Содержание
- 2. Description A fracture is a disruption or break in the continuity of the structure of bone
- 3. On the basis of Etiology: 1.Traumatic fractures Most commmon type of fractures Road accidents, falls, fight,
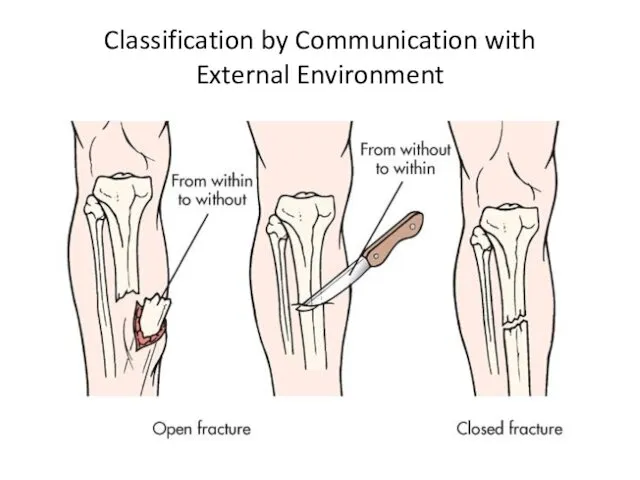
- 5. Classification by Communication with External Environment
- 6. On the basis of complexity of fractures: Simple fractures Complex fractures
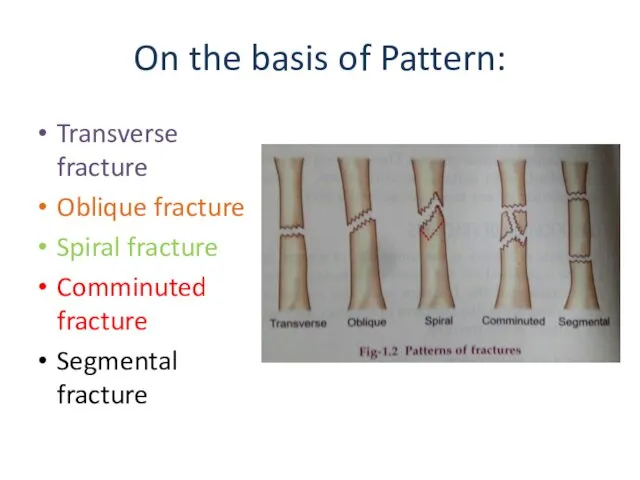
- 7. On the basis of Pattern: Transverse fracture Oblique fracture Spiral fracture Comminuted fracture Segmental fracture
- 8. On the basis of Displacements: Undisplaced fracture Displaced fracture
- 9. Signs of bone fractures Strong swelling, bruising, sometimes the limb is bent outside the joint; with
- 10. Closed Fractures There are closed fractures in which skin integrity is not broken.
