Содержание
- 2. What are Learning Styles? Information enters your brain three main ways: sight, hearing and touch, which
- 3. Visual Learners These learners need to see the teacher's body language and facial expression to fully
- 4. Auditory Learners They learn best through verbal lectures, discussions, talking things and listening to what others
- 5. Tactile or Kinesthetic Learners: learn through , moving, doing and touching... Tactile/kinesthetic persons learn best through
- 6. What is multiple intelligence? Conceived by Howard Gardner in his 1983 book Frames of Mind: The
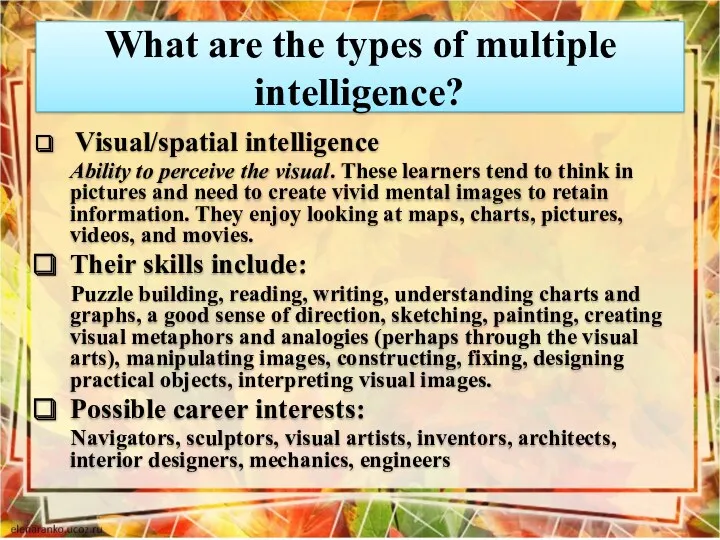
- 7. What are the types of multiple intelligence? Visual/spatial intelligence Ability to perceive the visual. These learners
- 8. Verbal/linguistic intelligence Ability to use words and language. These learners have highly developed auditory skills and
- 9. Logical/mathematical intelligence Ability to use reason, logic and numbers. These learners think conceptually in logical and
- 10. Bodily/kinesthetic intelligence Ability to control body movements and handle objects skillfully. These learners express themselves through
- 11. Musical/rhythmic intelligence Ability to produce and appreciate music. These musically inclined learners think in sounds, rhythms
- 12. Interpersonal intelligence Ability to relate and understand others. These learners try to see things from other
- 13. Intrapersonal intelligence Ability to self-reflect and be aware of one's inner state of being. These learners
- 14. Using Knowledge of Your Learning Style Knowing your learning style, both your strengths and your weaknesses,
- 16. Скачать презентацию












 Destinations in South Asia
Destinations in South Asia Lektsia_4_Glagol
Lektsia_4_Glagol Family relationships
Family relationships Will or going to
Will or going to Food and drinks
Food and drinks Ancient languages. Sanskrit
Ancient languages. Sanskrit Презентация по английскому языку учителя татарской гимназии №15. Тема: The media
Презентация по английскому языку учителя татарской гимназии №15. Тема: The media How to promote your business
How to promote your business How to learn English effectively
How to learn English effectively My favourite season
My favourite season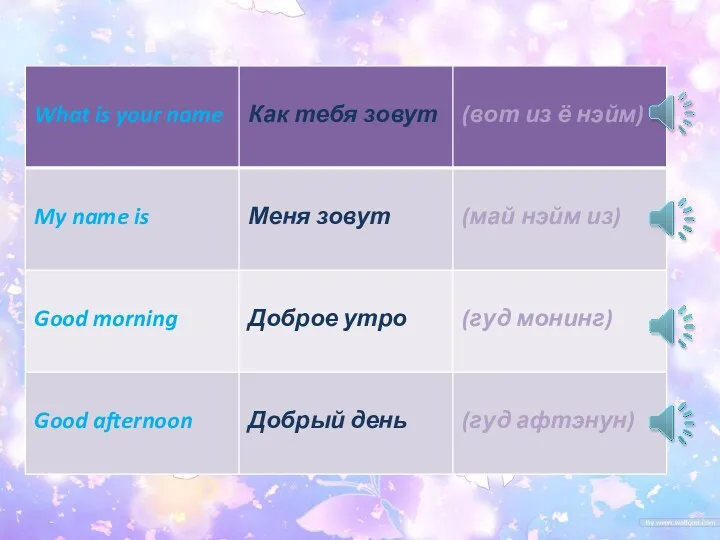 Приветствие, прощание
Приветствие, прощание Welcome to Belarus
Welcome to Belarus What am I up to?
What am I up to? How much
How much Обучаем чтению и письму с Английским в фокусе
Обучаем чтению и письму с Английским в фокусе Предлоги для обозначения конкретного момента во времени
Предлоги для обозначения конкретного момента во времени Marking Punctuation
Marking Punctuation Discuss what present to choose for your…
Discuss what present to choose for your… My favorite film (5 class)
My favorite film (5 class) Деятельностный подход в преподавании английского языка
Деятельностный подход в преподавании английского языка Structure of linguistic methodology
Structure of linguistic methodology Republic of Ireland
Republic of Ireland Black hole
Black hole Queen
Queen English lexicology
English lexicology Fantasy genre research
Fantasy genre research Legal English: Human Rights
Legal English: Human Rights How are you today?
How are you today?