- Главная
- Английский язык
- Legal English: Human Rights

Содержание
- 2. The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) is an
- 3. The Inter-American Court of Human Rights and the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights The Inter-American Court
- 4. The African Court on Human and Peoples' Rights and the African Commission on Human and Peoples'
- 5. The UN Human Rights Treaty-based Bodies (Committees and subcommittees) There are 10 human rights treaty bodies
- 6. Universal Declaration on Human Rights 10 December 1948 – 70 years next month! The Universal Declaration
- 8. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
The European Court
of Human Rights (ECtHR)
The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR)
The European Court
of Human Rights (ECtHR)
The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR)
Has jurisdiction in Russia (the right to consider complaints) since 1998. In 20 years, more than 3,000 decisions were delivered against Russia. The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation allowed the Russian authorities not to execute only two decisions of the ECHR - the case of YUKOS shareholders and ‘Anchugov and Gladkov v. Russia’.
To date, the ECHR has also resolved 4 interstate cases, including ‘Georgia vs. the Russian Federation’ (3 July 2014).
Слайд 3The Inter-American Court of Human Rights and the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights
The
The Inter-American Court of Human Rights and the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights
The
Unlike the ECHR, individuals cannot apply directly to the Court. The transfer of cases for consideration is carried out by the Commission and the States party to the Convention. Individuals may apply to the Commission.
The Inter-American Commission on human rights is an organ of the OAS. Considers complaints regarding violations of the Convention by States Parties and may refer these complaints to the Inter-American Court of Human Rights if the respondent State agrees to transfer it. The residence - Washington, USA.
Слайд 4The African Court on Human and Peoples' Rights and the African Commission on
The African Court on Human and Peoples' Rights and the African Commission on
The Court was established on the basis of the Protocol to the African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights. The Protocol entered into force in 2004 after its ratification by more than 15 countries. The residence of the Court - Arusha, Tanzania. The court resolves all cases and disputes arising out of the interpretation and application of the Charter, its Protocol and any other human rights instrument ratified by the states concerned. The court also has an advisory function.
The African Commission (established in 1987) promotes and protects human rights and also interprets the Charter. With the creation of the African Court, the Commission has the additional task of preparing cases for submission to the Court. The residence of the Commission - Banjul, Gambia.
Слайд 5The UN Human Rights Treaty-based Bodies
(Committees and subcommittees)
There are 10 human rights
The UN Human Rights Treaty-based Bodies
(Committees and subcommittees)
There are 10 human rights
Human Rights Committee (CCPR)
Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (CESCR)
Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination (CERD)
Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW)
Committee against Torture (CAT)
Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture (SPT)
Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW)
Committee on the Rights of the Child (CRC)
Committee on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD)
Committee on Enforced Disappearances (CED)
Слайд 6Universal Declaration on Human Rights
10 December 1948 – 70 years next month!
The
Universal Declaration on Human Rights
10 December 1948 – 70 years next month!
The
 States in the USA
States in the USA Согласование времен в английском языке
Согласование времен в английском языке Animals. Diapositivo
Animals. Diapositivo Уроки английского языка
Уроки английского языка Я рисую мир. Цветной урок
Я рисую мир. Цветной урок Present simple. Present continuous
Present simple. Present continuous Who is who
Who is who Education in Russia
Education in Russia English presentation Сountries, people, lifestyle: Ukraine
English presentation Сountries, people, lifestyle: Ukraine Урок-презентация по теме Еда
Урок-презентация по теме Еда The Alphabet (часть 3)
The Alphabet (часть 3)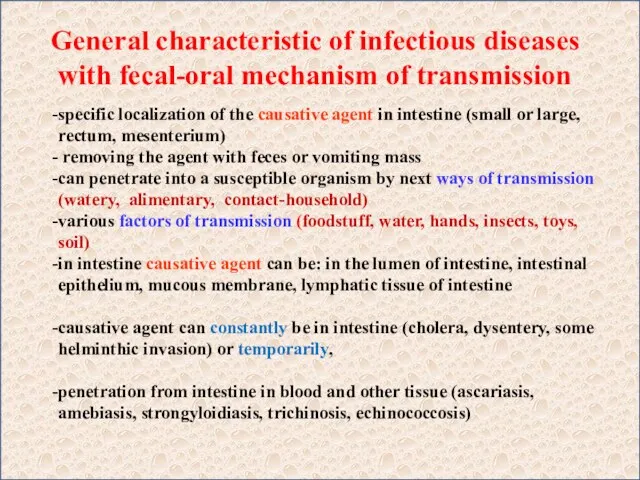 General characteristic of infectious diseases with fecal-oral mechanism of transmission
General characteristic of infectious diseases with fecal-oral mechanism of transmission Everybody knows that
Everybody knows that What’s the weather like
What’s the weather like Burns night. A Вurns supper is a celebration of the life and poetry of the poet Robert Burns
Burns night. A Вurns supper is a celebration of the life and poetry of the poet Robert Burns Corruption
Corruption Presentation on the topic: Wales
Presentation on the topic: Wales Things to do
Things to do The great patriotic war
The great patriotic war Употребление времен Present Simple или Present Continuous
Употребление времен Present Simple или Present Continuous Theoretical English grammar. Phrase (lecture 8)
Theoretical English grammar. Phrase (lecture 8) Exam practice (part 2). Tasks 1-2-3-4
Exam practice (part 2). Tasks 1-2-3-4 Job interview
Job interview My pet Tell about your pet
My pet Tell about your pet Inditex
Inditex Review of Past Tenses
Review of Past Tenses How to be healthy
How to be healthy Prepositions Review (intermediate)
Prepositions Review (intermediate)