Содержание
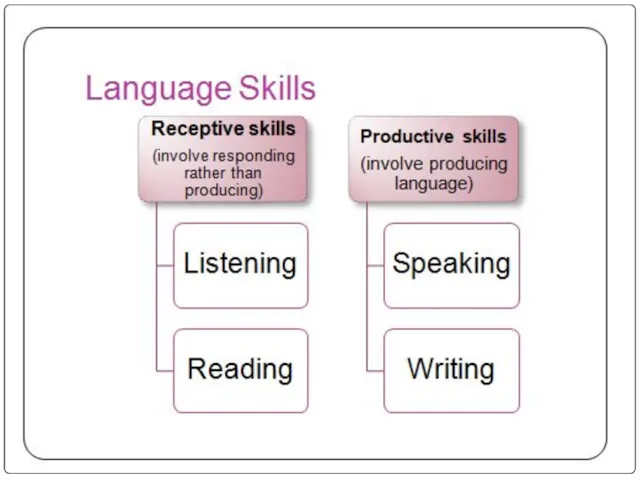
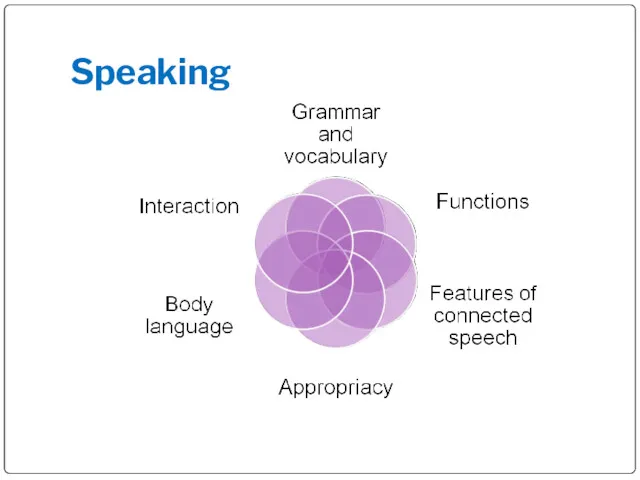
- 3. Speaking
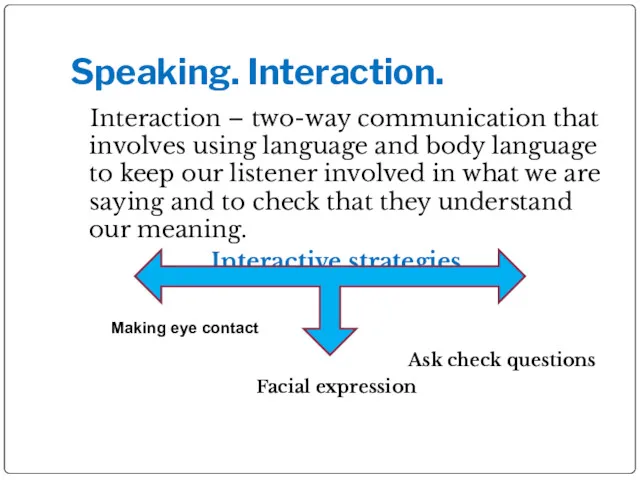
- 4. Speaking. Interaction. Interaction – two-way communication that involves using language and body language to keep our
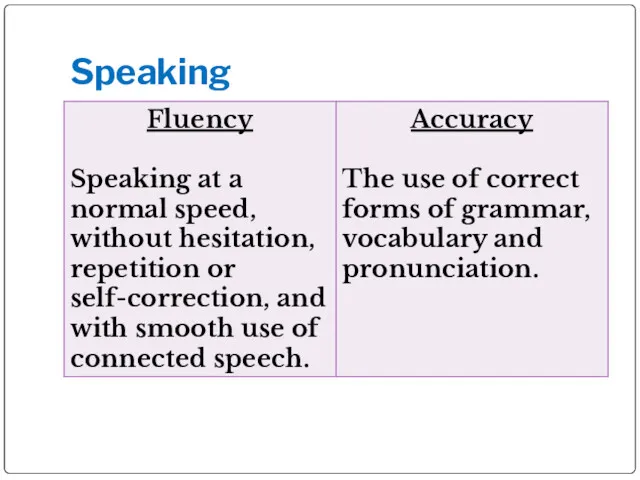
- 5. Speaking
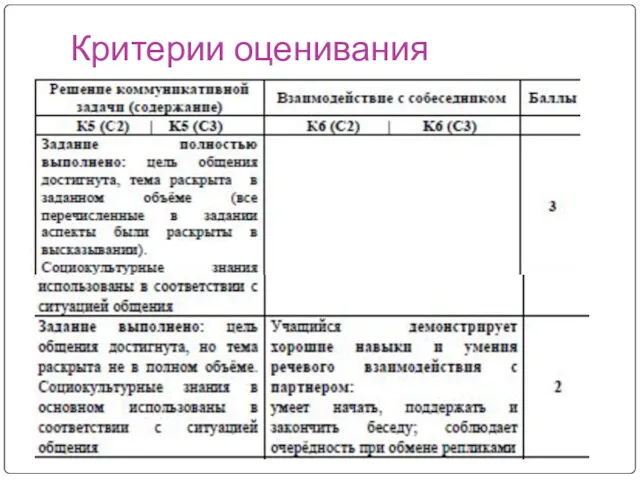
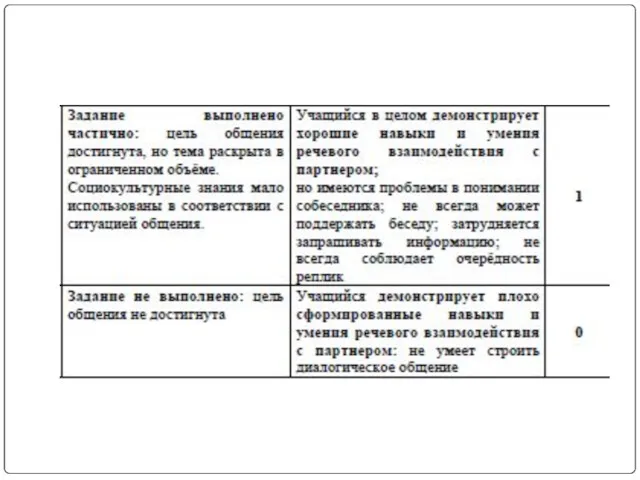
- 6. Критерии оценивания
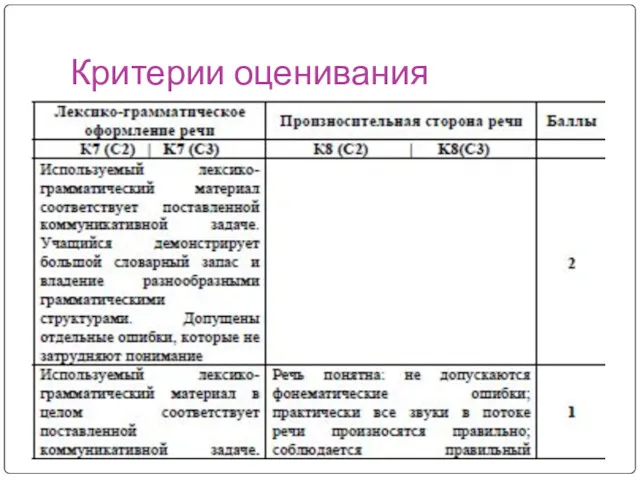
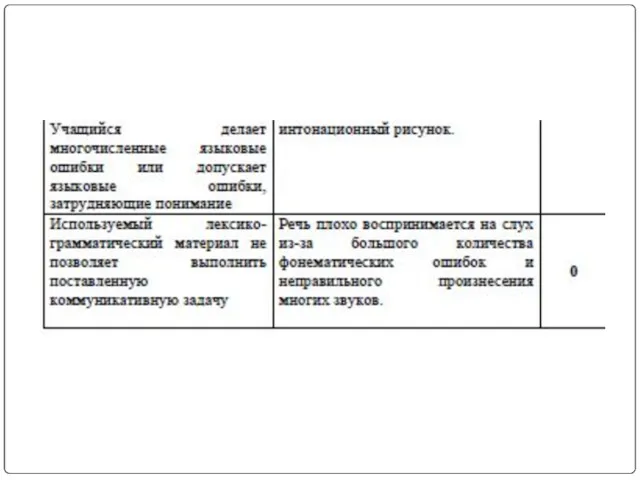
- 8. Критерии оценивания
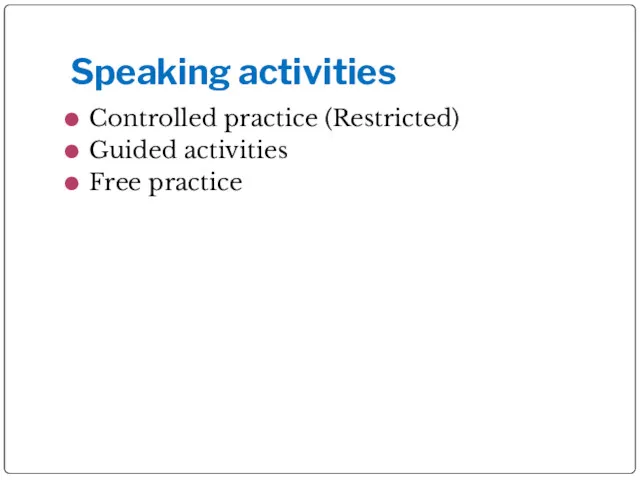
- 10. Speaking activities Controlled practice (Restricted) Guided activities Free practice
- 11. A speaking lesson Lead-in. An introduction to the topic of the lesson plus, sometimes, activities focusing
- 12. Обучение говорению Монолог Целенаправленность(соответствие речевой задаче) Непрерывный характер Логичность Смысловая законченность Самостоятельность Выразительность
- 13. Пути обучения монологу «Сверху вниз» На основе работы с текстом (создание речевой ситуации, обеспечение содержательной ценности,
- 14. Обучение говорению Диалог реактивность ситуативность
