Содержание
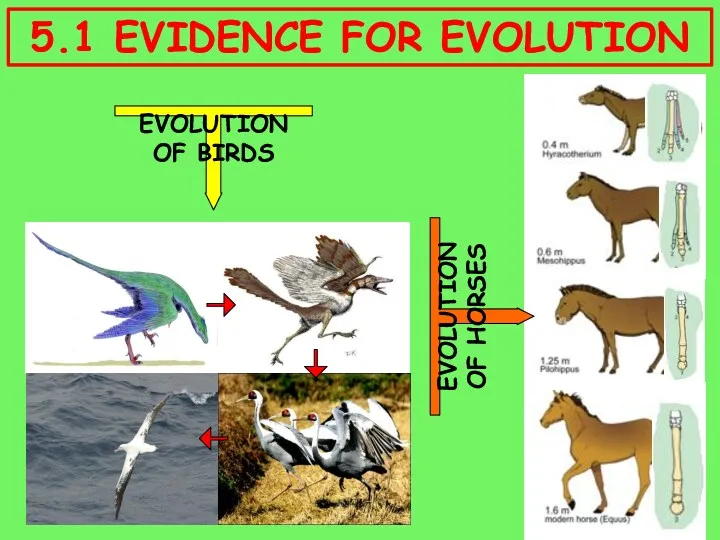
- 2. EVOLUTION OF BIRDS EVOLUTION OF HORSES 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
- 3. THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION “First” proposed by Charles Darwin. Based on data
- 4. WE SHOULD THANK ALFRED WALLACE… 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION In 1858 Wallace sent Darwin a letter
- 5. ANALYSING THE EVIDENCE 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION Most biologists accept the theory of evolution based on
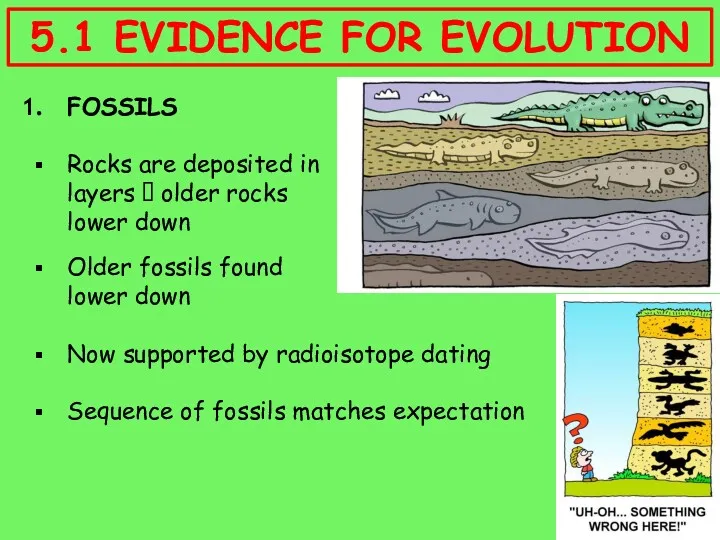
- 6. FOSSILS Rocks are deposited in layers ? older rocks lower down Older fossils found lower down
- 7. 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION FOSSILS Bacteria ? Algae ? Fungi ? Worms ? Fish ? Amphibians
- 8. FOSSILS Sequences of fossils found linking together current species with likely ancestors 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
- 9. 2. SELECTIVE BREEDING Artificial selection Repeatedly select & breed individuals with desired characteristics Produced breeds often
- 10. 2. SELECTIVE BREEDING 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION Auroch from Asia Belgian Blue
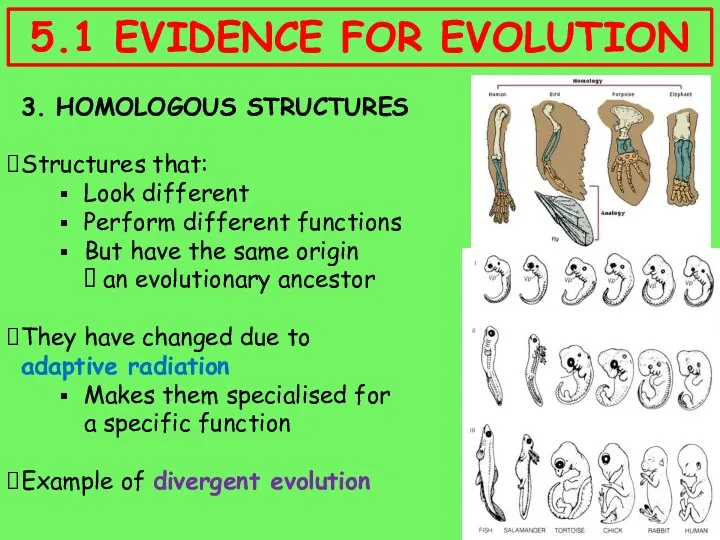
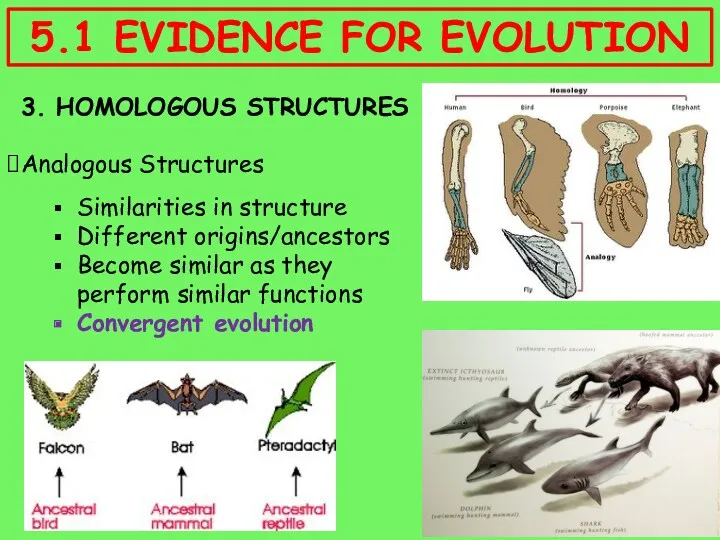
