announced the relocation of the American Embassy
- 10. Seat of a diplomatic mission Palestine Sues the United States in the ICJ re Jerusalem Embassy,
- 11. No diplomatic relations and missions States willing to establish and maintain relations, but evade the official
- 12. No diplomatic relations and missions E.g. on 12 August 2016 , the Head of the Palestinian
- 13. The functions of diplomatic mission (Art. 3 VCDR) Representation The protection of state and citizens interests
- 14. The functions of diplomatic mission (Art. 3 VCDR) The functions of diplomatic mission are to be
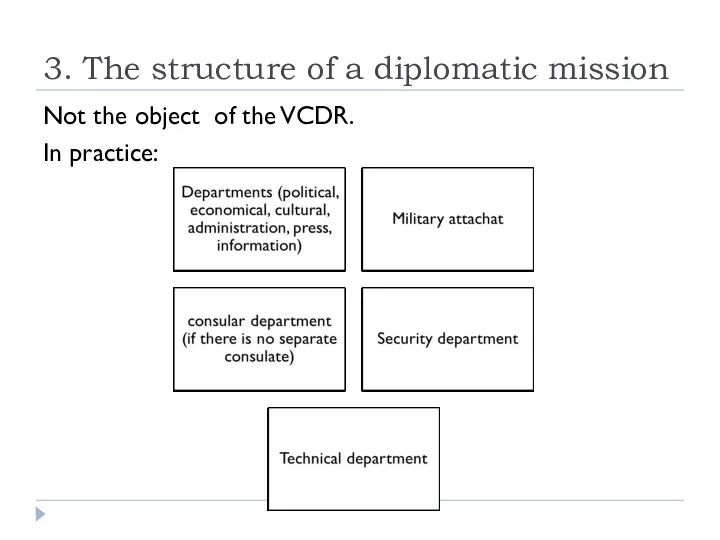
- 15. 3. The structure of a diplomatic mission Not the object of the VCDR. In practice:
- 16. Size of a mission Usually not limited but: see art. 11 VCDR; Limitations used in case
- 17. Size of a mission https://www.theguardian.com/world/2017/jul/30/russia-us-sanctions-retaliation-sergei-ryabkov Request of the Russian Federation to limit the diplomatic staff of
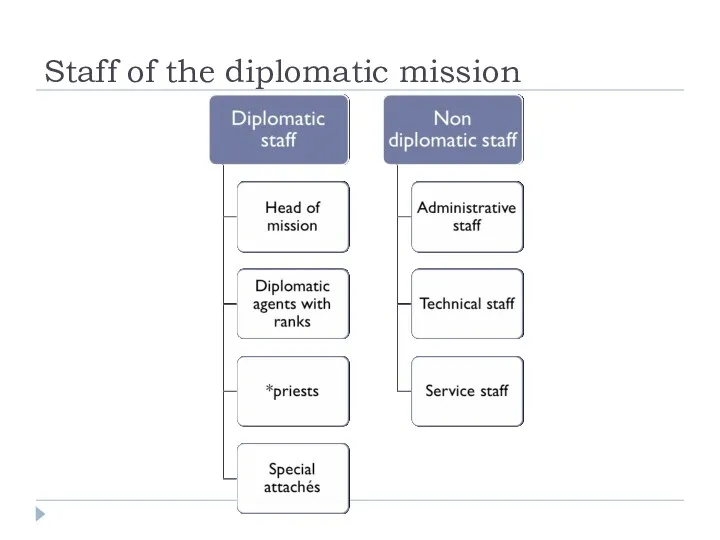
- 18. Staff of the diplomatic mission
- 19. Diplomatic corps / diplomatic body Diplomatic corps is understood: In the strict sense (comprises the heads
- 20. Head of diplomatic mission The head of the diplomatic mission: the person charged by the sending
- 21. Head of diplomatic mission On 17 August 2016, the Ambassador of Lithuania to Latvia Artūras Žurauskas
- 22. Head of diplomatic mission It would be interesting to read: http://www.eurojewcong.org/news-and-views/14718-egypt-sends-ambassador-to-israel-for-first-time-since-2012.html http://www.timesofisrael.com/israels-new-egypt-ambassador-presents-credentials-to-sissi/
- 23. Head of diplomatic mission Multiple accreditation – see VCDR Art. 5,6 – 1) sending of single
- 24. Appointment of the staff of the diplomatic mission VCDR Art. 4-11: The receiving state asks for:
- 25. Appointment of the staff of the diplomatic mission: rights of the receiving State It is open
- 26. Nationality of the diplomatic staff Art 8 of the VCDR General rule: members of the diplomatic
- 27. End of the function of the Head of diplomatic mission See Art 43 of the VCDR
- 28. End of the function of the Head of diplomatic mission When the head of the diplomatic
- 29. Diplomatic classes Diplomatic classes defined in Art. 14 of the VCDR (simplified version of the 1815
- 30. Diplomatic classes The diplomatic class is agreed between the States (Art 15 of the VCDR) No
- 32. Скачать презентацию



























 Индекс Административное давление — 2023
