Содержание
- 2. Direct Speech Прямая речь – это речь какого-нибудь лица, передаваемая без изменений, непосредственно так, как она
- 3. Direct Speech I like to read books.
- 4. Direct Speech Знаки препинания Pinocchio says, “I like to read books”.
- 5. Indirect (Reported) Speech Косвенная речь передает слова говорящего не слово в слово, а лишь по содержанию,
- 6. Indirect speech Pinocchio says that he likes to read books.
- 7. Слова автора Если глагол, вводящий косвенную речь (главное предложение), употреблен в настоящем или будущем времени, то
- 8. For example: He says, "I sent them the books on Monday." - Он говорит: «Я послал
- 9. He says to me, "I know it." – Он говорит мне: «Я знаю это». He says
- 10. Pronouns Личные и притяжательные местоимения прямой речи заменяются по смыслу, как и в русском языке: He
- 11. Pinocchio says, “The cat and the fox have taken my money." Pinocchio says that the cat
- 12. Просьбы Malawian says to her friends, “Do all the homework in time”. Malawian asks her friends
- 13. Запрет The bat says, “Do not open this door”. The bat warns not to open that
- 14. Общий вопрос общие вопросы переводятся придаточным предложением и вводятся союзами if, whether. Порядок слов прямой. He
- 15. Специальный вопрос передается придаточным предложением и вводятся союзом, соответствующим вопросительному слову. Порядок слов становится прямым. She
- 16. Remember! this that yesterday the day before yesterday these those tomorrow the next day here there
- 17. Let’s practice Pinocchio says, “Malawian, I love you”. Pinocchio says that he loves Malawian.
- 18. What is correct? She asks, “Where is Wales situated?” 1.She asks where is Wales situated? 2.She
- 19. What is correct? She asks, “Is Wales situated on the Isles?” 1.She asks, if Wales is
- 20. Слова автора Если глагол, вводящий косвенную речь (главное предложение), употреблен в прошедшем времени, то глагол в
- 21. Sequence of Tenses
- 24. Скачать презентацию





















 Квантификаторы
Квантификаторы Развиваться на протяжении всей жизни
Развиваться на протяжении всей жизни Numerals (числительные)
Numerals (числительные) London Attractions
London Attractions Portfolio
Portfolio Repetition game
Repetition game Местоимения. Pronouns. (2 класс)
Местоимения. Pronouns. (2 класс) Seasons and months of the year
Seasons and months of the year Anumals in danger
Anumals in danger Wh questions. Jeopardy game fun activities games. Games grammar
Wh questions. Jeopardy game fun activities games. Games grammar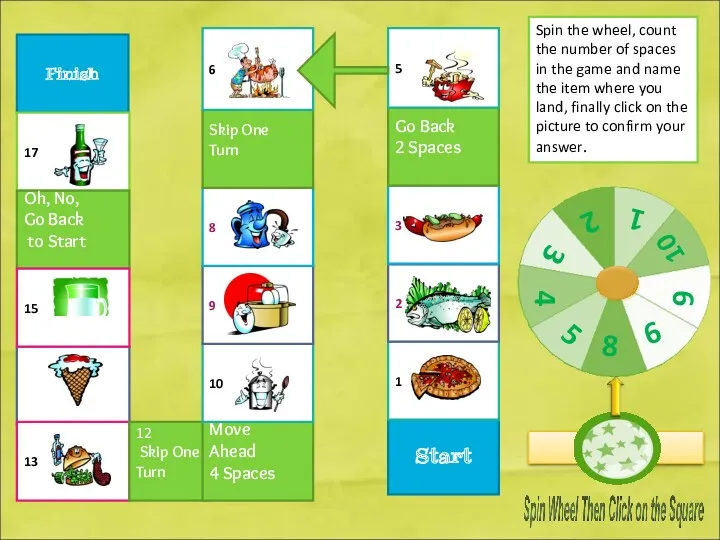 Food, drinks
Food, drinks Basic information about Las Vegas
Basic information about Las Vegas Great Britain
Great Britain Why is the earth crying?
Why is the earth crying? Self -education is impossible without computer skills
Self -education is impossible without computer skills Вспомогательные глаголы и модальные слова
Вспомогательные глаголы и модальные слова Word formation. Game
Word formation. Game Italy: presentation of my contry
Italy: presentation of my contry I think one of the best inventions of the gasoline internal combustion engine
I think one of the best inventions of the gasoline internal combustion engine American superstitions
American superstitions Christmas games Santa Claus
Christmas games Santa Claus Match the pictures with the film genres
Match the pictures with the film genres Fruits flashcards
Fruits flashcards Impressionism What is impressionism?
Impressionism What is impressionism? English Crossword Puzzles
English Crossword Puzzles Enjoy English 4. Unit 2. Enjoying your home
Enjoy English 4. Unit 2. Enjoying your home Winter holidays in Britain
Winter holidays in Britain Food
Food