- 11. Treatment of fractures can be considered in 3 phases: PHASE I: EMERGENCY CARE PHASE II: DEFINITIVE
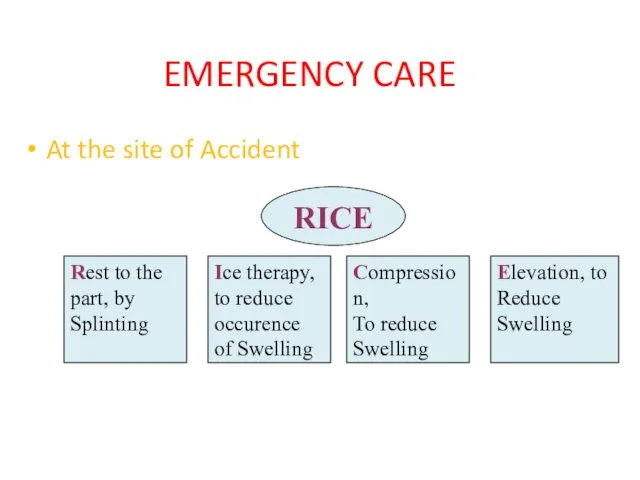
- 12. EMERGENCY CARE At the site of Accident RICE Rest to the part, by Splinting Ice therapy,
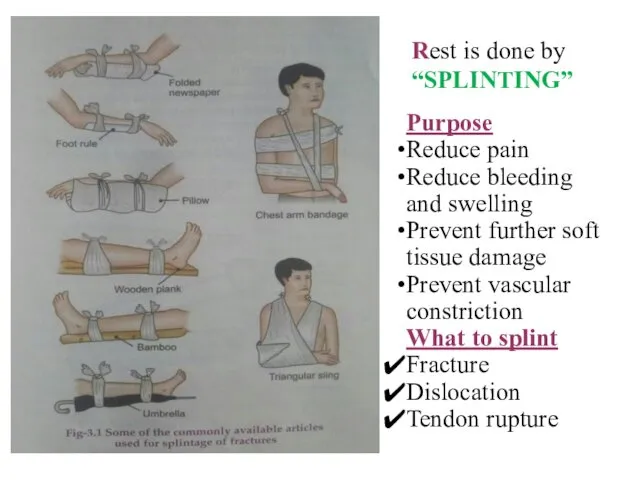
- 13. Rest is done by “SPLINTING” Purpose Reduce pain Reduce bleeding and swelling Prevent further soft tissue
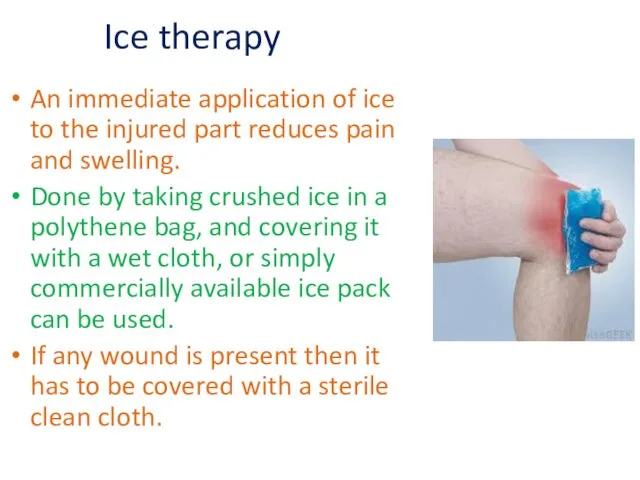
- 14. Ice therapy An immediate application of ice to the injured part reduces pain and swelling. Done
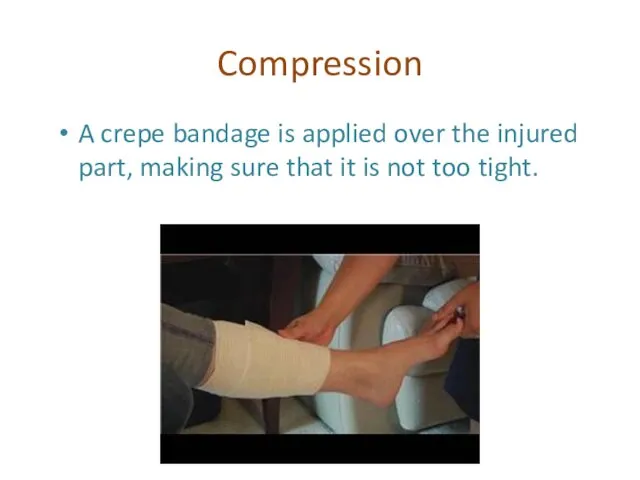
- 15. Compression A crepe bandage is applied over the injured part, making sure that it is not
- 16. Elevation Limb is elevated so that the injured part is above the level of the heart.