- 15. Пути обучения диалогу «Сверху вниз» Для обучения типовым(стандартным) диалогам. «Снизу вверх» От умения задавать вопросы различных
- 16. Трудности в обучении говорению Стесняются говорить из-за боязни сделать ошибку Нечего сказать Не понимают речевую задачу
- 17. Работа с диалогами
- 18. Did it hurt? I broke my arm. Yes, it did, at first. But it’s better now.
- 19. A: What happened? B: I broke my arm. A: How did it happen? B: I was
- 20. A: What happened? B: I broke my arm. A: How did it happen? B: I was
- 21. A: What happened? B: I broke my arm. A: How did it happen? B: I was
- 22. A: What happened? B: I broke my arm. A: How did it happen? B: I was
- 23. Do you like the dialogue? A: Hello, what’s your name? B: My name is Juan. A:
- 24. The rules of conversational “tennis”: Show interest, surprise, etc. Are you? Really? Return the question: What
- 25. A: Hello, what’s your name? B: My name is Juan. A: Hi Juan. I’m Kim. What
- 26. Magic formula 3 A Answer Add Ask
- 27. What do good speakers do? What can they do? work fast, be spontaneous, and cope with
- 28. Activities. Maintaining conversation Could you repeat that, please? Sorry, I don’t catch what you said, Could
- 29. Red tape is the most dangerous enemy of a free economy. (you don’t know what “red