- 11. 3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES Structures that: Look different Perform different functions But have the same origin ?
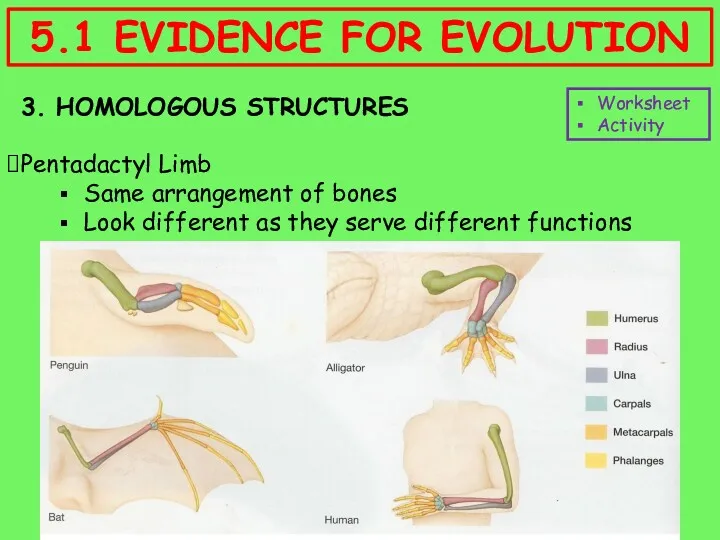
- 12. 3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES Pentadactyl Limb Same arrangement of bones Look different as they serve different functions
- 13. 3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES Vestigial organs Reduced structures that serve no function Difficult to explain without evolution
- 14. 3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES Analogous Structures Similarities in structure Different origins/ancestors Become similar as they perform similar
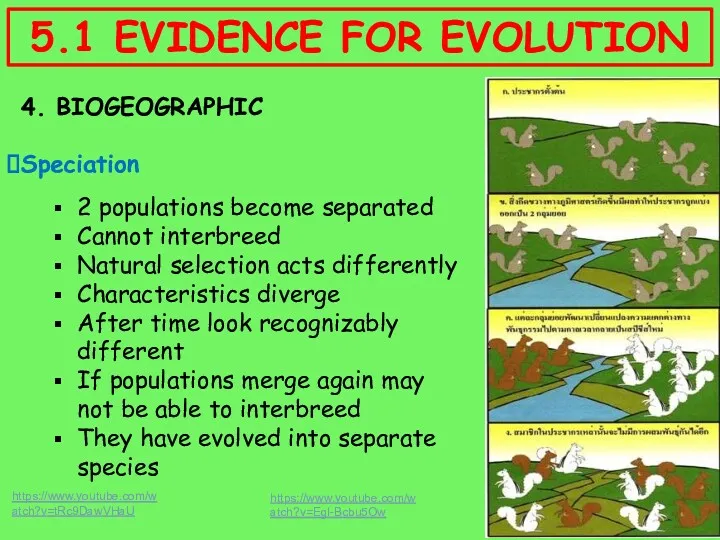
- 15. 4. BIOGEOGRAPHIC Speciation 2 populations become separated Cannot interbreed Natural selection acts differently Characteristics diverge After
- 16. 5.1 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
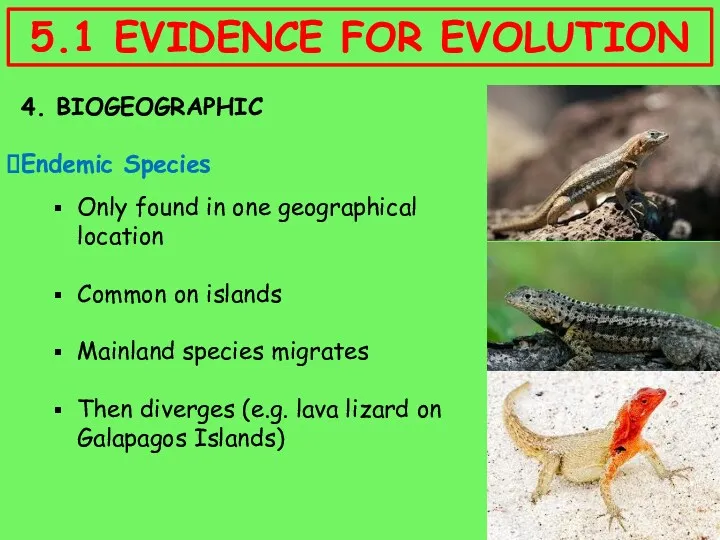
- 17. 4. BIOGEOGRAPHIC Endemic Species Only found in one geographical location Common on islands Mainland species migrates
- 19. Скачать презентацию









 History of Money
History of Money Guitar music
Guitar music How much. How many. I have plenty of time
How much. How many. I have plenty of time Soil pollution. Noise pollution