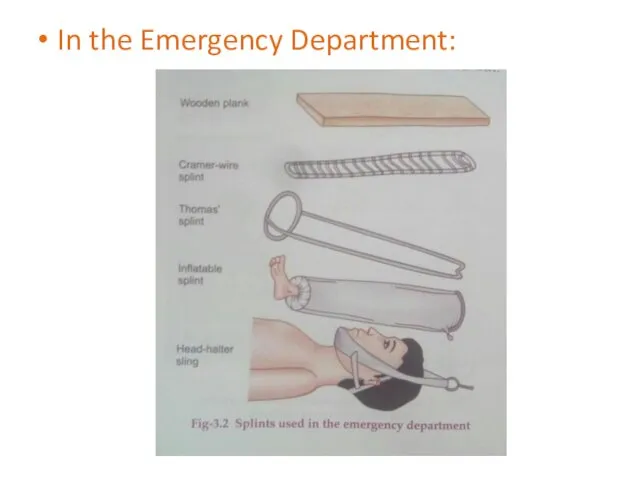
- 17. In the Emergency Department:
- 18. Open fractures An open fracture can be defined as ‘a break in the skin and underlying
- 19. Results from high-energy trauma, often with extensive soft tissue injury and contamination. Therefore, they carry a
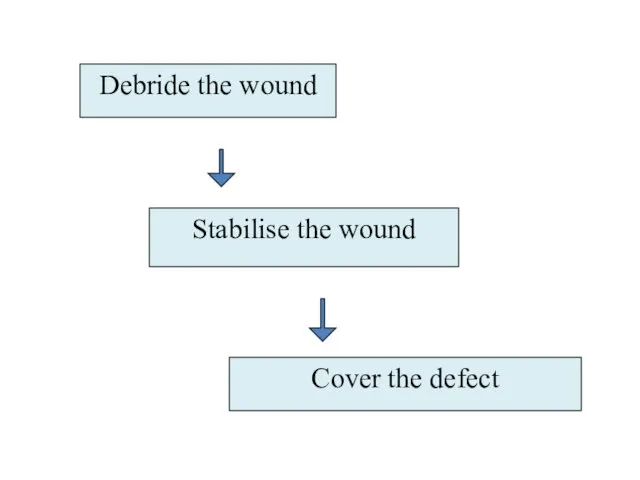
- 21. Debride the wound Stabilise the wound Cover the defect
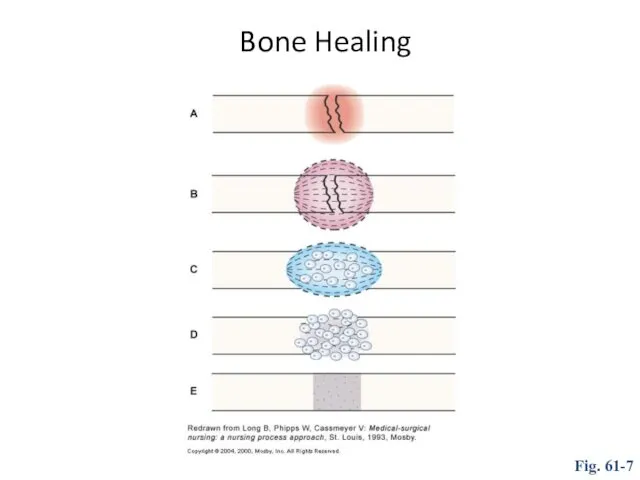
- 24. Bone Healing Fig. 61-7
- 26. Скачать презентацию













 What’s the weather like
What’s the weather like Christmas cookies
Christmas cookies Education in Kazakhstan
Education in Kazakhstan National flags of different countries
National flags of different countries Who am I? Describing people
Who am I? Describing people Урок іноземної мови
Урок іноземної мови What do they look like
What do they look like The Traditions Of Great Britain
The Traditions Of Great Britain Russian dumplings
Russian dumplings International organisations and the united nations
International organisations and the united nations Учимся читать
Учимся читать Christmas vocabulary quiz
Christmas vocabulary quiz Places of interest in London
Places of interest in London Spotlight 3. Food
Spotlight 3. Food Tradition korean food
Tradition korean food Our faculty
Our faculty My room. My family
My room. My family Past Simple. Present Perfect
Past Simple. Present Perfect The Title of my project is Welcome to Russia!
The Title of my project is Welcome to Russia! She’s got blue eyes. Лицо
She’s got blue eyes. Лицо Let’s recall irregular verbs
Let’s recall irregular verbs Christmas advent calendar
Christmas advent calendar Spotlight 7. Revision
Spotlight 7. Revision Спорт. Кроссворд на английском языке
Спорт. Кроссворд на английском языке I’ve got
I’ve got Animal spaceman game hangman
Animal spaceman game hangman Time to travel, USA
Time to travel, USA A typical english house (5 класс)
A typical english house (5 класс)