Содержание
- 2. Chapter 5 Personality and Values
- 3. After studying this chapter you should be able to: Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 5- Describe
- 4. Personality Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Personality - the sum total of ways in which an
- 5. Measuring Personality Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Self-report surveys Most common Prone to error Evaluate on
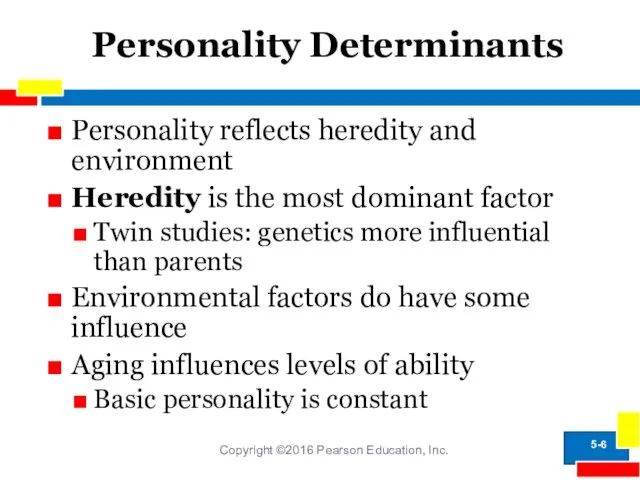
- 6. Personality Determinants Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Personality reflects heredity and environment Heredity is the most
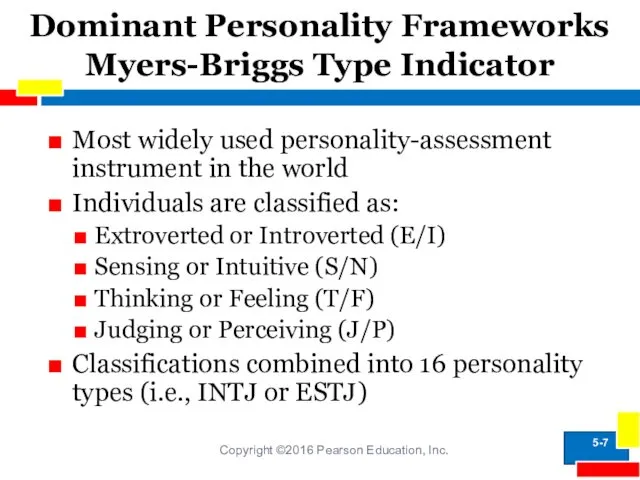
- 7. Dominant Personality Frameworks Myers-Briggs Type Indicator Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Most widely used personality-assessment instrument
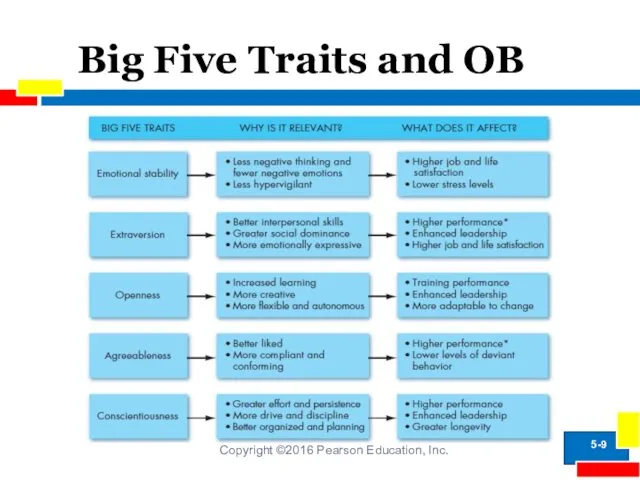
- 8. Measuring Personality Traits: The Big-Five Model Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Five Traits: Extraversion Agreeableness Conscientiousness
- 9. Big Five Traits and OB Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 5-
- 10. Other Personality Frameworks Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Dark Triad Machiavellianism High machs tend to
- 11. Other Personality Frameworks Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The approach-avoidance framework Approach motivation – our attention
- 12. Other Personality Traits Relevant to OB Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Core self-evaluation People with positive
- 13. Personality and Situations Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The effect of particular traits on organization behavior
- 14. Personality and Situations Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Situation strength theory – the way personality translates
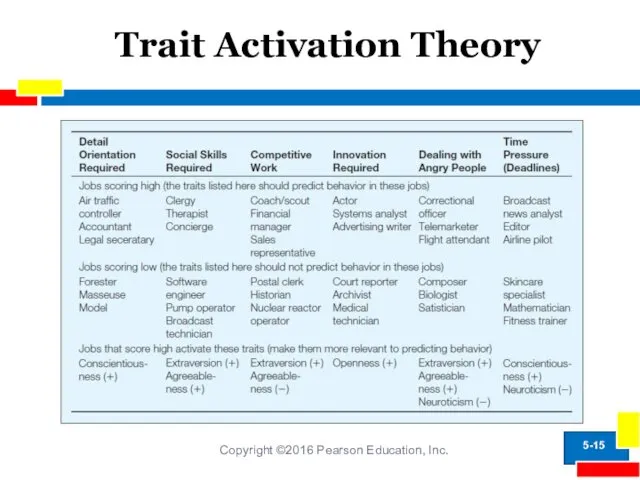
- 15. Trait Activation Theory Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 5-
- 16. Values Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Values represent basic, enduring convictions that "a specific mode of
- 17. Value Systems Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Represent a prioritizing of individual values by: Content –
- 18. Rokeach Value Survey Terminal values: desirable end-states of existence Goals that a person would like to
- 19. Personality-Job Fit: Holland’s Hexagon Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Job satisfaction and turnover depend on congruency
- 20. Personality-Job Fit: Holland’s Hexagon Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 5-
- 21. Person-Organization Fit Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. It is more important that employees’ personalities fit with
- 22. International Values Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Values differ across cultures Two frameworks for assessing culture:
- 23. Hofstede’s Framework for Assessing Cultures Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Five factors: Power Distance Individualism vs.
