Содержание
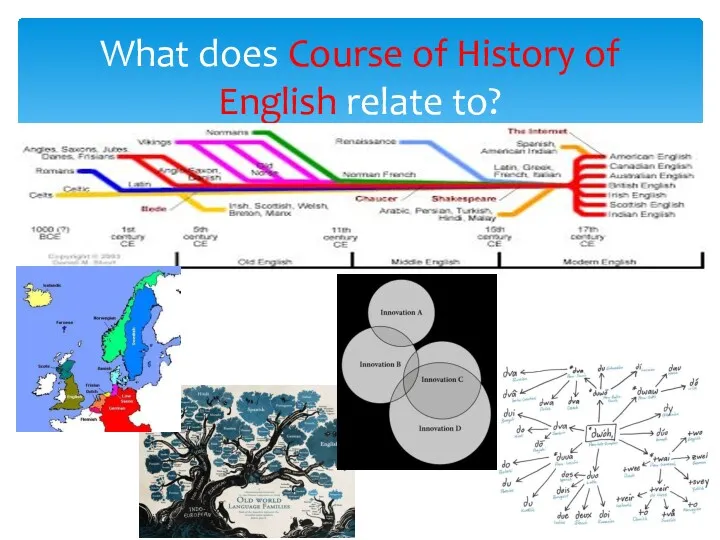
- 2. What does Course of History of English relate to?
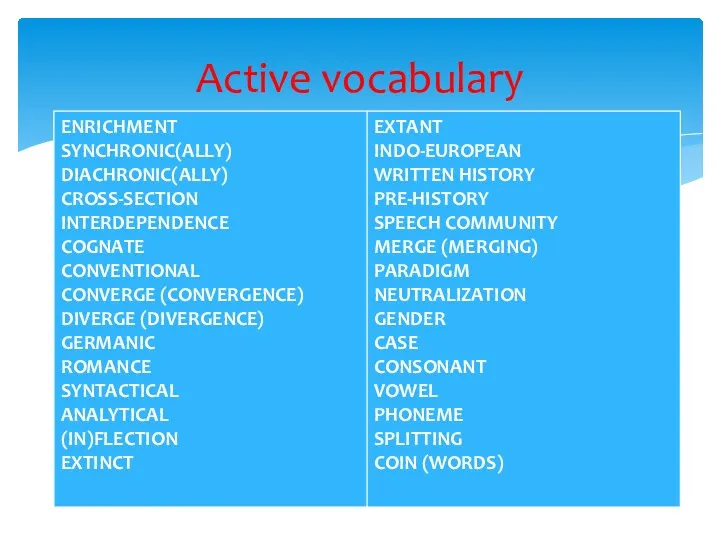
- 3. Active vocabulary
- 4. Subject and aim of HISTORY OF ENGLISH. Its sources. Different approaches to language development. Evolution of
- 5. Watch the video and give assumptions what this subject will help us understand: 1. Subject and
- 6. THIS SUBJECT WILL HELP US UNDERSTAND
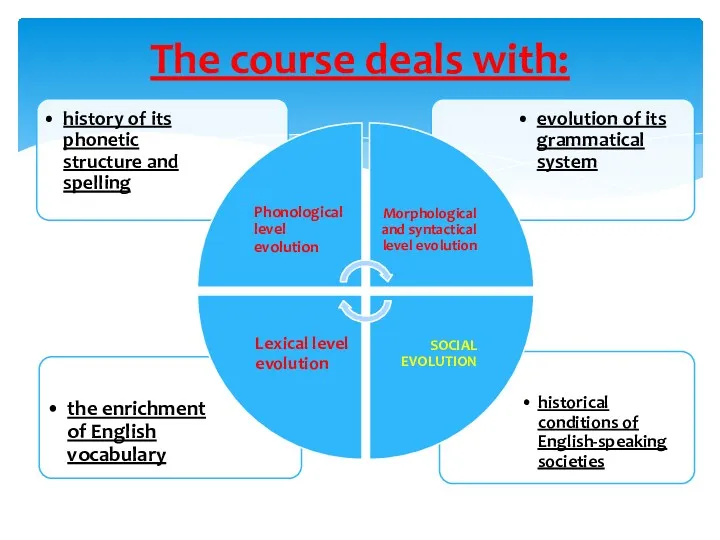
- 7. The course deals with:
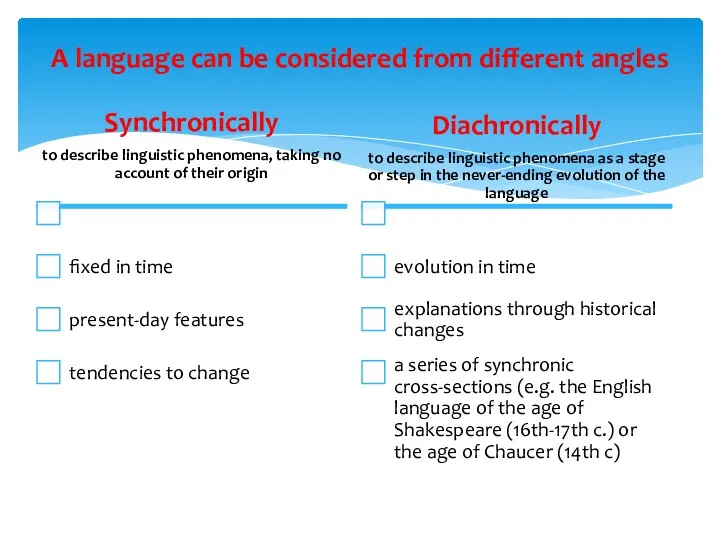
- 8. A language can be considered from different angles
- 9. Aims of the course: It helps us understand: – the essence of language evolution; – the
- 10. PHONETICS: The English word is conventional rather than phonetic (vs German or Latin) How many letters
- 11. VOCABULARY: What are English cognate words or roots with other Germanic languages (German, Swedish, Danish and
- 12. GRAMMAR: Does English have an analytical or syntactical structure? What English inflexions do you know? Why
- 13. How often do languages develop? Do we notice language changes? What is language reconstruction? What unites
- 14. HISTORICAL COMPARATIVE METHOD early 19th C - 1920s Language = a series of disconnected partial changes
- 15. QUIZZ: What is his name?
