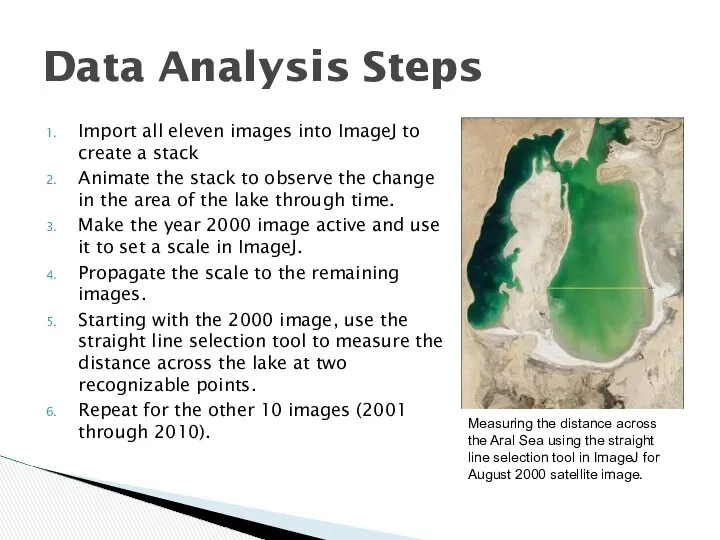
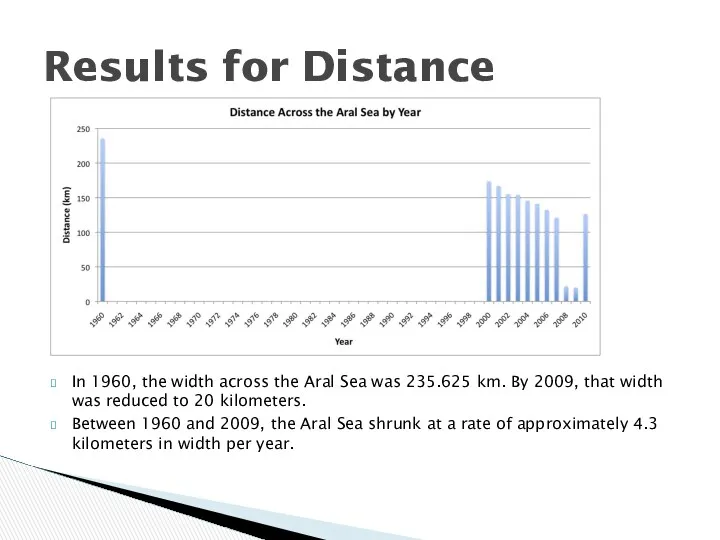
In 1960, the width across the Aral Sea was 235.625 km.
By 2009, that width was reduced to 20 kilometers.
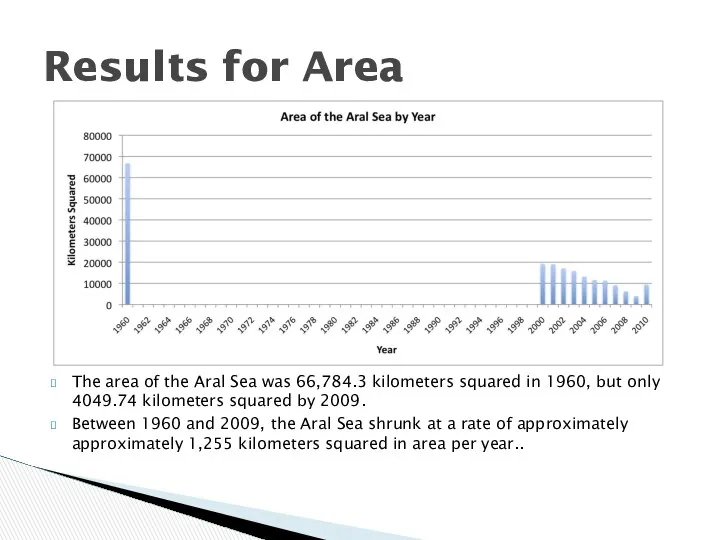
In a similar manner, the area of the Aral Sea was 66,784.3 kilometers squared in 1960, but only 4049.74 kilometers squared by 2009.
We took the difference between the 2009 widths and areas and the 1960 measurements, dividing this difference by the number of years (50) to calculate average yearly rates of change.