Индекс Административное давление — 2023 Организация электронного документооборота в сфере бухгалтерского и налогового учета
Организация электронного документооборота в сфере бухгалтерского и налогового учета Криминалистическая фотография
Криминалистическая фотография Конституция России – история и современность
Конституция России – история и современность Органы внутренних дел РФ
Органы внутренних дел РФ Информационно-справочная документация
Информационно-справочная документация Принятие законов. Право законодательной инициативы. Стадии законодательного процесса
Принятие законов. Право законодательной инициативы. Стадии законодательного процесса Право в системе нормативного регулирования
Право в системе нормативного регулирования Реализация и применение права. Юридический процесс
Реализация и применение права. Юридический процесс урок-игра Мы выбираем
урок-игра Мы выбираем Основной закон ФРГ
Основной закон ФРГ Судова влада, правосуддя, судова система та їх демократичні основи. Тема 2
Судова влада, правосуддя, судова система та їх демократичні основи. Тема 2 Права несовершеннолетних
Права несовершеннолетних Зарубежный опыт организации МСУ
Зарубежный опыт организации МСУ О внесении изменений в законодательные акты по назначению государственной социальной и академической стипендии
О внесении изменений в законодательные акты по назначению государственной социальной и академической стипендии Краткий обзор основных показателей отдела МСЭ № 5 за 9 мес. 2023 г
Краткий обзор основных показателей отдела МСЭ № 5 за 9 мес. 2023 г Аренда земельных участков
Аренда земельных участков Юридична грамотність кандидата: вибори в міську раду
Юридична грамотність кандидата: вибори в міську раду Несостоятельность (банкротство) предпринимателей
Несостоятельность (банкротство) предпринимателей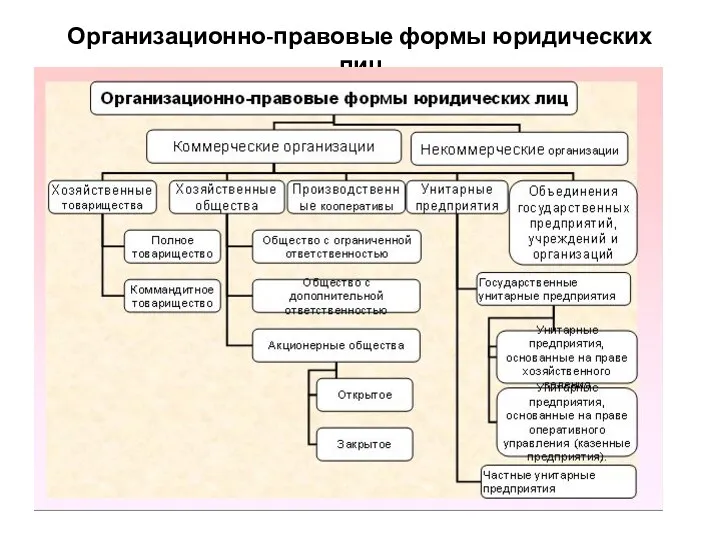 Организационно-правовые формы юридических лиц
Организационно-правовые формы юридических лиц Социальное обеспечение военнослужащих и членов их семей
Социальное обеспечение военнослужащих и членов их семей Аренда. Договор аренды. Лизинг и его виды
Аренда. Договор аренды. Лизинг и его виды Оформление реквизитов официальных документов организации (учреждения)
Оформление реквизитов официальных документов организации (учреждения) Семейные правоотношения
Семейные правоотношения Правове регулювання відносин в сфері захисту персональних даних. Тема 10
Правове регулювання відносин в сфері захисту персональних даних. Тема 10 Рабочее время и время отдыха
Рабочее время и время отдыха Защита прав потребителя
Защита прав потребителя Стратегия письменных деловых коммуникаций
Стратегия письменных деловых коммуникаций