- 16. What is his name?
- 17. What is his name?
- 18. PROS AND CONS OF HISTORICAL COMPARATIVE METHOD
- 19. STRUCTURAL LINGUISTICS Structural linguistics is an examination of a language as a STATIC SYSTEM of interconnected
- 20. Everyone: Learn theoretical aspects of language evolution. Do exercises on “Language Development” handout. Watch episode “Birth
- 22. Скачать презентацию















 The Present Indefinite Tense
The Present Indefinite Tense Using Smart-services. Green technology in ICT. Teleconference. Telemedicine
Using Smart-services. Green technology in ICT. Teleconference. Telemedicine Грамматические трансформации
Грамматические трансформации Untranslatables
Untranslatables Five Senses
Five Senses Animals at the zoo
Animals at the zoo Ecological situation in Republic of Kazakhstan
Ecological situation in Republic of Kazakhstan Dvizh. Lesson 1
Dvizh. Lesson 1 The structure of the letter
The structure of the letter Formal letters. Module №3
Formal letters. Module №3 English - language authors
English - language authors History of Cosmonautics in Russia
History of Cosmonautics in Russia National dishes in Russia. Национальные блюда России
National dishes in Russia. Национальные блюда России Many, much, a lot of
Many, much, a lot of ОГЭ: Английский язык
ОГЭ: Английский язык Voronezh state university
Voronezh state university Лекция 15. Триггеры, их классификация. RS-, D-, JK, T-триггеры
Лекция 15. Триггеры, их классификация. RS-, D-, JK, T-триггеры What is your name? Where are you from?
What is your name? Where are you from? Present indefinite (simple) tense. Настоящее неопределенное (простое) время
Present indefinite (simple) tense. Настоящее неопределенное (простое) время My favourite season
My favourite season Foreign languages in our life
Foreign languages in our life Monuments to Aleksandr Isayevich Solzhenitsyn
Monuments to Aleksandr Isayevich Solzhenitsyn Business project
Business project Russian Federation
Russian Federation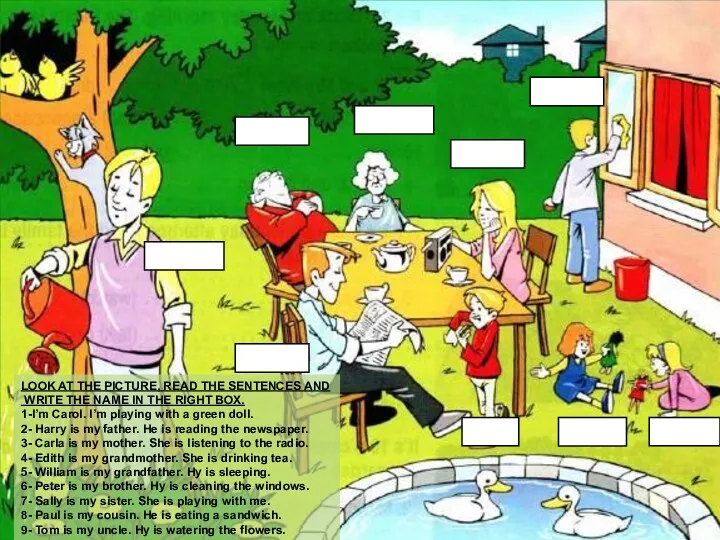 The family - present progressive
The family - present progressive Peculiarities of Kazakh and English sound systems
Peculiarities of Kazakh and English sound systems Чтение сочетаний ir, er, ur
Чтение сочетаний ir, er, ur Environment
Environment