Содержание
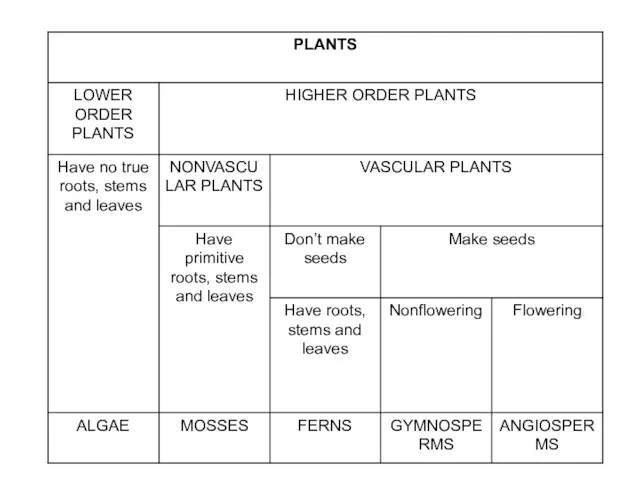
- 2. What is a Plant? Plants are the base for the food chain on land. Provide shade,
- 4. Monocots and Dicots Cotyledons-Seed leaves in the plant embryo Monocots-One seed leaf, parallel veins, multiples of
- 5. Monocots and Dicots
- 6. Kingdom Fungi
- 7. Characteristics of all Fungi Eukaryotic Most are multicellular & filamentous A few are single celled (yeasts)
- 8. Structure of Fungi Each cell has a cell wall made of chitin Hyphae are hair-like filamentous
- 9. Reproduction Fungi can reproduce asexually by budding and by asexual spore production. The hyphae and asexual
- 10. Classification of Fungi Fungi are classified into 4 phyla (divisions) depending on the type of fruiting
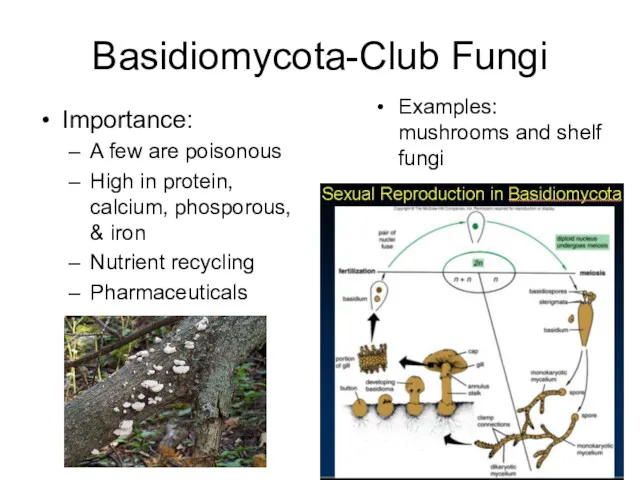
- 11. Basidiomycota-Club Fungi Importance: A few are poisonous High in protein, calcium, phosporous, & iron Nutrient recycling
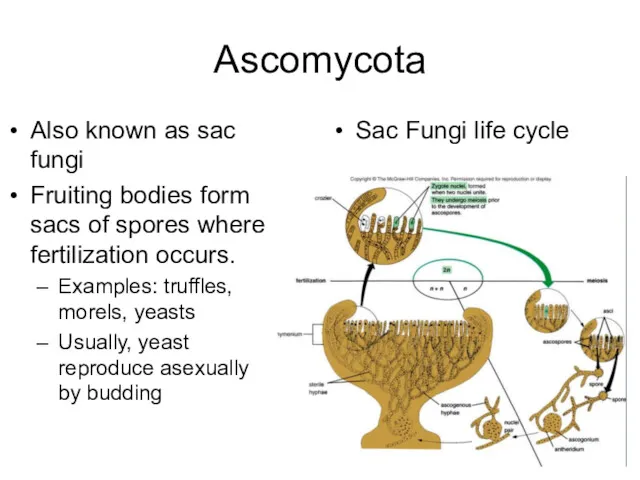
- 12. Ascomycota Also known as sac fungi Fruiting bodies form sacs of spores where fertilization occurs. Examples:
- 13. Importance of Ascomycota Truffles and morels have been prized for centuries. Morel Truffles
- 14. Importance of Ascomycota (continued) Ergot fungus may infect rye and other grains. Ergotism (poisoning) may occur
- 15. Importance of Ascomycota (continued) Yeast is very important for humans in that Yeast enzymes aid in
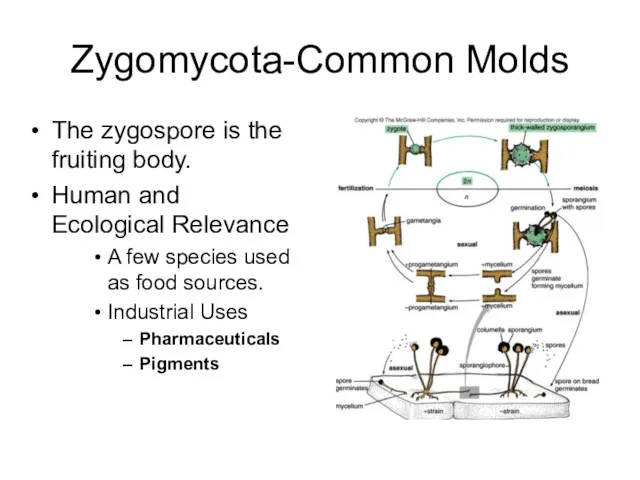
- 16. Zygomycota-Common Molds The zygospore is the fruiting body. Human and Ecological Relevance A few species used
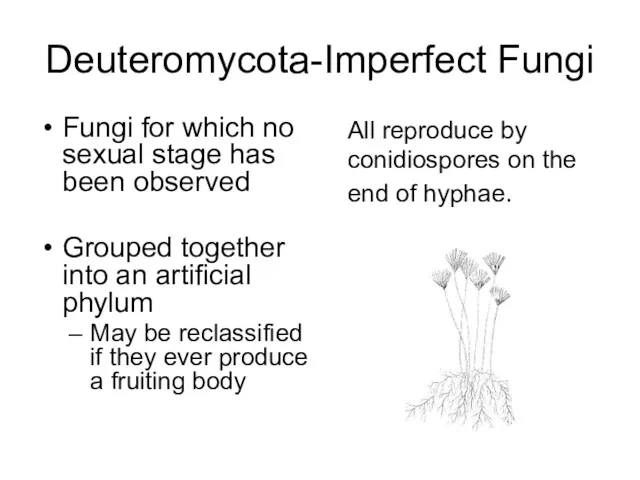
- 17. Deuteromycota-Imperfect Fungi Fungi for which no sexual stage has been observed Grouped together into an artificial