- 24. Hofstede’s Framework for Assessing Cultures Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 5-
- 25. GLOBE Framework for Assessing Cultures Assertiveness Future orientation Gender differentiation Uncertainty avoidance Power distance Individualism/ collectivism
- 26. Implications for Managers Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Consider screening job candidates for high conscientiousness Use
- 27. Keep in Mind… Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Personality The sum total of ways in which
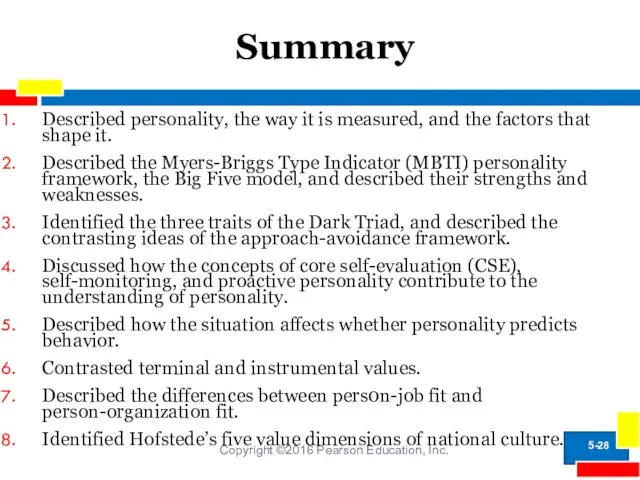
- 28. Summary Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 5- Described personality, the way it is measured, and the
- 30. Скачать презентацию


















 Past Tenses
Past Tenses Seasons and months
Seasons and months English Lapbook ISN Templates
English Lapbook ISN Templates What makes all people kin (что делает всех людей родней)
What makes all people kin (что делает всех людей родней) Степени сравнения прилагательных Adjectives Degrees of Comparison
Степени сравнения прилагательных Adjectives Degrees of Comparison What do you think we are going to speak about?
What do you think we are going to speak about? Do what you can, with what you have, where you are
Do what you can, with what you have, where you are Scotland
Scotland The middle english period
The middle english period Учим новую фразу. I like it
Учим новую фразу. I like it Английский за 2 месяца. www.englishfortravel.com
Английский за 2 месяца. www.englishfortravel.com Birthday party!
Birthday party! Future simple
Future simple Fruit And Vegetable Riddles Fun Activities Games
Fruit And Vegetable Riddles Fun Activities Games Where are the toys. Grammar drills
Where are the toys. Grammar drills Relative Clauses (Относительные придаточные предложения)
Relative Clauses (Относительные придаточные предложения) I have got a pet
I have got a pet Game Travelling. Level A2 – B1
Game Travelling. Level A2 – B1 Тренинг “Учимся читать и писать за 4 дня”
Тренинг “Учимся читать и писать за 4 дня” Обучаем чтению и письму с Английским в фокусе
Обучаем чтению и письму с Английским в фокусе Past continuous. At the museum
Past continuous. At the museum Wild animals game
Wild animals game Sentence Structure: Sentence Types
Sentence Structure: Sentence Types Sport
Sport Complex Object (Сложное дополнение). 11 класс
Complex Object (Сложное дополнение). 11 класс Past Simple was / were
Past Simple was / were Colors
Colors Аяқталған келер шақ
Аяқталған келер шақ