Between 1960 and 2009, the Aral Sea shrunk at a rate of approximately 4.3 kilometers in width per year and at a rate of approximately 1,255 kilometers squared in area per year.
Findings & Discussion









 London
London Around town
Around town Asking and Giving directions
Asking and Giving directions Past progressive tense
Past progressive tense Устная часть по английскому языку Основного Государственного Экзамена (ОГЭ)
Устная часть по английскому языку Основного Государственного Экзамена (ОГЭ) Грамматические вопросы перевода (структура предложения, артикль, глаголы в пассивном залоге, инфинитив и инфинитивные обороты)
Грамматические вопросы перевода (структура предложения, артикль, глаголы в пассивном залоге, инфинитив и инфинитивные обороты)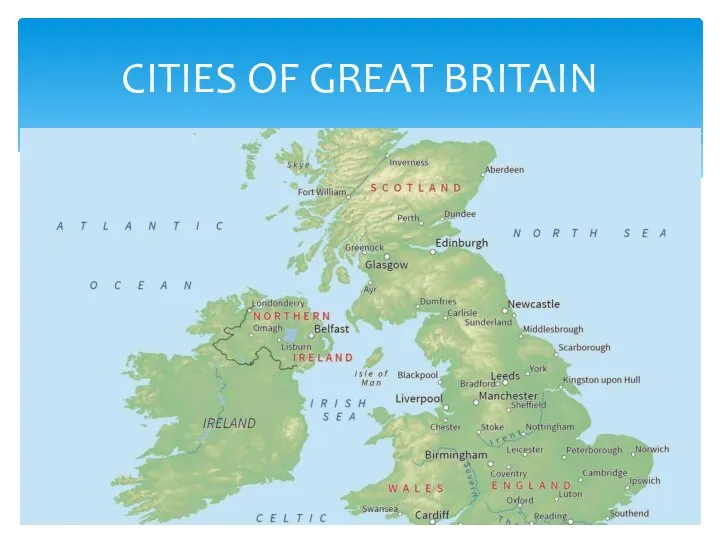 Cities Of Great Britain
Cities Of Great Britain Saint Patrick's day
Saint Patrick's day Тренажёр. ЕГЭ. Устная часть. Task 3
Тренажёр. ЕГЭ. Устная часть. Task 3 Clothes
Clothes Fitness. A sound mind in a sound body
Fitness. A sound mind in a sound body How old are you?
How old are you? How to get a job
How to get a job Говорение (монологическая речь)
Говорение (монологическая речь) The Object Model
The Object Model My home
My home klass_po_teme
klass_po_teme Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela)
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela) Famous people of Great Britain
Famous people of Great Britain Alexander Ovechkin
Alexander Ovechkin Change of guard
Change of guard Winter holidays. Is It for the rich only?
Winter holidays. Is It for the rich only? Harry Potter (game)
Harry Potter (game) Daily Routines
Daily Routines Direct and reported speech (Прямая и косвенная речь)
Direct and reported speech (Прямая и косвенная речь) The water cycle
The water cycle Present simple - to be
Present simple - to be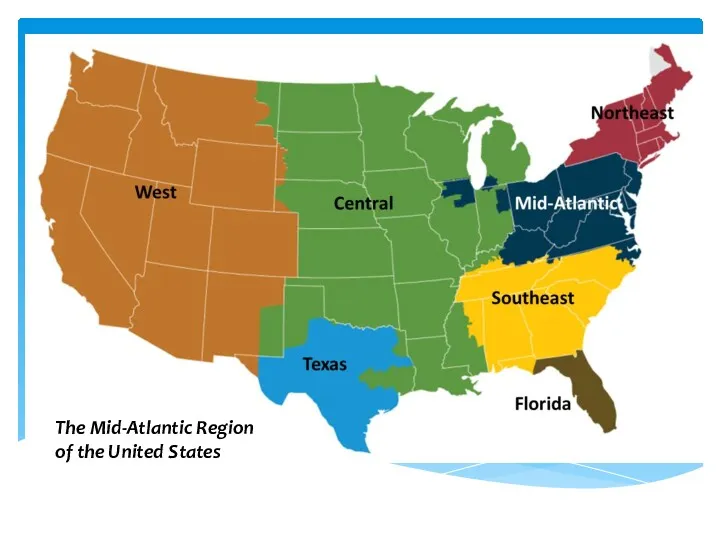 The Mid-Atlantic Region of the United States
The Mid-Atlantic Region of the United States