- 18. Importance of Deuteromycota Penicillium Molds Antibiotics Gourmet Cheese Aspergillus Citric Acid Soy Sauce Aspergilloses (Respiratory Disease)
- 19. Symbiotic Relationships Mutualism-two species living together, both benefit Example: Lichen The fungus hangs on to the
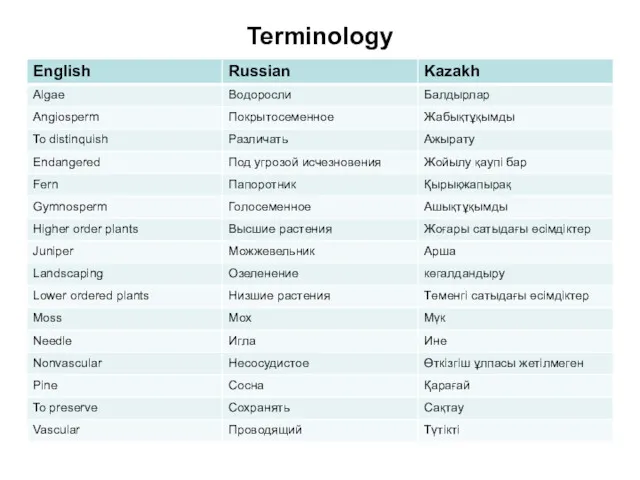
- 20. Terminology
- 22. Скачать презентацию













 At the school shop
At the school shop Приемы работы над лексическим материалом на уроках английского языка в начальной школе
Приемы работы над лексическим материалом на уроках английского языка в начальной школе Guess the room
Guess the room There are four types of Future
There are four types of Future Single-storey with a mansard house
Single-storey with a mansard house My school
My school “How” to see the British Isles
“How” to see the British Isles Достопримечательности Лондона
Достопримечательности Лондона About newspapers
About newspapers Holidays in september
Holidays in september Учись писать эссе
Учись писать эссе At the airport
At the airport My family
My family Discrimination
Discrimination Events breaking the law
Events breaking the law Opposites. Colours
Opposites. Colours Personal letter
Personal letter What do you do
What do you do Conditional sentences. Условные предложения
Conditional sentences. Условные предложения Furniture. Guess the card
Furniture. Guess the card Spotlight C14-16
Spotlight C14-16 The programmer
The programmer Briefly about yourself
Briefly about yourself My favourite hobby
My favourite hobby What’s the weather like
What’s the weather like Artists and writers of Great Britain and America
Artists and writers of Great Britain and America Comparison and superlative adjectives
Comparison and superlative adjectives An American breakfast!
An American breakfast!