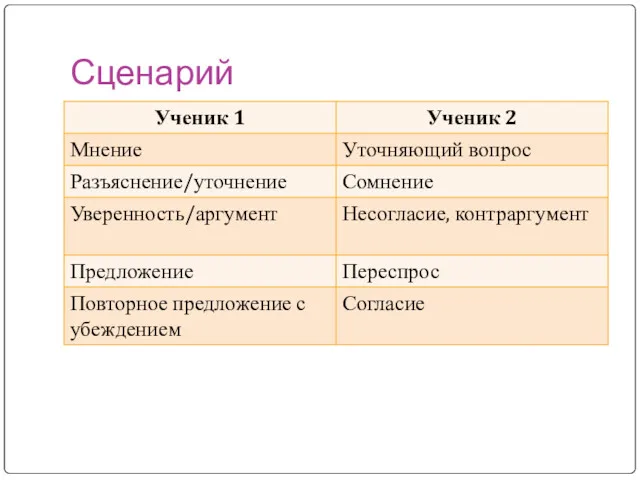
- 30. Сценарий
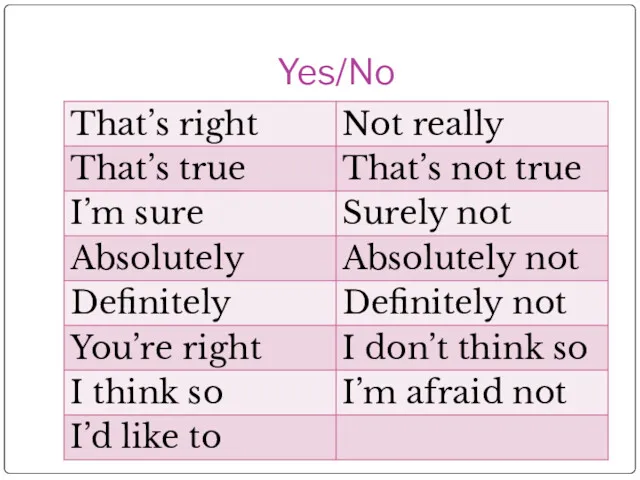
- 31. Yes/No
- 32. Стимул для говорения Текстовая опора Информационное неравновесие Проблема Видео эпизод
- 33. Навыки коммуникативного взаимодействия Insistance questions Help to tell the story Continue the chain (because, and, but,…)
- 35. Скачать презентацию





















 We are going
We are going Parts of Body
Parts of Body How to promote your business
How to promote your business Australia is a fascinating country
Australia is a fascinating country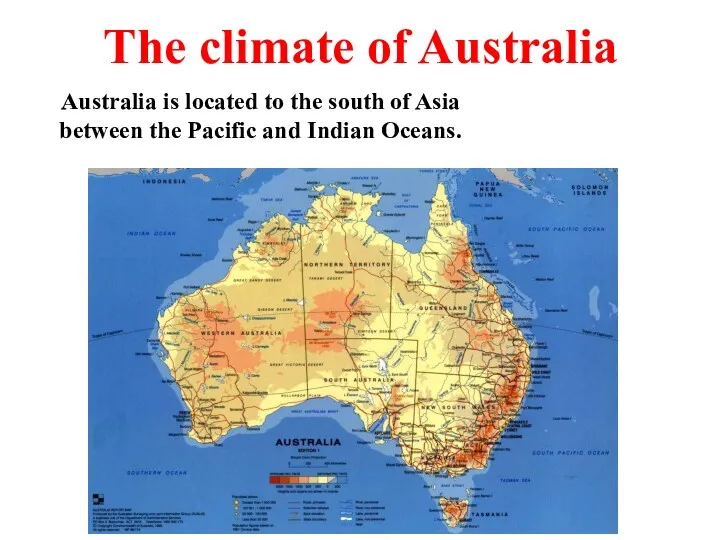 Климат Австралии. The climate of Australia
Климат Австралии. The climate of Australia Языковой лагерь English drive
Языковой лагерь English drive Prefab simulator
Prefab simulator Стратегии написания эссе с элементами рассуждения
Стратегии написания эссе с элементами рассуждения The natural movement of the population
The natural movement of the population Past simple regular verbs game fun activities games - games grammar drills
Past simple regular verbs game fun activities games - games grammar drills Forget + to inf
Forget + to inf Dynamic Presentation Template
Dynamic Presentation Template Places, where Harry Potter stories were filmed
Places, where Harry Potter stories were filmed Categorization
Categorization Пассивный залог
Пассивный залог ОГЭ 2023. Написание электронного письма
ОГЭ 2023. Написание электронного письма My School
My School Phrasal verbs
Phrasal verbs Revise general vocabulary and phrasal verbs
Revise general vocabulary and phrasal verbs Источники международного публичного права. (Лекция 3)
Источники международного публичного права. (Лекция 3) Man-made disasters and natural disasters: any connection between them
Man-made disasters and natural disasters: any connection between them The formation of aesthetic values in elementary school students on the example of Gorodets painting
The formation of aesthetic values in elementary school students on the example of Gorodets painting PPT - common animals with sounds
PPT - common animals with sounds Photo description. Description de la photo
Photo description. Description de la photo Personal pronouns
Personal pronouns Enjoy your Meal
Enjoy your Meal Parks and gardens of our town. К уроку английского языка в 6 классе
Parks and gardens of our town. К уроку английского языка в 6 классе Containerization Types & Markings
Containerization Types & Markings