Soil pollution. Noise pollution Welcome to Hseimun diplomacy club
Welcome to Hseimun diplomacy club Benchmarking
Benchmarking Американские и английские песенки
Американские и английские песенки Compounded nouns. Prepositions
Compounded nouns. Prepositions Ukraine
Ukraine Моя семья. Spotlight (5 класс)
Моя семья. Spotlight (5 класс) Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal Appearance. Well - dressed, elegant
Appearance. Well - dressed, elegant Leading teams
Leading teams Phonetic exercise
Phonetic exercise Present perfect. Simple past
Present perfect. Simple past Adverbs of manner
Adverbs of manner Thanksgiving activities
Thanksgiving activities Etymological Characteristics of the English Vocabulary
Etymological Characteristics of the English Vocabulary The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Was-were (
Was-were ( Summer holidays oral practice
Summer holidays oral practice World monuments in danger. “Passive Voice”
World monuments in danger. “Passive Voice” What? Where? When? food
What? Where? When? food Describing people
Describing people Food and taste
Food and taste Методы и формы контроля при изучении иностранного языка
Методы и формы контроля при изучении иностранного языка Writing film reviews
Writing film reviews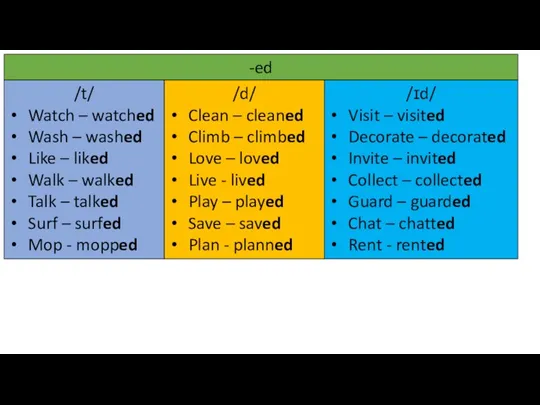 Past simple
Past simple